1.2.6 Occlusal and functional requirements
Prior to restoring compromised teeth or replacing missing teeth with fixed or removable dental prostheses, a thorough occlusal analysis has to be performed, as Part of the initial clinical examination. Occlusion and function play a significant role for the long-term behavior of all-ceramic restorations.
The basic principle of occlusion is to distribute the occlusal load as much as possible on all teeth and/or restorations. Premature occlusal contacts have been shown to increase the muscular activity during mastication 25 – 28. Hence, any contact or restoration that causes elevate muscular activity can cause muscle tenderness and even lead to TMD 25 , 29. On restorations, premature contacts increase the risk for technical complications. The occlusal load should preferably follow the long axis of teeth and implants and horizontal load should be avoided as much as possible 30 – 33. The height of the cusps should be enough to break up the food.
Occlusal concepts and their focus have changed over the years. They can broadly be classified into three categories: bilateral balanced occlusion, unilateral balanced occlusion (group function), and mutually protected occlusion (canine guidance).
The concept of bilateral balanced occlusion is to have as many teeth as possible in contact, both in maximal intercuspal position (MIP) and in all excursive positions. This is very difficult to achieve in the natural dentition and can cause additional tooth wear on the balance side. Bilateral balanced occlusion has been propagated for removable prostheses to maintain better denture stability. More recent studies on edentulous patients with conventional dentures have, however, not been able to show that bilateral balanced occlusion significantly increases the chewing capacity compared with patients wearing dentures with unilateral balance occlusion 34 – 36.
In the concept of unilateral balanced occlusion, multiple teeth in the maxilla and mandible, both anterior and posterior, on the working side are in contacts during lateral movements. The idea is that simultaneous contact of several teeth acts as a group to distribute occlusal load and by that may reduce the risk of trauma from occlusion and fracture or chipping of the restoration. No teeth on the balanced side should be in contact and during protrusive movements there should also be no posterior contacts. Long-centric or freedom in centric has been propagated as a Part of unilateral balanced occlusion, especially by patients in whom MIP and centric occlusion (CO) are not identical 37 – 39. This allows for a certain freedom of movement (0.5–1.5 mm) in the anterior-posterior direction.
The concept of mutually protected occlusion assumes that MIP = CO and that the six anterior teeth in the maxilla and mandible guide the excursive movements of the mandible, and that the posterior teeth only come into contact in CO.
Evaluation
The following factors have to be evaluated and registered.
Centric relation
Centric relation (CR) should be evaluated. CR is defined as the maxillo-mandibular relationship, independent of tooth contact, in which the condyles articulate in the anterior-superior position against the posterior slopes of the articular eminences. In CR, the mandible is restricted to a purely rotary movement, so this is a repeatable reference position.
Centric occlusion
Centric occlusion (CO) should be registered with a wax plate in the conventional workflow (Fig 1-2-7). CO is traditionally defined as the occlusion of opposing teeth when the mandible is in CR position.
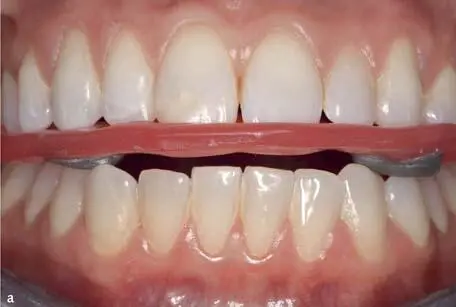
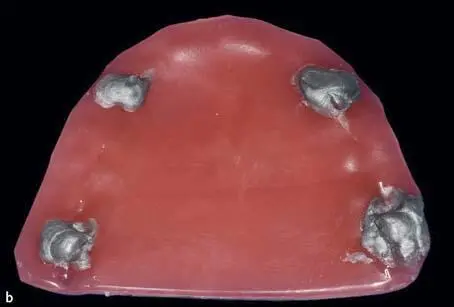
Fig 1-2-7a and 1-2-7b Centric occlusion (CO) is registered by putting a double layer wax plate with additional aluminum wax dots on the occlusal surface of the maxillary teeth; the patient is asked to close their jaws in the centric relation (CR) position until touching the wax dots.
Maximal intercuspal position
Maximal intercuspal position (MIP) should be registered with a wax or a bite paste (Fig 1-2-8). MIP is defined as the complete intercuspation of the opposing teeth independent of condylar position, sometimes referred to as the best fit of the teeth regardless of the condylar position (CR).
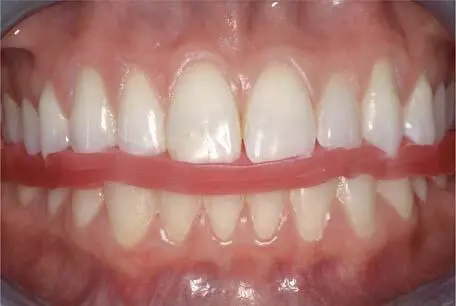
Fig 1-2-8 Maximal intercuspal position (MIP) can be registered with a double layer wax plate.
Occlusal position
The occlusal position or the Angle classification should be registered (Fig 1-2-9). This represents the relationship of the mandible and maxilla when the jaw is closed and the teeth are in MIP.
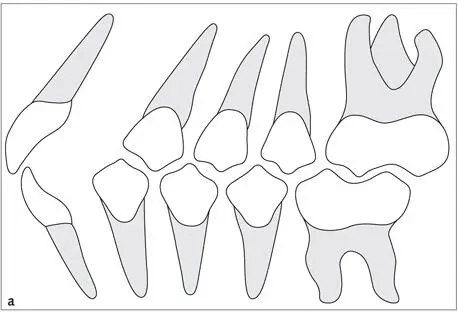
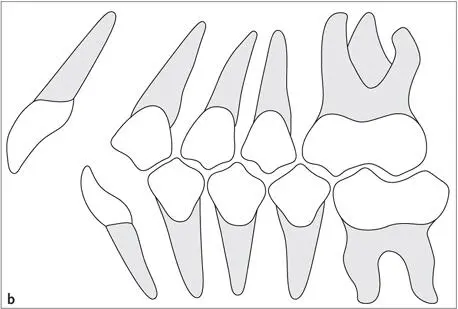
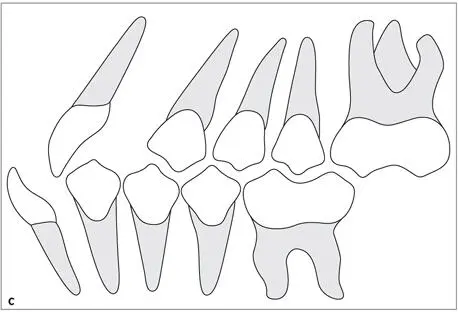
Fig 1-2-9a to 1-2-9c Schematic drawing showing (a)Angle Class I, (b)Angle Class II, and (c)Angle Class III occlusal relationship of the first molars, canines, and anterior teeth.
Premature contacts and sliding
Premature contacts and sliding in MIP should be registered and a decision should be made whether it is reasonable to reduce the premature contacts to make MIP = CO prior to the insertion of a new restoration. This is simply done to stabilize the occlusion, not to treat or prevent temporomandibular disorders 40 , 41. According to studies evaluating the location of CO and MIP, the incidence of patients was MIP = CO and ranged from 10% to 43% 42 – 44. The position of the premature contacts can be evaluated intraorally, or on articulated study casts mounted according to a CO registration.
Occlusal contacts
The occlusal contacts on the working side during laterotrusion should be analyzed and recorded. According to these contacts the patients are classified using canine guidance (Fig 1-2-10), in which the vertical and horizontal overlap of the canine teeth discludes the posterior teeth in the excursive movements of the mandible. In patients with group function (Fig 1-2-11), multiple contact relations between the maxillary and mandibular teeth exist on the working side at lateral movements, whereby simultaneous contact of several teeth as a group distributes the occlusal forces.
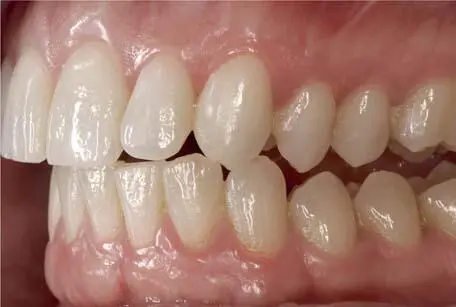
Fig 1-2-10 Canine guidance on the working side in lateral movements.
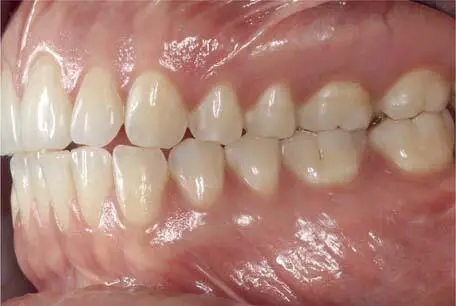
Fig 1-2-11 Group function on the working side in lateral movements.
The absence or presence of occlusal contacts on the non-working balance side should be evaluated and registered.
The absence or presence of posterior occlusal contacts in the protrusive movement of the mandible should be evaluated and registered.
Читать дальше




















