The volumes of solid radioactive waste generated during the decommissioning of the various nuclear fuel cycle facilities are very variable, with a clear preponderance from the deconstruction of nuclear power reactors ( Table 1.10).
Table 1.10. Quantities of radioactive waste generated during the decommissioning of various nuclear fuel cycle facilities (source: [OJO 14])
| Step |
Type of waste |
Quantity (m 3.GW -1.yr -1) |
| UF 6conversion |
Solid |
0.5–1 |
| UF 6enrichment |
Solid |
5 |
| UO 2manufacturing |
Solid |
1–2 |
| Reactor |
Solid |
375 |
| Reprocessing |
Solid |
5 |
Ojovan and Lee [OJO 14] quantify these various categories of waste from the dismantling of a nuclear power reactor ( Table 1.11).
Table 1.11. Typical waste during reactor shutdown (source: [OJO 14])
| Step |
Type of waste |
Quantity (m 3.GW -1.yr -1) |
| Miscellaneous (scrap metal) |
Solid |
15 |
| Sludge |
Solid |
0.02 |
| Effluents with tritium |
Liquids |
70 |
| HLW |
Liquids |
28 |
| ILW |
Liquids |
25 |
| LLW |
Liquids |
15 |
| LLW |
Solid |
65 |
1.4.7. Waste from nuclear accidents
The NEA Expert Group on Fukushima Waste Management and Decommissioning Research and Development (EGFWMD) was established in 2014 to advise Japanese authorities on the management of large quantities of on-site waste with complex properties and to share their experiences with the international community [NEA 16a].
1.5. The global radioactive waste balance
Radioactive waste inventory data are an important element in the development of a national radioactive waste management program because they affect the design and selection of final disposal methods.
The inventory data are generally presented as quantities of radioactive waste in different waste classes, according to the waste classification system developed and adopted by the country or national program in question.
The diversity of classification systems among countries has limited the comparability of waste inventories and made it difficult to interpret waste management practices, both nationally and internationally. To help improve this situation, the Nuclear Energy Agency has developed a methodology that ensures consistency in national radioactive waste and spent fuel inventory data when submitted. This report is a follow-up to the 2016 report [NEA 16b] that presented the methodology and layout for spent fuel submission. It now extends this methodology and layout to all types of radioactive waste and the corresponding management strategies [NEA 17d].
National radioactive waste management programs require very large amounts of data and information across multiple and disparate disciplines. These programs tend to span a period of several decades, resulting in a serious risk of data and information loss, which in turn can threaten the production and maintenance of robust safety records. The NEA has taken the lead in creating a Radioactive Waste Repository Metadata Management (RepMet) project [NEA 18a].
In 2011, Ojovan and Lee [OJO 14] estimated 68.10 6m 3of waste stored and 76,10 6m 3of waste disposed ( Table 1.12).
At the end of 2013, the quantities of spent fuel discharged from nuclear reactors amounted to 367,600 metric tons, of which about half was stored in wet form, one-third needed to be reprocessed, and the rest was stored in dry form [IAE 18a] ( Table 1.13).
Table 1.12. Global estimate of the global radioactive waste inventory in 2011 (source: [OJO 14])
| Waste category |
Stored waste (m 3) |
Disposed waste (m 3) |
| VLLW |
153.10 3 |
113.10 3 |
| LLW |
56,663.10 3 |
64,792.10 3 |
| ILW |
8,723.10 3 |
10,587.10 3 |
| HLW |
2,743.10 3 |
72.10 3 |
| Total volume |
~68.106 |
~76.106 |
Table 1.13. Quantities of discharged spent fuel (in ton) at the end of 2013 (source: [IAEA 18a]). NP: not provided
| Geographical area |
Wet storage |
Dry storage |
Reprocessing |
Total |
| Africa |
850 |
50 |
NP |
900 |
| Eastern Europe |
28,600 |
7,700 |
3,200 |
40,000 |
| Western Europe |
37,000 |
4,600 |
108,000 |
154,100 |
| Far East |
32,100 |
5,700 |
8,600 |
46,400 |
| North America |
79,300 |
41,900 |
NP |
131,200 |
| Latin America |
3,000 |
2,000 |
NP |
5,000 |
| Grand total |
180,800 |
56,900 |
120,300 |
367,600 |
The storage of spent fuel is carried out for 81% near the producing reactor (59% under water and 22% dry) and for 15% far from this reactor (13% under water and 2% dry), and for the remaining 4% the storage is not known [IAE 18a].
Figure 1.4highlights the significant quantities of solid radioactive waste worldwide. The less hazardous categories of waste (VLLW and LLW) are larger than the more hazardous ones (ILW and HLW). However, it should be noted that the final solutions are more effective for the former categories compared to the solutions not found for the more hazardous ones.
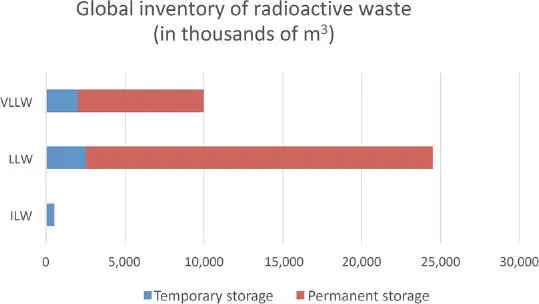
Figure 1.4. Summary of global inventories of solid radioactive waste in storage and disposal (source: [IAE 18a]). For a color version of this figure, see www.iste.co.uk/amiard/radioactive.zip
The distribution of solid waste at the end of 2013 by major waste categories and by geographical area is presented in Table 1.14.
Table 1.14. Quantities of solid waste (in m3) at the end of 2013 (source: [IAE 18a])
| Geographical area |
VLLW |
LLW |
ILW |
HLW |
| Africa |
7,000 |
20,000 |
1,000 |
0 |
| Eastern Europe |
15,000 |
2,479,000 |
101,000 |
7,000 |
| Western Europe |
224,000 |
355,000 |
269,000 |
6,000 |
| Far East |
5,000 |
331,000 |
4,000 |
0 |
| North America |
2,105,000 |
248,000 |
84,000 |
8,000 |
| Latin America |
0 |
37,000 |
0 |
0 |
| Middle East and South Asia |
0 |
3,000 |
0 |
0 |
| East Asia and Pacific |
0 |
5,000 |
1,000 |
0 |
| Grand total |
2,356,600 |
3,479,000 |
460,000 |
22,000 |
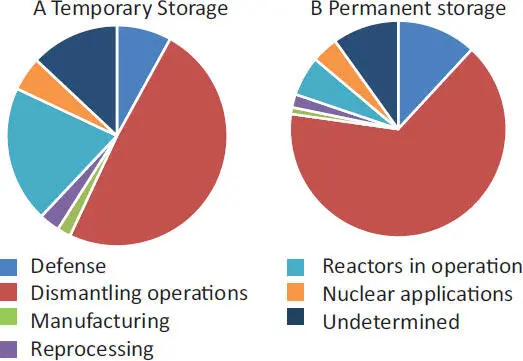
Figure 1.5. Global origins of radioactive waste in 2013 for A) storage and B) final disposal (source: [IAE 18a]). For a color version of this figure, see www.iste.co.uk/amiard/radioactive.zip
Worldwide, the majority of radioactive waste comes from dismantling operations (49% and 66%, respectively, depending on whether the storage is interim or final) ( Figure 1.5).
Читать дальше














