Before providing two recent examples of twenty‐first century computational statistics ( Section 3), we present three easily quantified Core Challenges within computational statistics that we believe will always exist: big 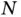 , or inference from many observations; big
, or inference from many observations; big 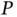 , or inference with high‐dimensional models; and big
, or inference with high‐dimensional models; and big 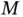 , or inference with nonconvex objective – or multimodal density – functions. In twenty‐first century computational statistics, these challenges often co‐occur, but we consider them separately in this section.
, or inference with nonconvex objective – or multimodal density – functions. In twenty‐first century computational statistics, these challenges often co‐occur, but we consider them separately in this section.
Having a large number of observations makes different computational methods difficult in different ways. A worst case scenario, the exact permutation test requires the production of 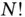 datasets. Cheaper alternatives, resampling methods such as the Monte Carlo permutation test or the bootstrap, may require anywhere from thousands to hundreds of thousands of randomly produced datasets [8, 10]. When, say, population means are of interest, each Monte Carlo iteration requires summations involving
datasets. Cheaper alternatives, resampling methods such as the Monte Carlo permutation test or the bootstrap, may require anywhere from thousands to hundreds of thousands of randomly produced datasets [8, 10]. When, say, population means are of interest, each Monte Carlo iteration requires summations involving 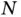 expensive memory accesses. Another example of a computationally intensive model is Gaussian process regression [16, 17]; it is a popular nonparametric approach, but the exact method for fitting the model and predicting future values requires matrix inversions that scale
expensive memory accesses. Another example of a computationally intensive model is Gaussian process regression [16, 17]; it is a popular nonparametric approach, but the exact method for fitting the model and predicting future values requires matrix inversions that scale 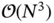 . As the rest of the calculations require relatively negligible computational effort, we say that matrix inversions represent the computational bottleneck for Gaussian process regression.
. As the rest of the calculations require relatively negligible computational effort, we say that matrix inversions represent the computational bottleneck for Gaussian process regression.
To speed up a computationally intensive method, one only needs to speed up the method's computational bottleneck. We are interested in performing Bayesian inference [18] based on a large vector of observations 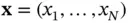 . We specify our model for the data with a likelihood function
. We specify our model for the data with a likelihood function 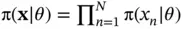 and use a prior distribution with density function
and use a prior distribution with density function 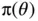 to characterize our belief about the value of the
to characterize our belief about the value of the 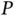 ‐dimensional parameter vector
‐dimensional parameter vector 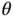 a priori . The target of Bayesian inference is the posterior distribution of
a priori . The target of Bayesian inference is the posterior distribution of 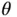 conditioned on
conditioned on 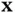
(1) 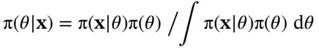
The denominator's multidimensional integral quickly becomes impractical as 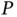 grows large, so we choose to use the MetropolisHastings (M–H) algorithm to generate a Markov chain with stationary distribution
grows large, so we choose to use the MetropolisHastings (M–H) algorithm to generate a Markov chain with stationary distribution 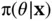 [19, 20]. We begin at an arbitrary position
[19, 20]. We begin at an arbitrary position 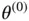 and, for each iteration
and, for each iteration 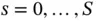 , randomly generate the proposal state
, randomly generate the proposal state 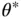 from the transition distribution with density
from the transition distribution with density 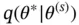 . We then accept proposal state
. We then accept proposal state 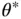 with probability
with probability
(2) 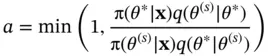
The ratio on the right no longer depends on the denominator in Equation (1), but one must still compute the likelihood and its 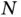 terms
terms 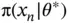 .
.
It is for this reason that likelihood evaluations are often the computational bottleneck for Bayesian inference. In the best case, these evaluations are 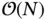 , but there are many situations in which they scale
, but there are many situations in which they scale 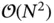 [21, 22] or worse. Indeed, when
[21, 22] or worse. Indeed, when 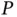 is large, it is often advantageous to use more advanced MCMC algorithms that use the gradient of the log‐posterior to generate better proposals. In this situation, the log‐likelihood gradient may also become a computational bottleneck [21].
is large, it is often advantageous to use more advanced MCMC algorithms that use the gradient of the log‐posterior to generate better proposals. In this situation, the log‐likelihood gradient may also become a computational bottleneck [21].
One of the simplest models for big 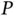 problems is ridge regression [23], but computing can become expensive even in this classical setting. Ridge regression estimates the coefficient
problems is ridge regression [23], but computing can become expensive even in this classical setting. Ridge regression estimates the coefficient 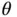 by minimizing the distance between the observed and predicted values
by minimizing the distance between the observed and predicted values 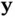 and
and 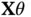 along with a weighted square norm of
along with a weighted square norm of 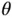 :
:
Читать дальше

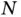 , or inference from many observations; big
, or inference from many observations; big 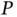 , or inference with high‐dimensional models; and big
, or inference with high‐dimensional models; and big 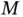 , or inference with nonconvex objective – or multimodal density – functions. In twenty‐first century computational statistics, these challenges often co‐occur, but we consider them separately in this section.
, or inference with nonconvex objective – or multimodal density – functions. In twenty‐first century computational statistics, these challenges often co‐occur, but we consider them separately in this section. datasets. Cheaper alternatives, resampling methods such as the Monte Carlo permutation test or the bootstrap, may require anywhere from thousands to hundreds of thousands of randomly produced datasets [8, 10]. When, say, population means are of interest, each Monte Carlo iteration requires summations involving
datasets. Cheaper alternatives, resampling methods such as the Monte Carlo permutation test or the bootstrap, may require anywhere from thousands to hundreds of thousands of randomly produced datasets [8, 10]. When, say, population means are of interest, each Monte Carlo iteration requires summations involving 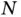 expensive memory accesses. Another example of a computationally intensive model is Gaussian process regression [16, 17]; it is a popular nonparametric approach, but the exact method for fitting the model and predicting future values requires matrix inversions that scale
expensive memory accesses. Another example of a computationally intensive model is Gaussian process regression [16, 17]; it is a popular nonparametric approach, but the exact method for fitting the model and predicting future values requires matrix inversions that scale 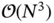 . As the rest of the calculations require relatively negligible computational effort, we say that matrix inversions represent the computational bottleneck for Gaussian process regression.
. As the rest of the calculations require relatively negligible computational effort, we say that matrix inversions represent the computational bottleneck for Gaussian process regression.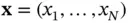 . We specify our model for the data with a likelihood function
. We specify our model for the data with a likelihood function  and use a prior distribution with density function
and use a prior distribution with density function 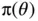 to characterize our belief about the value of the
to characterize our belief about the value of the 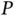 ‐dimensional parameter vector
‐dimensional parameter vector 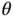 a priori . The target of Bayesian inference is the posterior distribution of
a priori . The target of Bayesian inference is the posterior distribution of 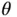 conditioned on
conditioned on 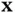
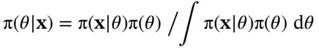
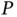 grows large, so we choose to use the MetropolisHastings (M–H) algorithm to generate a Markov chain with stationary distribution
grows large, so we choose to use the MetropolisHastings (M–H) algorithm to generate a Markov chain with stationary distribution 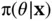 [19, 20]. We begin at an arbitrary position
[19, 20]. We begin at an arbitrary position 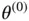 and, for each iteration
and, for each iteration 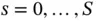 , randomly generate the proposal state
, randomly generate the proposal state 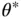 from the transition distribution with density
from the transition distribution with density 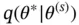 . We then accept proposal state
. We then accept proposal state 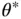 with probability
with probability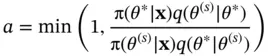
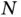 terms
terms 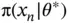 .
.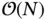 , but there are many situations in which they scale
, but there are many situations in which they scale 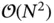 [21, 22] or worse. Indeed, when
[21, 22] or worse. Indeed, when 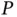 is large, it is often advantageous to use more advanced MCMC algorithms that use the gradient of the log‐posterior to generate better proposals. In this situation, the log‐likelihood gradient may also become a computational bottleneck [21].
is large, it is often advantageous to use more advanced MCMC algorithms that use the gradient of the log‐posterior to generate better proposals. In this situation, the log‐likelihood gradient may also become a computational bottleneck [21]. problems is ridge regression [23], but computing can become expensive even in this classical setting. Ridge regression estimates the coefficient
problems is ridge regression [23], but computing can become expensive even in this classical setting. Ridge regression estimates the coefficient 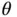 by minimizing the distance between the observed and predicted values
by minimizing the distance between the observed and predicted values 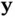 and
and 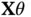 along with a weighted square norm of
along with a weighted square norm of 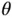 :
:![Роман Зыков - Роман с Data Science. Как монетизировать большие данные [litres]](/books/438007/roman-zykov-roman-s-data-science-kak-monetizirova-thumb.webp)










