Thanks to these advanced computational methods, one can employ more flexible models that lend themselves to more realistic reconstructions and uncertainty quantification. Following a random‐effects relaxed clock model, they model the evolutionary rate 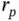 of branch
of branch 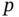 on a phylogeny as the product of a global treewise mean parameter
on a phylogeny as the product of a global treewise mean parameter 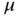 and a branch‐specific random effect
and a branch‐specific random effect 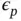 . They model the random‐effect
. They model the random‐effect 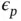 s as independent and identically distributed from a lognormal distribution such that
s as independent and identically distributed from a lognormal distribution such that 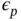 has mean 1 and variance
has mean 1 and variance 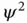 under a hierarchical model where
under a hierarchical model where 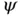 is the scale parameter. To accommodate the difference in scales of the variability in the parameter space for the HMC sampler, the authors adopt preconditioning with adaptive mass matrix informed by the diagonal entries of the Hessian matrix. More precisely, the nonzero diagonal elements of the mass matrix truncate the values from the first
is the scale parameter. To accommodate the difference in scales of the variability in the parameter space for the HMC sampler, the authors adopt preconditioning with adaptive mass matrix informed by the diagonal entries of the Hessian matrix. More precisely, the nonzero diagonal elements of the mass matrix truncate the values from the first 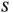 HMC iterations of
HMC iterations of 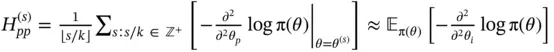 so that the matrix remains positive‐definite and numerically stable. They estimate the treewise (fixed‐effect) mean rate
so that the matrix remains positive‐definite and numerically stable. They estimate the treewise (fixed‐effect) mean rate  with posterior mean 4.75 (
with posterior mean 4.75 (  Bayesian credible interval:
Bayesian credible interval: 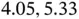 )
)  substitutions per site per year with rate variability characterized by scale parameter with posterior mean
substitutions per site per year with rate variability characterized by scale parameter with posterior mean 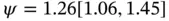 for serotype 3 of Dengue virus with a sample size of 352 [69]. Figure 1illustrates the estimated maximum clade credible evolutionary tree of the Dengue virus dataset.
for serotype 3 of Dengue virus with a sample size of 352 [69]. Figure 1illustrates the estimated maximum clade credible evolutionary tree of the Dengue virus dataset.
The authors report relative speedup in terms of the effective sample size per second (ESS/s) of the HMC samplers compared to a univariate transition kernel. The “vanilla” HMC sampler with an identity mass matrix gains 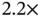 speedup for the minimum ESS/s and
speedup for the minimum ESS/s and 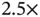 speedup for the median ESS/s, whereas the “preconditioned” HMC sampler gains
speedup for the median ESS/s, whereas the “preconditioned” HMC sampler gains 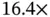 and
and 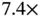 speedups, respectively. Critically, the authors make these performance gains available to scientists everywhere through the popular, open‐source software package for viral phylogenetic inference Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees (BEAST) [75]. In Section 4.1, we discuss how software package such as BEAST addresses Core Challenge 4, the creation of fast, flexible, and friendly statistical algo‐ware.
speedups, respectively. Critically, the authors make these performance gains available to scientists everywhere through the popular, open‐source software package for viral phylogenetic inference Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees (BEAST) [75]. In Section 4.1, we discuss how software package such as BEAST addresses Core Challenge 4, the creation of fast, flexible, and friendly statistical algo‐ware.
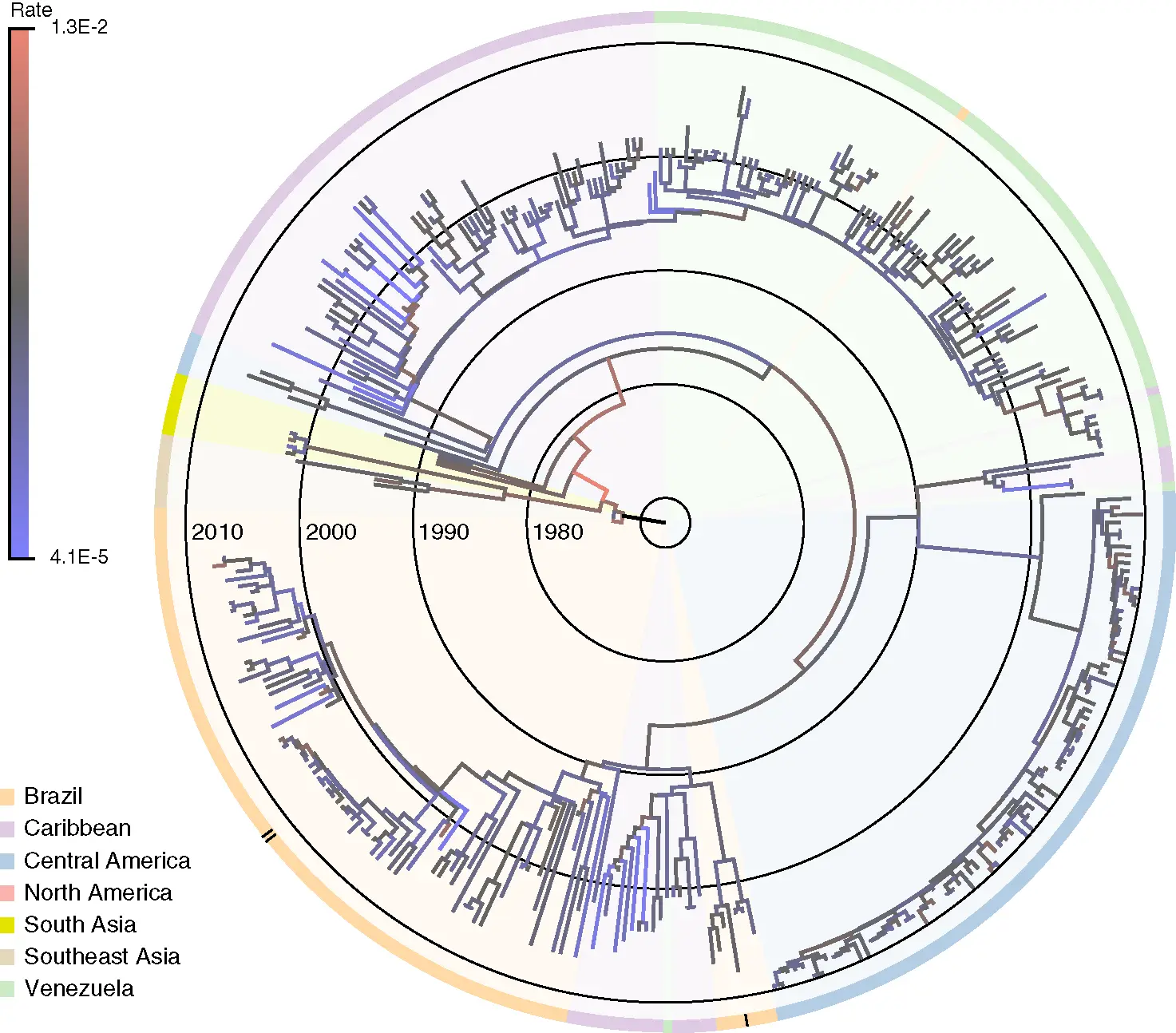
Figure 1 A nontraditional and critically important application in computational statistics is the reconstruction of evolutionary histories in the form of phylogenetic trees. Here is a maximum clade credible tree of the Dengue virus example. The dataset consists of 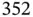 sequences of the serotype
sequences of the serotype 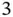 of the Dengue virus. Branches are coded by the posterior means of the branch‐specific evolutionary rates according to the gradient bar on the top left. The concentric circles indicate the timescale with the year numbers. The outer ring indicates the geographic locations of the samples by the color code on the bottom left. ‘ I’ and ‘ II’ indicate the two Brazilian lineages as in the original study.
of the Dengue virus. Branches are coded by the posterior means of the branch‐specific evolutionary rates according to the gradient bar on the top left. The concentric circles indicate the timescale with the year numbers. The outer ring indicates the geographic locations of the samples by the color code on the bottom left. ‘ I’ and ‘ II’ indicate the two Brazilian lineages as in the original study.
4 Core Challenges 4 and 5
Section 3provides examples of how computational statisticians might address Core Challenges 1–3 (big 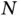 , big
, big 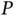 , and big
, and big 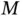 ) for individual models. Such advances in computational methods must be accompanied by easy‐to‐use software to make them accessible to end users. As Gentle et al . [76] put it, “While referees and editors of scholarly journals determine what statistical theory and methods are published, the developers of the major statistical software packages determine what statistical methods are used.” We would like statistical software to be widely applicable yet computationally efficient at the same time. Trade‐offs invariably arise between these two desiderata, but one should nonetheless strive to design algorithms that are general enough to solve an important class of problems and as efficiently as possible in doing so.
) for individual models. Such advances in computational methods must be accompanied by easy‐to‐use software to make them accessible to end users. As Gentle et al . [76] put it, “While referees and editors of scholarly journals determine what statistical theory and methods are published, the developers of the major statistical software packages determine what statistical methods are used.” We would like statistical software to be widely applicable yet computationally efficient at the same time. Trade‐offs invariably arise between these two desiderata, but one should nonetheless strive to design algorithms that are general enough to solve an important class of problems and as efficiently as possible in doing so.
Section 4.1presents Core Challenge 4, achieving “algo‐ware” (a neologism suggesting an equal emphasis on the statistical algorithm and its implementation) that is sufficiently efficient, broad, and user‐friendly to empower everyday statisticians and data scientists. Core Challenge 5 ( Section 4.2) explores the mapping of these algorithms to computational hardware for optimal performance. Hardware‐optimized implementations often exploit model‐specific structures, but good, general‐purpose software should also optimize common routines.
Читать дальше

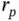 of branch
of branch 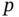 on a phylogeny as the product of a global treewise mean parameter
on a phylogeny as the product of a global treewise mean parameter 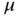 and a branch‐specific random effect
and a branch‐specific random effect 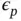 . They model the random‐effect
. They model the random‐effect 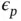 s as independent and identically distributed from a lognormal distribution such that
s as independent and identically distributed from a lognormal distribution such that 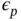 has mean 1 and variance
has mean 1 and variance 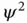 under a hierarchical model where
under a hierarchical model where 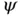 is the scale parameter. To accommodate the difference in scales of the variability in the parameter space for the HMC sampler, the authors adopt preconditioning with adaptive mass matrix informed by the diagonal entries of the Hessian matrix. More precisely, the nonzero diagonal elements of the mass matrix truncate the values from the first
is the scale parameter. To accommodate the difference in scales of the variability in the parameter space for the HMC sampler, the authors adopt preconditioning with adaptive mass matrix informed by the diagonal entries of the Hessian matrix. More precisely, the nonzero diagonal elements of the mass matrix truncate the values from the first 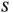 HMC iterations of
HMC iterations of 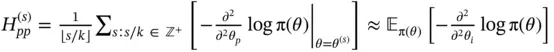 so that the matrix remains positive‐definite and numerically stable. They estimate the treewise (fixed‐effect) mean rate
so that the matrix remains positive‐definite and numerically stable. They estimate the treewise (fixed‐effect) mean rate 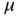 with posterior mean 4.75 (
with posterior mean 4.75 ( 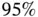 Bayesian credible interval:
Bayesian credible interval: 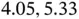 )
)  substitutions per site per year with rate variability characterized by scale parameter with posterior mean
substitutions per site per year with rate variability characterized by scale parameter with posterior mean 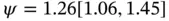 for serotype 3 of Dengue virus with a sample size of 352 [69]. Figure 1illustrates the estimated maximum clade credible evolutionary tree of the Dengue virus dataset.
for serotype 3 of Dengue virus with a sample size of 352 [69]. Figure 1illustrates the estimated maximum clade credible evolutionary tree of the Dengue virus dataset.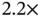 speedup for the minimum ESS/s and
speedup for the minimum ESS/s and 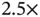 speedup for the median ESS/s, whereas the “preconditioned” HMC sampler gains
speedup for the median ESS/s, whereas the “preconditioned” HMC sampler gains 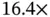 and
and 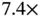 speedups, respectively. Critically, the authors make these performance gains available to scientists everywhere through the popular, open‐source software package for viral phylogenetic inference Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees (BEAST) [75]. In Section 4.1, we discuss how software package such as BEAST addresses Core Challenge 4, the creation of fast, flexible, and friendly statistical algo‐ware.
speedups, respectively. Critically, the authors make these performance gains available to scientists everywhere through the popular, open‐source software package for viral phylogenetic inference Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees (BEAST) [75]. In Section 4.1, we discuss how software package such as BEAST addresses Core Challenge 4, the creation of fast, flexible, and friendly statistical algo‐ware.
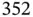 sequences of the serotype
sequences of the serotype 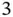 of the Dengue virus. Branches are coded by the posterior means of the branch‐specific evolutionary rates according to the gradient bar on the top left. The concentric circles indicate the timescale with the year numbers. The outer ring indicates the geographic locations of the samples by the color code on the bottom left. ‘ I’ and ‘ II’ indicate the two Brazilian lineages as in the original study.
of the Dengue virus. Branches are coded by the posterior means of the branch‐specific evolutionary rates according to the gradient bar on the top left. The concentric circles indicate the timescale with the year numbers. The outer ring indicates the geographic locations of the samples by the color code on the bottom left. ‘ I’ and ‘ II’ indicate the two Brazilian lineages as in the original study.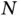 , big
, big 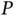 , and big
, and big 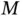 ) for individual models. Such advances in computational methods must be accompanied by easy‐to‐use software to make them accessible to end users. As Gentle et al . [76] put it, “While referees and editors of scholarly journals determine what statistical theory and methods are published, the developers of the major statistical software packages determine what statistical methods are used.” We would like statistical software to be widely applicable yet computationally efficient at the same time. Trade‐offs invariably arise between these two desiderata, but one should nonetheless strive to design algorithms that are general enough to solve an important class of problems and as efficiently as possible in doing so.
) for individual models. Such advances in computational methods must be accompanied by easy‐to‐use software to make them accessible to end users. As Gentle et al . [76] put it, “While referees and editors of scholarly journals determine what statistical theory and methods are published, the developers of the major statistical software packages determine what statistical methods are used.” We would like statistical software to be widely applicable yet computationally efficient at the same time. Trade‐offs invariably arise between these two desiderata, but one should nonetheless strive to design algorithms that are general enough to solve an important class of problems and as efficiently as possible in doing so.![Роман Зыков - Роман с Data Science. Как монетизировать большие данные [litres]](/books/438007/roman-zykov-roman-s-data-science-kak-monetizirova-thumb.webp)










