A quantum computer acts on complex data vectors of magnitude 1 called qubits with gates that are mathematically equivalent to unitary operators [100]. Assuming that engineers overcome the tremendous difficulties involved in building a practical quantum computer (where practicality entails simultaneous use of many quantum gates with little additional noise), twenty‐first century statisticians might have access to quadratic or even exponential speedups for extremely specific statistical tasks. We are particularly interested in the following four quantum algorithms: quantum search [101], or finding a single 1 amid a collection of 0s, only requires 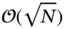 queries, delivering a quadratic speedup over classical search; quantum counting [102], or finding the number of 1s amid a collection of 0s, only requires
queries, delivering a quadratic speedup over classical search; quantum counting [102], or finding the number of 1s amid a collection of 0s, only requires  (where
(where 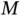 is the number of 1s) and could be useful for generating p‐values within Monte Carlo simulation from a null distribution ( Section 2.1); to obtain the gradient of a function (e.g., the log‐likelihood for Fisher scoring or HMC) with a quantum computer, one only needs to evaluate the function once [103] as opposed to
is the number of 1s) and could be useful for generating p‐values within Monte Carlo simulation from a null distribution ( Section 2.1); to obtain the gradient of a function (e.g., the log‐likelihood for Fisher scoring or HMC) with a quantum computer, one only needs to evaluate the function once [103] as opposed to 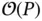 times for numerical differentiation, and there is nothing stopping the statistician from using, say, a GPU for this single function call; and finally, the HHL algorithm [104] obtains the scalar value
times for numerical differentiation, and there is nothing stopping the statistician from using, say, a GPU for this single function call; and finally, the HHL algorithm [104] obtains the scalar value 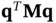 for the
for the 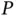 ‐vector
‐vector 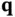 satisfying
satisfying 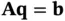 and
and 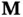 and
and  matrix in time
matrix in time 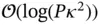 , delivering an exponential speedup over classical methods. Technical caveats exist [105], but HHL may find use within high‐dimensional hypothesis testing (big
, delivering an exponential speedup over classical methods. Technical caveats exist [105], but HHL may find use within high‐dimensional hypothesis testing (big 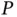 ). Under the null hypothesis, one can rewrite the score test statistic
). Under the null hypothesis, one can rewrite the score test statistic
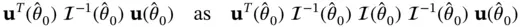
for 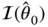 and
and 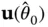 , the Fisher information and log‐likelihood gradient evaluated at the maximum‐likelihood solution under the null hypothesis. Letting
, the Fisher information and log‐likelihood gradient evaluated at the maximum‐likelihood solution under the null hypothesis. Letting 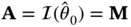 and
and 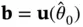 , one may write the test statistic as
, one may write the test statistic as 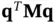 and obtain it in time logarithmic in
and obtain it in time logarithmic in 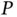 . When the model design matrix
. When the model design matrix 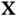 is sufficiently sparse – a common enough occurrence in large‐scale regression – to render
is sufficiently sparse – a common enough occurrence in large‐scale regression – to render 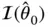 itself sparse, the last criterion for the application of the HHL algorithm is met.
itself sparse, the last criterion for the application of the HHL algorithm is met.
Core Challenges 4 and 5 – fast, flexible, and user‐friendly algo‐ware and hardware‐optimized inference – embody an increasing emphasis on application and implementation in the age of data science. Previously undervalued contributions in statistical computing, for example, hardware utilization, database methodology, computer graphics, statistical software engineering, and the human–computer interface [76], are slowly taking on greater importance within the (rather conservative) discipline of statistics. There is perhaps no better illustration of this trend than Dr. Hadley Wickham's winning the prestigious COPSS Presidents' Award for 2019
[for] influential work in statistical computing, visualization, graphics, and data analysis; for developing and implementing an impressively comprehensive computational infrastructure for data analysis through R software; for making statistical thinking and computing accessible to large audience; and for enhancing an appreciation for the important role of statistics among data scientists [106].
This success is all the more impressive because Presidents' Awardees have historically been contributors to statistical theory and methodology, not Dr. Wickham's scientific software development for data manipulation [107–109] and visualization [110, 111].
All of this might lead one to ask: does the success of data science portend the declining significance of computational statistics and its Core Challenges? Not at all! At the most basic level, data science's emphasis on application and implementation underscores the need for computational thinking in statistics. Moreover, the scientific breadth of data science brings new applications and models to the attention of statisticians, and these models may require or inspire novel algorithmic techniques. Indeed, we look forward to a golden age of computational statistics, in which statisticians labor within the intersections of mathematics, parallel computing, database methodologies, and software engineering with impact on the entirety of the applied sciences. After all, significant progress toward conquering the Core Challenges of computational statistics requires that we use every tool at our collective disposal.
AJH is supported by NIH grant K25AI153816. MAS is supported by NIH grant U19AI135995 and NSF grant DMS1264153.
1 1Statistical inference is an umbrella term for hypothesis testing, point estimation, and the generation of (confidence or credible) intervals for population functionals (mean, median, correlations, etc.) or model parameters.
Читать дальше

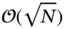 queries, delivering a quadratic speedup over classical search; quantum counting [102], or finding the number of 1s amid a collection of 0s, only requires
queries, delivering a quadratic speedup over classical search; quantum counting [102], or finding the number of 1s amid a collection of 0s, only requires  (where
(where 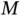 is the number of 1s) and could be useful for generating p‐values within Monte Carlo simulation from a null distribution ( Section 2.1); to obtain the gradient of a function (e.g., the log‐likelihood for Fisher scoring or HMC) with a quantum computer, one only needs to evaluate the function once [103] as opposed to
is the number of 1s) and could be useful for generating p‐values within Monte Carlo simulation from a null distribution ( Section 2.1); to obtain the gradient of a function (e.g., the log‐likelihood for Fisher scoring or HMC) with a quantum computer, one only needs to evaluate the function once [103] as opposed to 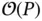 times for numerical differentiation, and there is nothing stopping the statistician from using, say, a GPU for this single function call; and finally, the HHL algorithm [104] obtains the scalar value
times for numerical differentiation, and there is nothing stopping the statistician from using, say, a GPU for this single function call; and finally, the HHL algorithm [104] obtains the scalar value 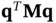 for the
for the 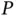 ‐vector
‐vector 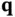 satisfying
satisfying 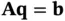 and
and 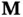 and
and  matrix in time
matrix in time 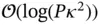 , delivering an exponential speedup over classical methods. Technical caveats exist [105], but HHL may find use within high‐dimensional hypothesis testing (big
, delivering an exponential speedup over classical methods. Technical caveats exist [105], but HHL may find use within high‐dimensional hypothesis testing (big 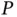 ). Under the null hypothesis, one can rewrite the score test statistic
). Under the null hypothesis, one can rewrite the score test statistic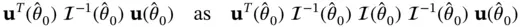
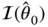 and
and 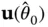 , the Fisher information and log‐likelihood gradient evaluated at the maximum‐likelihood solution under the null hypothesis. Letting
, the Fisher information and log‐likelihood gradient evaluated at the maximum‐likelihood solution under the null hypothesis. Letting 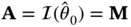 and
and 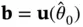 , one may write the test statistic as
, one may write the test statistic as 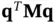 and obtain it in time logarithmic in
and obtain it in time logarithmic in 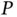 . When the model design matrix
. When the model design matrix 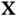 is sufficiently sparse – a common enough occurrence in large‐scale regression – to render
is sufficiently sparse – a common enough occurrence in large‐scale regression – to render  itself sparse, the last criterion for the application of the HHL algorithm is met.
itself sparse, the last criterion for the application of the HHL algorithm is met.![Роман Зыков - Роман с Data Science. Как монетизировать большие данные [litres]](/books/438007/roman-zykov-roman-s-data-science-kak-monetizirova-thumb.webp)










