Computational Statistics in Data Science
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Computational Statistics in Data Science» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Computational Statistics in Data Science
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Computational Statistics in Data Science: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Computational Statistics in Data Science»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Computational Statistics in Data Science
Computational Statistics in Data Science
Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online
Computational Statistics in Data Science

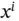 in the input layer to a node
in the input layer to a node 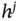 in the hidden layer as
in the hidden layer as 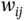 . The weight from a node
. The weight from a node 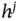 in the hidden layer to a node
in the hidden layer to a node 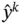 in the output layer will be denoted
in the output layer will be denoted 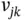 . In each of the input and hidden layers, we introduce intercept nodes , denoted
. In each of the input and hidden layers, we introduce intercept nodes , denoted 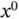 and
and 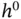 , respectively. Weights from them to any other node are called biases . Each node in a given layer is connected by a weight to every node in the layer above except the intercept node.
, respectively. Weights from them to any other node are called biases . Each node in a given layer is connected by a weight to every node in the layer above except the intercept node.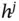 ,
, 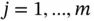 , is given by
, is given by 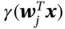 , where
, where 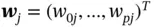 ,
, 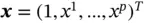 , and
, and 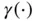 is a nonlinear transformation with range in the interval
is a nonlinear transformation with range in the interval 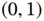 . Similarly, the value of
. Similarly, the value of 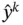 ,
, 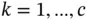 , is given by
, is given by 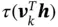 , where
, where 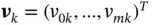 ,
,  , and
, and 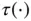 is also a nonlinear transformation with a range in the interval
is also a nonlinear transformation with a range in the interval 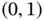 .
. provided by an MLP from a sample
provided by an MLP from a sample 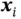 to
to 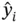 can be written as follows:
can be written as follows: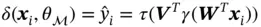
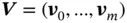 ,
, 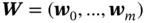 ,
, 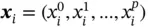 , and
, and  and
and  are nonlinear functions.
are nonlinear functions.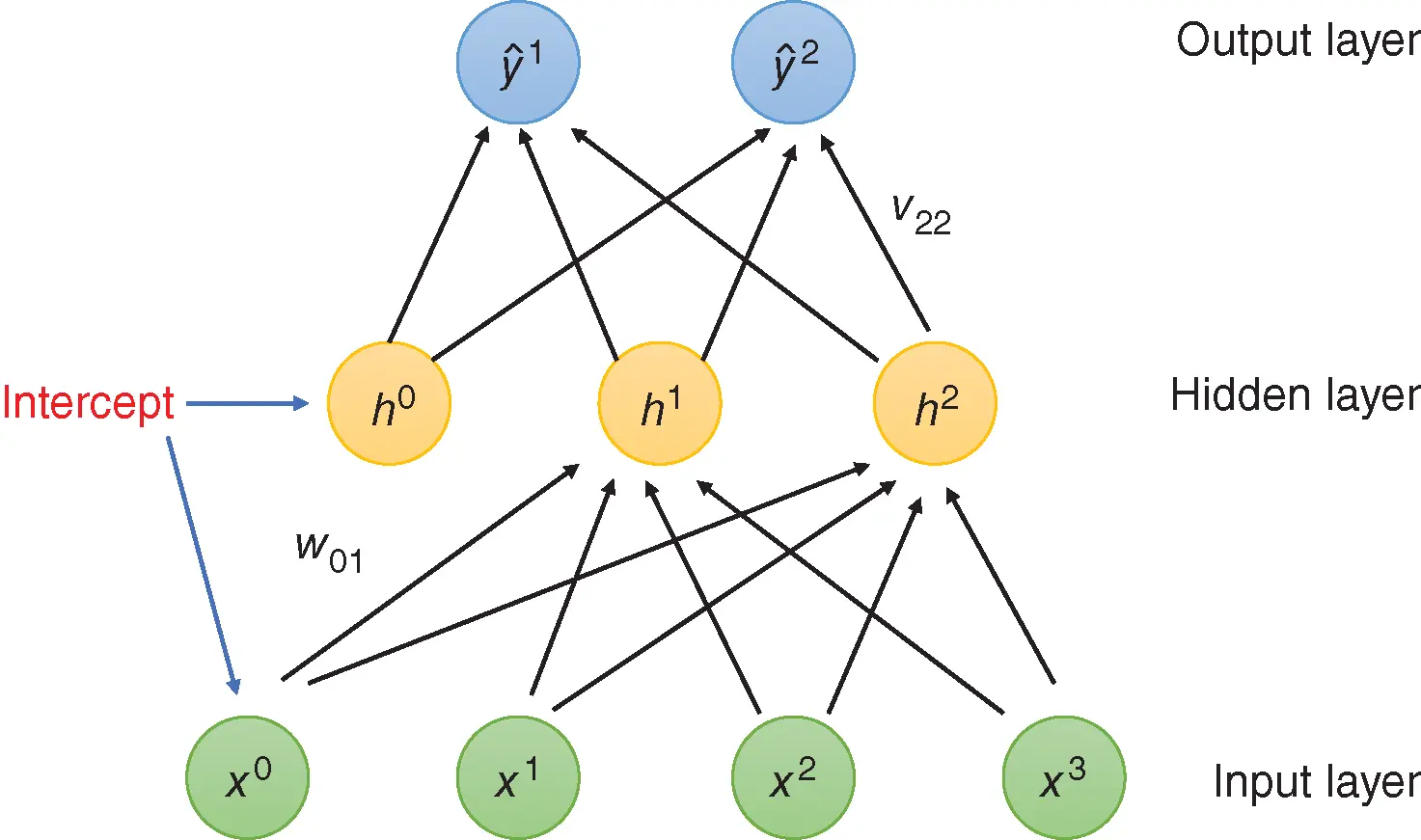
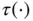 and
and 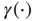 are chosen to be the logistic function
are chosen to be the logistic function 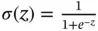 . This function is often chosen for the following desirable properties: (i) it is highly nonlinear, (ii) it is monotonically increasing, (iii) it is asymptotically bounded at some finite value in both the negative and positive directions, and (iv) its output lies in the interval
. This function is often chosen for the following desirable properties: (i) it is highly nonlinear, (ii) it is monotonically increasing, (iii) it is asymptotically bounded at some finite value in both the negative and positive directions, and (iv) its output lies in the interval 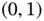 , so that it stays relatively close to 0. However, Yann LeCun recommends that a different function be used:
, so that it stays relatively close to 0. However, Yann LeCun recommends that a different function be used: 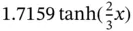 . This function retains all of the desirable properties of the logistic function and has the additional advantage of being symmetric about the origin, which results in outputs closer to 0 than the logistic function.
. This function retains all of the desirable properties of the logistic function and has the additional advantage of being symmetric about the origin, which results in outputs closer to 0 than the logistic function.![Роман Зыков - Роман с Data Science. Как монетизировать большие данные [litres]](/books/438007/roman-zykov-roman-s-data-science-kak-monetizirova-thumb.webp)










