Factors that decrease pain:
Empathetic others. The presence of an empathetic other is an important factor in reducing pain levels in specific populations. However, it appears that much depends on the existence of a pre‐established bond and strong attachment. One study indicated that the utterance of empathetic statements by trained personnel, who did not previous know the patients, during a painful procedure was not helpful (Lang et al. 2008). Children benefit from the presence of a supportive other, as do laboring women. There is extensive research exploring the role of spouses although some spousal behaviors can worsen pain. It appears that the nature of the relationship (attachment) may have a predominant effect on the efficacy of empathetic support in reducing pain (Meredith et al. 2005).
Distraction. Distraction is a well‐established approach for the reduction of transient or mild pain (Primack et al. 2012). It is known that playing video games is an effective technique for reducing pain in some populations, especially children (Gold et al. 2006). It is possible that distraction shows a ceiling effect and may not be sufficient for settings where severe pain is anticipated.
Hypnosis. Hypnosis has a long and somewhat rocky association with allopathic medicine. Nonetheless, there is some evidence to support the view that hypnosis is among the interventions that may be useful in mitigating pain. A recent Cochrane database review indicated that self‐hypnosis may be beneficial in laboring women (Madden et al. 2016), and a recent study indicated that hypnosis is one of several skills‐based psychosocial interventions that may be beneficial for cancer pain [Sheinfeld Gorin]. Importantly, many adults are not hypnotizable whereas children often are. If a patient is open to the idea of hypnosis, a course of therapy may be worthwhile.
Diffuse Noxious inhibitory control. Diffuse Noxious Inhibitory Control (DNIC) is a brain mechanism that suppresses a mild pain when a stronger pain stimulus is encountered. For example, if a person has a scrape on the knee and a broken arm, they may not feel the pain of the knee as long as the arm pain is not controlled. If local measures, e.g. immobilization, icing, nerve blocks, are used to control the arm pain, the patient may become aware of the milder injury to the leg. This has important implications for multi‐trauma patients as they may not feel all of their injuries and important problems may be overlooked. Many people do not have effective DNIC and a subset of patients experience heightened pain perception in the presence of other pain problems. It is unclear how to utilize DNIC clinically.
1 Burns, J.W., Holly, A., Quartana, P. et al. (2008). Trait anger management style moderates effects of actual (“state”) anger regulation on symptom‐specific reactivity and recovery among chronic low back pain patients. Psychosomatic Medicine 70: 898–905.
2 Gold, J.I., Kim, S.H., Kant, A.J. et al. (2006). Effectiveness of virtual reality for pediatric pain distraction during i.v. placement. CyberPsychology and Behaviour 9 (2): 207–212.
3 Lang, E.V., Berbaum, K.S., Pauker, S.G. et al. (2008). Beneficial effects of hypnosis and adverse effects of empathic attention during percutaneous tumor treatment: when being nice does not suffice. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology 19 (6): 897–905.
4 Madden K, Middleton P, Cyna AM, Matthewson M, Jones L. Hypnosis for pain management during labour and childbirth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 19; 2016(5):CD009356
5 Meredith, P.J., Strong, J., and Feeney, J.A. (2005). Evidence of a relationship between adult attachment variables and appraisals of chronic pain. Pain Research and Management 10: 191–200.
6 Primack, B.A., Carroll, M.V., McNamara, M. et al. (2012). Role of video games in improving health‐related outcomes: a systematic review. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 42 (6): 630–638.
7 Quartana, P.J., Campbell, C.M., and Edwards, R.R. (2009). Pain catastrophizing: a critical review. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics 9 (5): 745–758.
8 Rainville, P., Bao, Q.V., and Chrétien, P. (2005). Pain‐related emotions modulate experimental pain perception and autonomic responses. Pain 118 (3): 306–318.
9 Turk, D.C. (2003). Cognitive‐behavioral approach to the treatment of chronic pain patients. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine 28 (6): 573–579.
10 Yarns, B.C., Lumley, M.A., Cassidy, J.T. et al. (2020). Emotional awareness and expression therapy achieves greater pain reduction than cognitive behavioral therapy in older adults with chronic musculoskeletal pain: a preliminary randomized comparison trial. Pain Medicine 21 (11): 2811–2822. 2020 May 25:pnaa145. PMID: 32451528.
8 Approach to the patient with pain: conceptual models of care and related terminology
In treating patients with pain, some conceptual models organize care that is both compassionate and competent. Together, these models provide a robust foundation for approaching the patient in pain.
Balancing treatment and diagnosis: parallel pathway model
The “parallel pathway” model explains the balancing of diagnostic reasoningwith compassionate action( Figure 8.1). Because pain is both a symptom and a cause of suffering, we must attend to patients' need for pain‐relief even as diagnosis proceeds. Once we discover pain, we start preliminary pain treatments while simultaneously initiating a diagnostic plan. The parallel pathway model shows how diagnosis and treatment develop in parallel (Murinson et al. 2008). Both are important and time‐sensitive. If definitive treatment precedes clear diagnosis, unnecessary harm can occur if we lose the diagnostic information contained in the patient's report of pain. If diagnosis dominates and treatment is delayed while testing takes place, this unnecessarily prolongs suffering. Thus, in the ideal scenario, safe and effective preliminary pain treatments are given, while diagnostic studies are simultaneously undertaken. In the end, “making a diagnosis” will identify disease modifying approaches that more effectively alleviate pain.
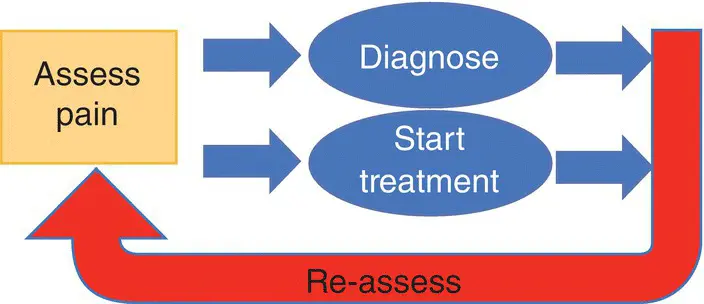
Figure 8.1 Parallel pathway model. Diagnosis and initiation of treatment proceed in parallel so that suffering is relieved as diagnostic efforts are underway.
Understanding pain and choosing rational pharmacotherapy: mechanism based‐classification
The mechanism‐based classification of pain is a simple yet elegant way to think about pain and pain treatments ( Chapter 3). In basic terms, pain arises due to three major pathways: the nociceptive pathway, dedicated to sensing injury to the organism; the inflammatory pathway, in which sensory endings are sensitized by the action of inflammatory signaling molecules; and the neuropathic pathway, which involves an error in nervous system processing of sensory information. Thinking about pain in terms of these mechanisms can 1) elucidate the disease process that is causing the problem, 2) attune us distinctive characteristic qualities associated with each mechanism which the patient will include in the pain narrative, and 3) guide the design of a treatment plan ( Figure 8.2). Most of the pain treatments available are particularly effective for certain mechanisms of pain and less so for other mechanisms. For example, NSAIDs are very useful for treating inflammatory forms of pain; but not effective against neuropathic pain. The management approaches for pain described in this book reflect the conceptual frame that pain is nociceptive, inflammatory, neuropathic, or a combination.
Читать дальше