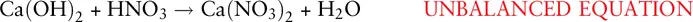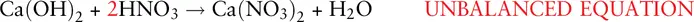1 ...8 9 10 12 13 14 ...28
0.7.2 Writing and balancing chemical equations
A chemical equation provides a shorthand method for describing the process taking place in a chemical reaction. The chemical formulae for the reactants are written on the left‐hand side of the equation and the formulae for the products on the right‐hand side. The number of each type of atom on the left‐hand side of the equation must be the same as the number of each type of atom on the right‐hand side. This involves balancingthe equation by writing the number of moles of each substance in front of the formula for the substance. These numbers are called stoichiometric coefficients.
The moleis the term used in chemistry to describe a specific amount of a material. It will be explained fully in Chapter 3.
To balance a chemical equation, first write the reactants and products separated by a reaction arrow. For example, in the reaction of hydrogen gas with oxygen gas to form water, the reactants hydrogen and oxygen should be written on the left‐hand side and the product water on the right‐hand side of the reaction arrow. Note that both hydrogen and oxygen exist as molecules whose formulae are H 2and O 2, respectively. The formula for water is H 2O.

The numbers of atoms of hydrogen are balanced on both sides, but the equation shows 2 atoms of oxygen on the left and only 1 atom on the right. To balance the equation, we therefore need to increase the number of oxygen atoms on the right to 2 by including 2 moles (or units) of H 2O, as shown in red:

However, we now have 4 atoms of hydrogen on the right and only 2 on the left. In order to fully balance the equation, we must increase the number of atoms of hydrogen on the left to 4, as shown:

The equation is now balanced. The total number of atoms on the left of the equation is equal to the number on the right.
As another example, consider the reaction of calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH) 2, with nitric acid, HNO 3. The products in this reaction are calcium nitrate, Ca(NO 3) 2, and water.
Calcium has a charge of +2 and so requires two hydroxide ions of charge −1 for the compound to remain neutral. Calcium also requires two nitrate ions, NO 3 −, to form a neutral formula unit of calcium nitrate, Ca(NO 3) 2.
Again, write the formulae for the reactants on the left‐hand side of the equation and the products on the right‐hand side, as shown:
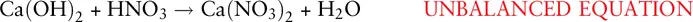
In this case, it is simpler to treat the nitrate ion as a unit with formula NO 3 −rather than separately balancing nitrogen and oxygen atoms on both sides of the equation. It can be seen that there is one nitrate ion on the left‐hand side but there are two on the right. Therefore we need to add 2 moles of nitric acid to the left‐hand side:
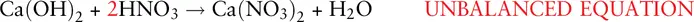
This has balanced the nitrate ions but not the hydrogen and oxygen atoms. There are 4 hydrogen atoms on the left‐hand side but only 2 on the right. There are also 2 oxygen atoms (apart from in the NO 3 −ion) on the left‐hand side but only 1 on the right. We therefore need to increase the number of water molecules to 2:

The equation is now balanced.
If a formula unit is written with a number in front of it in a chemical equation, for example, 2Ca(NO 3) 2, this means that there are 2 units or lots of Ca(NO 3) 2taking part in the reaction. The scientific term for this quantity is a mole . You will meet the mole and its definition in Chapter 3.
The word equation for this reaction is spoken as:
1 mole of calcium hydroxide reacts with 2 moles of nitric acid to give 1 mole of calcium nitrate and 2 moles of water.
Balance the following equations:
1 Mg + O2 → MgO
2 NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
3 CO + NO → CO2 + N2
4 C2H5OH + O2 → CO2 + H2O
1 Mg + O2 → MgOThis requires 2 atoms of O on the right‐hand side: Mg + O2 → 2MgO.And the left‐hand side now requires 2 atoms of Mg: 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO.
2 NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2OThe left‐hand side requires 2 atoms of Na: 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O.Now the right‐hand side needs 2 moles of H2O: 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O.
3 CO + NO → CO2 + N2The left‐hand side needs 2 atoms of N: CO + 2NO → CO2 + N2.The left‐hand side now has 3 atoms of O and the right‐hand side has 2, so increase the number of moles of CO2 on the right: CO + 2NO → 2CO2 + N2.Now the left‐hand side needs one more atom of C and one more atom of O: 2CO + 2NO → 2CO2 + N2.
4 C2H5OH + O2 → CO2 + H2OWhen a hydrocarbon is burnt in oxygen, the products are carbon dioxide and water. First balance the number of atoms of carbon on each side of the equation: C2H5OH + O2 → 2CO2 + H2O.Now balance the number of atoms of hydrogen by increasing the number of moles of water to 3: C2H5OH + O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O.Next balance the number of atoms of oxygen by adding 3 moles of O2 on the left‐hand side: C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O.
0.7.3 Indicating the physical state of reactants and products in chemical equations
When writing chemical equations, it is sometimes helpful to include the physical state of the reactants and products in the equation. This is especially important in equations relating to energy changes, as the energy required or released in the reaction depends upon the physical state of the products.
The common symbols used to describe the physical state of a reactant or product are given in Table 0.5.
Table 0.5State symbols commonly used in chemical equations.
|
|
Example |
| State |
Symbol |
Formula |
Substance |
| Gas |
g |
H 2O(g) |
Water vapour or steam |
| Liquid |
l |
H 2O(l) |
Liquid water |
| Solid |
s |
H 2O(s) |
Ice |
| Solid 1 |
gr |
C(gr) |
Graphite |
| Solid 1 |
d |
C(d) |
Diamond |
| Aqueous 2 |
aq |
NaCl(aq) |
Sodium chloride dissolved in water |
1The forms (called allotropes ) of carbon, i.e. graphite and diamond, have specific symbols as energy changes are slightly different depending upon the form of carbon used in the reaction.
2Aqueous means that the substance is dissolved in water or is in aqueous solution.
The measurement system used in chemistry is the SI system. There are six base units commonly used in chemistry. All units used in chemistry can be reduced to these six base units.
Читать дальше