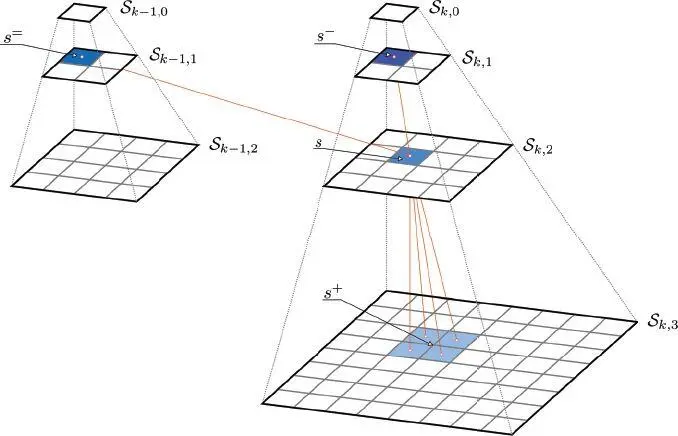
Figure 1.4. Quad-trees associated with the input multisensor and multiresolution time series and related notations. For a color version of this figure, see www.iste.co.uk/atto/change2.zip
Given this multiple quad-tree topology, a probabilistic graphical model based on a hierarchical MRF is defined. It is made of a series of random fields associated with the various scales and connected by transition relations associated with the links 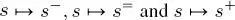 among the sites. In particular, the quad-trees are meant to be in cascade, consistently with the input time series. Let
among the sites. In particular, the quad-trees are meant to be in cascade, consistently with the input time series. Let 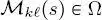 be the class label of site
be the class label of site 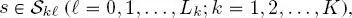 and let
and let 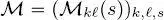 be the corresponding time series of random fields associated with all multiscale layers. Each realization of
be the corresponding time series of random fields associated with all multiscale layers. Each realization of 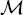 corresponds to a set of classification maps for all images in the series and all scales in the corresponding quad-trees.
corresponds to a set of classification maps for all images in the series and all scales in the corresponding quad-trees.
The key assumption in the hierarchical MRF model is that the random fields 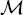 are Markovian, both across scales and time
are Markovian, both across scales and time 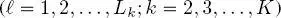 (Kato and Zerubia 2012):
(Kato and Zerubia 2012):
[1.1] 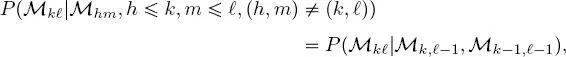
where P (·) indicates the probability mass function (pmf) of discrete random variables and fields. Equation [1.1]implies that the distribution of the labels in each layer of each quad-tree, conditioned on the labels in all above layers of the same quad-tree and of the previous quad-trees in the series, can only be restricted to the distribution conditioned on the labels of the upper layers in the same and previous quad-trees. Furthermore, this distribution factorizes in a conditionally independent fashion – a common assumption in the area of latent Markov models 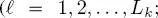
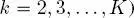 (Li 2009; Kato and Zerubia 2012):
(Li 2009; Kato and Zerubia 2012):
[1.2] 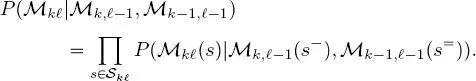
In the case of the first quad-tree in the series, these Markovianity and conditional independence assumptions are naturally adapted as follows 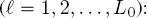
[1.3] 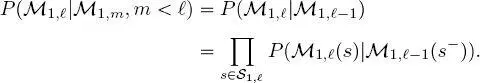
Finally, the feature vectors in the image time series 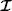 are also assumed to be conditionally independent on the labels in
are also assumed to be conditionally independent on the labels in 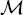 :
:
[1.4] 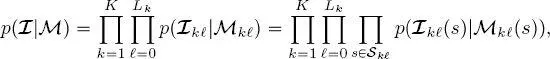
where p (·) denotes the PDF of continuous random variables and fields. Again, this assumption is widely accepted in the literature of latent MRF models (Li 2009; Kato and Zerubia 2012).
To ease the notations, in the following, we will simply write the feature vector 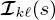 ) and the class label
) and the class label 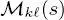 of site
of site 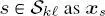 and cs , respectively, dropping the explicit dependence on k and
and cs , respectively, dropping the explicit dependence on k and 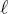 for the sake of clarity. For this reason, we will explain the formulation of the first proposed method in the case of a series composed of K = 2 images
for the sake of clarity. For this reason, we will explain the formulation of the first proposed method in the case of a series composed of K = 2 images 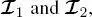 acquired by two different sensors and at two different resolutions on the considered area. In this case, two quad-trees in cascade are used. The extension to the case K > 2 is straightforward.
acquired by two different sensors and at two different resolutions on the considered area. In this case, two quad-trees in cascade are used. The extension to the case K > 2 is straightforward.
The formulation of MPM defined in Hedhli et al. (2016) with regard to the case of multitemporal classification of single-sensor multiresolution imagery is generalized here to the case of multisensor data. The MPM decision rule assigns site 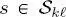
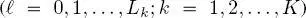 the class label that maximizes the posterior marginal probability
the class label that maximizes the posterior marginal probability 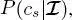 i.e. the distribution of its own individual label, given all feature vectors in the image series (Li 2009; Kato and Zerubia 2012). This decision rule is especially advantageous in the case of hierarchical graphs because it penalizes classification errors as a function of the scale at which they occur. Intuitively, an error on a site in the leaves layer only directly affects the corresponding pixel, whereas an error in a single pixel in the root layer may propagate into many erroneously labeled pixels on the leaves layer. MPM correctly penalizes the latter scenario more strongly than the former (Laferté et al. 2000).
i.e. the distribution of its own individual label, given all feature vectors in the image series (Li 2009; Kato and Zerubia 2012). This decision rule is especially advantageous in the case of hierarchical graphs because it penalizes classification errors as a function of the scale at which they occur. Intuitively, an error on a site in the leaves layer only directly affects the corresponding pixel, whereas an error in a single pixel in the root layer may propagate into many erroneously labeled pixels on the leaves layer. MPM correctly penalizes the latter scenario more strongly than the former (Laferté et al. 2000).
Читать дальше


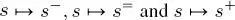 among the sites. In particular, the quad-trees are meant to be in cascade, consistently with the input time series. Let
among the sites. In particular, the quad-trees are meant to be in cascade, consistently with the input time series. Let 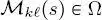 be the class label of site
be the class label of site 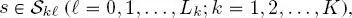 and let
and let 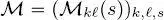 be the corresponding time series of random fields associated with all multiscale layers. Each realization of
be the corresponding time series of random fields associated with all multiscale layers. Each realization of 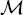 corresponds to a set of classification maps for all images in the series and all scales in the corresponding quad-trees.
corresponds to a set of classification maps for all images in the series and all scales in the corresponding quad-trees.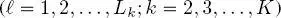 (Kato and Zerubia 2012):
(Kato and Zerubia 2012):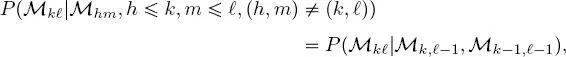
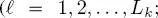
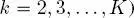 (Li 2009; Kato and Zerubia 2012):
(Li 2009; Kato and Zerubia 2012):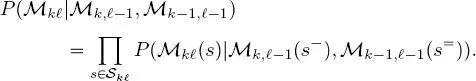
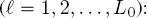
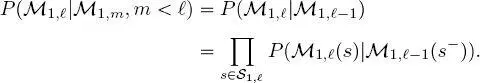
 are also assumed to be conditionally independent on the labels in
are also assumed to be conditionally independent on the labels in 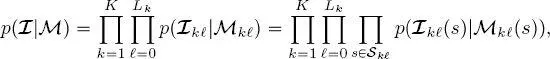
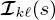 ) and the class label
) and the class label 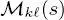 of site
of site 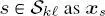 and cs , respectively, dropping the explicit dependence on k and
and cs , respectively, dropping the explicit dependence on k and 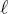 for the sake of clarity. For this reason, we will explain the formulation of the first proposed method in the case of a series composed of K = 2 images
for the sake of clarity. For this reason, we will explain the formulation of the first proposed method in the case of a series composed of K = 2 images 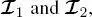 acquired by two different sensors and at two different resolutions on the considered area. In this case, two quad-trees in cascade are used. The extension to the case K > 2 is straightforward.
acquired by two different sensors and at two different resolutions on the considered area. In this case, two quad-trees in cascade are used. The extension to the case K > 2 is straightforward.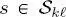
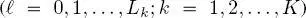 the class label that maximizes the posterior marginal probability
the class label that maximizes the posterior marginal probability 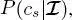 i.e. the distribution of its own individual label, given all feature vectors in the image series (Li 2009; Kato and Zerubia 2012). This decision rule is especially advantageous in the case of hierarchical graphs because it penalizes classification errors as a function of the scale at which they occur. Intuitively, an error on a site in the leaves layer only directly affects the corresponding pixel, whereas an error in a single pixel in the root layer may propagate into many erroneously labeled pixels on the leaves layer. MPM correctly penalizes the latter scenario more strongly than the former (Laferté et al. 2000).
i.e. the distribution of its own individual label, given all feature vectors in the image series (Li 2009; Kato and Zerubia 2012). This decision rule is especially advantageous in the case of hierarchical graphs because it penalizes classification errors as a function of the scale at which they occur. Intuitively, an error on a site in the leaves layer only directly affects the corresponding pixel, whereas an error in a single pixel in the root layer may propagate into many erroneously labeled pixels on the leaves layer. MPM correctly penalizes the latter scenario more strongly than the former (Laferté et al. 2000).










