1 ...6 7 8 10 11 12 ...17 Mandibular foramen:The entrance to the mandibular canal.
Mandibular fossa:Concave depression in the temporal bone that articulates with the mandibular head.
Mandibular head:Articular head of the condylar process.
Mandibular neck:Neck of the condylar process.
Mandibular notch:The notch on the caudal aspect, between the coronoid and condylar processes; not to be confused with the facial vascular notch.
Mandibular symphysis (SYM):Joint between the left and right mandibles (intermandibular joint).
Maxilla/maxillary (MX):Referring to the upper jaw; all mammals have two maxillas (or maxillae) and two mandibles. The adjective “maxillary” is often used in a wider sense, e.g. “maxillary fractures,” to include other facial bones, in addition to the maxillary bone itself.
Mental foramen(plural, foramina): Rostral, middle, and caudal mental foramina in the dog and cat.
Mesial/Distal:Mesial and distal are terms applicable to tooth surfaces. The mesial surface of the first incisor is next to the median plane; on other teeth it is directed toward the first incisor. The distal surface is opposite from the mesial surface.
Mixed dentition period:That period during which both deciduous and permanent teeth are present.
Molars (M):Molar tooth.
Molar part:The part that carries the premolars and molars; premolar‐molar part would probably have been more accurate.
Permanent dentition period:That period during which only permanent teeth are present.
Premolars (P):In the cat, the tooth immediately distal to the maxillary canine is the second premolar, the tooth immediately distal to the mandibular canine is the third premolar.
Pulp cavity:Space within the tooth.
Pulp chamber:Space within the crown of a tooth.
Ramus of the mandible:The part that carries the three processes; often incorrectly referred to as the vertical ramus.
Retroarticular process:A projection of the temporal bone that protrudes ventrally from the caudal end of the zygomatic arch and carries part of the mandibular fossa.
Root (RO):Radicular portion of a tooth.
Root canal:Space within the root of a tooth.
Rostral/Caudal:Rostral and caudal are the positional and directional anatomical terms applicable to the head in a sagittal plane in non‐human vertebrates. Rostral refers to a structure closer to, or a direction toward the most forward structure of the head. Caudal refers to a structure closer to, or a direction toward the tail. Anterior and posterior are terms used for mesial and distal in human dentistry.
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ):The area where the condylar process of the mandible articulates with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone.
Tooth (T):Hard structure embedded in the jaw; used for biting and chewing.
Tooth numbering:The existence of the conventional anatomical naming of teeth as well as the various tooth numbering systems is recognized. In cats and dogs, the correct anatomical names of teeth are (right or left), (maxillary or mandibular), (first, second, third or fourth), (incisor, canine, premolar, molar), as applicable, written out in full or abbreviated. The modified Triadan system is presently considered to be the tooth numbering system of choice in veterinary dentistry; gaps are left in the numbering sequence where there are missing teeth (for example, the first premolar encountered in the feline left maxilla is numbered 206, not 205; the two lower right premolars are 407 and 408, not 405 and 406). The use of both anatomical naming and the modified Triadan system are acceptable for recording and storing veterinary dental information. The use of anatomical names in publications is required by many leading journals and is recommended. It offers an advantage in that veterinary dental publications are more understood by other health professionals and scientists with an interest in veterinary dentistry.
Ventral margin:Free ventral border.
Vestibular/Buccal/Labial:Vestibular is the correct term referring to the surface of the tooth facing the vestibule or lips; buccal and labial are acceptable alternatives. Labial refers to the facial surface of the incisors and canines. Buccal refers to the facial surface of the premolars and molars.
Zygomatic arch (ZYG):Consisting of the zygomatic process of the temporal bone and the temporal process of the zygomatic bone; also called zygoma.
An understanding and appreciation of feline dental pathology, treatment, and prevention requires detailed knowledge of the structure and function of oral tissues including the teeth, supporting periodontal tissues, bones, tongue, lymph nodes, salivary glands, blood supply, muscles, and nerves.
The oral cavity extends from the lips to the pharynx, bounded laterally by the cheeks, dorsally by the palate, and ventrally by the tongue and intermandibular tissues. The oral cavity is divided into the oral cavity proper and the oral vestibule. Within the oral cavity proper are the hard palate, soft palate, tongue, and the floor of the mouth. The hard palate is formed by the palatine processes of the incisive and maxillary bones and the horizontal laminae of the palatine bones. The mucosa covering the hard palate consists of cornified stratified squamous epithelium, which is developed into seven or eight transverse curved ridges (palatine rugae). The palatine rugae have thick tough connective tissue support, the mucoperiosteum, which is continuous with the periodontal ligaments of the upper teeth. The mucosa of the hard palate ends abruptly laterally at its junction with the short palatal free gingiva. The incisive papilla is located on the midline cranial to the first transverse ridge and just caudal to the upper central incisor teeth. On either side of this papilla are the incisive ducts that extend caudodorsally through the palatine fissures into the floor of the nasal fossae. This duct communicates with the vomeronasal organ. Caudally, the oral cavity proper ends at the palatoglossal folds.
The palatoglossal arch (also called palatoglossal fold) is a fold of mucous membrane which extends from the soft palate to the side of the tongue. The palatoglossal arch marks where the mouth becomes the pharynx. The palatoglossus muscle is one of the four extrinsic muscles of the tongue. The paired muscles create ridges of mucous membrane in the lateral pharyngeal wall called the palatoglossal arches (also known as the anterior pillars of the fauces). The palatoglossus muscle runs in the anterior palatoglossal arch, and the palatopharyngeus muscle runs in the palatopharyngeal arch of the tonsillar fossa. These muscles pull the back of the tongue upward toward the soft palate to seal the oral cavity from the pharynx. The palatine tonsils lie in shallow fossae located approximately 1.5 cm caudal to the palatoglossal folds.
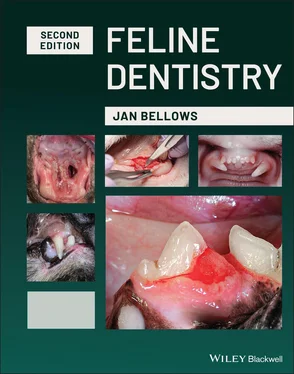
The oral vestibule spans between the lips, cheeks, and dental arches. The labial vestibule is the space between the incisors, canines, and lips. The buccal vestibule is the space between the cheek teeth and the cheeks ( Figure 1.1a–c).
Oral mucosa covers the surface of the mouth with the exception of the gingiva which is a specialized form of mucoperiosteum. The outer layer of mucosa is composed of variably pigmented nonkeratinized and parakeratinized stratified squamous epithelium. The submucosa is composed of loose connective tissue, salivary glands, blood vessels, muscle fibers, lymphatics, and salivary ducts. The submucosa of the palate is composed of dense collagen.
Читать дальше