In spite of the enormous diversity in the chemistry of non‐molecular, solid state materials, examples of which are given above, it is important not to lose sight of the fundamental principles associated with structure, bonding, properties, thermodynamics and kinetics of solids, since these provide a framework on which to understand and appreciate them in all their glory and complexity.
This book focuses on inorganic solids: their crystal structures, defect structures and bonding; the methods used to synthesise them and determine their structures; their physical properties and applications. Organic and other molecular materials are included in the coverage if their properties in the solid state complement, or relate to, those of inorganic solids. Physical properties are an intrinsic part of solid state chemistry since the whole area of structure–property relations requires the insights and input of chemistry to synthesise and characterise materials, as well as a good understanding of physical properties and the factors that control them.
1 Crystal Structures, Crystal Chemistry, Symmetry and Space Groups
Solid state chemistry is concerned mainly with crystalline inorganic materials, their synthesis, structures, properties and applications. A good place to begin is with crystal structures and crystal chemistry . All necessary crystal structure information is contained in data on unit cells, their dimensions and the positions or atomic coordinates of atoms inside the unit cell. Crystal chemistry combines this basic structural information with information about the elements, their principal oxidation states, ionic radii, coordination requirements and preferences for ionic/covalent/metallic bonding. A working knowledge of the Periodic Table and the properties of elements is, of course, invaluable to be able appreciate crystal chemistry, but conversely, knowledge of crystal structures and especially crystal chemistry provides a very useful way to gain increased understanding of the elements and their compounds.
Many of the properties and applications of crystalline inorganic materials revolve around a surprisingly small number of structure types. In this chapter, the main families of inorganic structures are reviewed, especially those which have interesting properties; more details of the vast array of structures may be found in the encyclopaedic text by Wells and also in the Wyckoff Crystal Structures book series. First, however, we must consider some basic concepts of crystallography.
1.1 Unit Cells and Crystal Systems
Crystals are built up of regular arrangements of atoms in three dimensions; these arrangements can be represented by a repeat unit or motif called the unit cell . The unit cell is defined as the smallest repeating unit which shows the full symmetry of the crystal structure . Let us see exactly what this means, first in two dimensions. A section through the NaCl structure is shown in Fig. 1.1(a); possible repeat units are given in (b) to (e). In each, the repeat unit is a square and adjacent squares share edges and corners. Adjacent squares are identical, as they must be by definition; thus, all the squares in (b) have Cl −ions at their corners and centres. The repeat units in (b), (c) and (d) are all of the same size and, in fact, differ only in their relative position. The choice of origin of the repeat unit is to some extent a matter of personal taste, even though its size, shape and orientation are fixed. The repeat unit of NaCl is usually chosen as (b) or (c) rather than (d) because it is easier to draw and visualise the structure as a whole if the repeat unit contains atoms or ions at special positions such as corners and edge centres. Another guideline is that usually the origin is chosen so that the symmetry of the structure is evident ( Section 1.3).
In the hypothetical case that two‐dimensional (2D) crystals of NaCl could form, the repeat unit shown in (e), or its equivalent with Cl at the corners and Na in the middle, would be the correct unit. Comparing (e) and, for example, (c), both repeat units are square and show the 2D symmetry of the structure; as the units in (e) are half the size of those in (c), (e) would be preferred according to the above definition of the unit cell. In three dimensions, however, the unit cell of NaCl is based on (b) or (c), rather than (e) because only they show the cubic symmetry of the structure (see later).
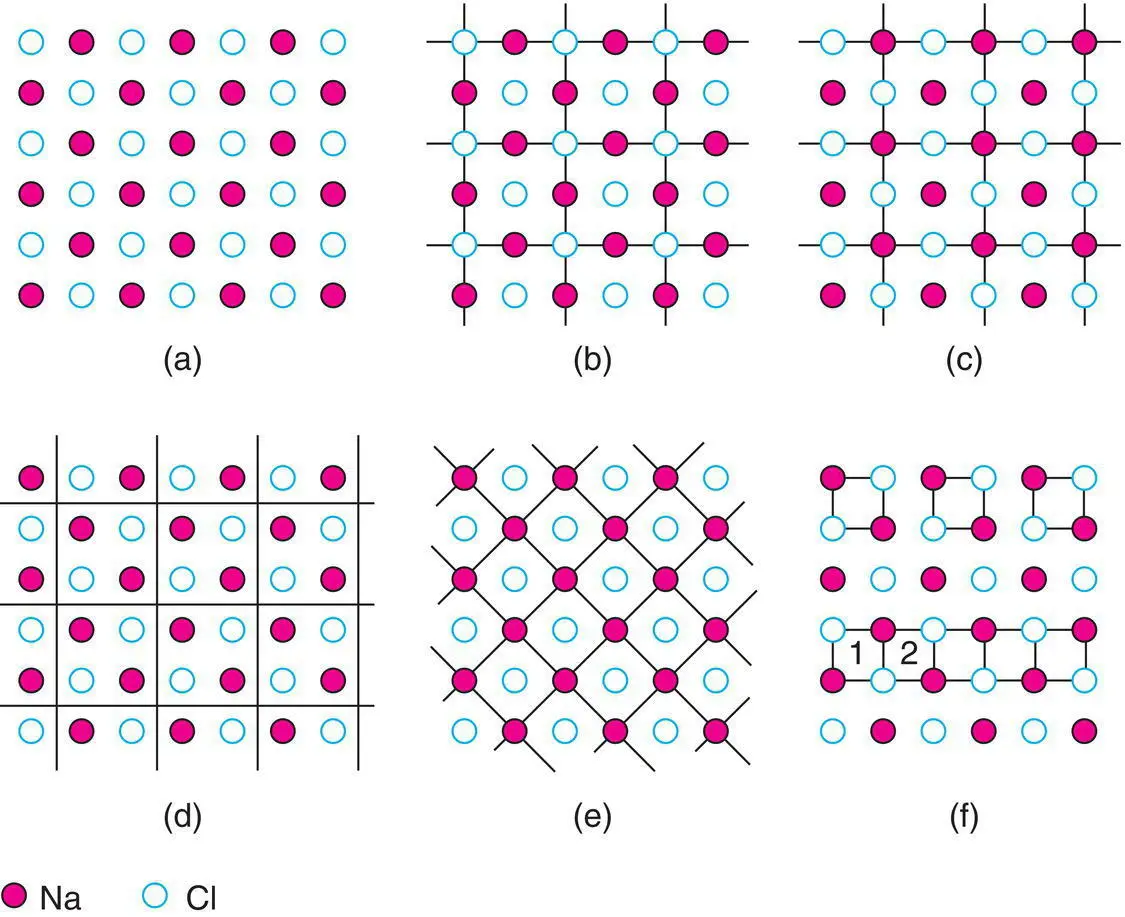
Figure 1.1 (a) Section through the NaCl structure, showing (b–e) possible repeat units and (f) incorrect units.
In (f) are shown two examples of what is not a repeat unit. The top part of the diagram contains isolated squares whose area is one‐quarter of the squares in (c). It is true that each square in (f) is identical but it is not permissible to isolate unit cells or areas from each other, as happens here. The bottom part of the diagram contains units that are not identical; thus square 1 has Na in its top right corner whereas 2 has Cl in this position.
The unit cell of NaCl in three dimensions is shown in Fig. 1.2; it contains Na at the corner and face centre positions with Cl at the edge centres and body centre. Each face of the unit cell looks like the unit area shown in Fig. 1.1(c). As in the 2D case, the choice of origin is arbitrary; an equally valid unit cell could be chosen in which Na and Cl are interchanged. The unit cell of NaCl is cubic . The three edges: a, b and c are equal in length. The three angles: α (between b and c ), β (between a and c ) and γ (between a and b ) are all 90°. A cubic unit cell also possesses certain symmetry elements and these, together with the shape define the cubic unit cell.
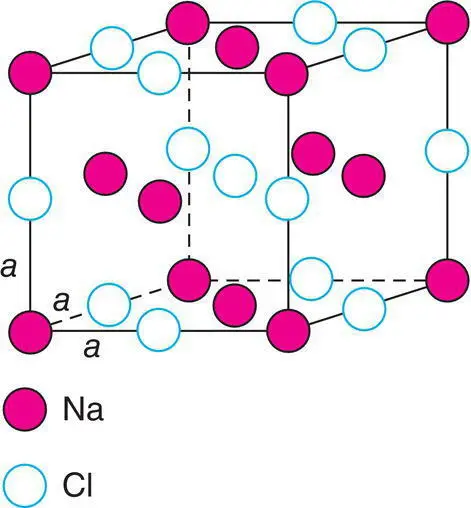
Figure 1.2 Cubic unit cell of NaCl, a = b = c.
Table 1.1 The seven crystal systems
| Crystal system |
Unit cell shape b |
Essential symmetry |
Allowed lattices |
| Cubic |
a = b = c , α = β = γ = 90° |
Four threefold axes |
P, F, I |
| Tetragonal |
a = b ≠ c , α = β = γ = 90° |
One fourfold axis |
P, I |
| Orthorhombic |
a ≠ b ≠ c , α = β = γ = 90° |
Three twofold axes or mirror planes |
P, F, I, A (B or C) |
| Hexagonal |
a = b ≠ c , α = β = 90°, γ = 120° |
One sixfold axis |
P |
| Trigonal (a) |
a = b ≠ c , α = β = 90°, γ = 120° |
One threefold axis |
P |
| Trigonal (b) |
a = b = c , α = β = γ ≠ 90° |
One threefold axis |
R |
| Monoclinic a |
a ≠ b ≠ c , α = γ = 90°, β ≠ 90° |
One twofold axis or mirror plane |
P, C |
| Triclinic |
a ≠ b ≠ c , α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90° |
None |
P |
a Two settings of the monoclinic cell are used in the literature, the most commonly used one given here, with b as the unique axis and the other with c defined as the unique axis: a ≠ b ≠ c , α = β = 90°, γ ≠ 90°.
Читать дальше














