Take-home message: It is possible to model the first TE mode of cylindrical dielectric resonators, at the cost of manually writing the mode’s field expression and numerically solving a set of equations .
Conventional MR coils, like the solenoid, have been extensively studied from a theoretical point of view and several design tools are now readily available to optimize their performance. So far, theoretical approaches have been proposed to describe the resonant modes of dielectric resonators, but rarely in the context of their use in MRI. This implies that the noise contributions of the ceramic coil need to be identified and quantified in order to estimate the achievable SNR. Provided that transmit power is enough to reach a desired flip angle (as in the case of MRM), the SNR can be evaluated as for other transceiver probes. In this section, we describe an approximate method to calculate the magnetic and electric fields of the first TE mode (TE 01δ) of a cylindrical resonator sketched in Figure 2.1; however, the methodology used to study this particular mode can be applied to any higher-order or different mode type.
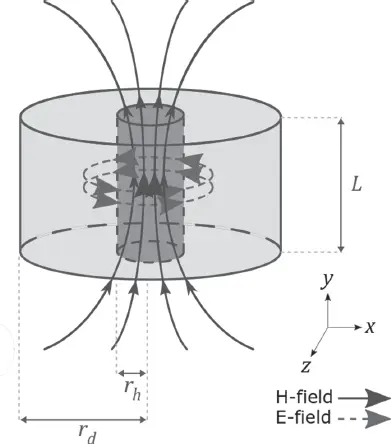
Figure 2.1 TE 01δmode of a cylindrical resonator: field-line schematic and notations.
2.3.1 Dielectric Cylindrical Resonator Modes
Describing the eigenmodes of dielectric structures relies on a similar methodology as for metallic cavities. Here we focus on resonators with circular cross sections, therefore all the equations will be expressed in a cylindrical coordinates system ( ρ , θ , y ) with ρ the radius, θ the azimuth, and y the altitude. ρ and θ relate to the Cartesian coordinates system ( x , y , z ) according to 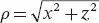 and θ = arctan z / x . The unit vectors associated with this coordinates system are denoted eρ , eθ , and ey .
and θ = arctan z / x . The unit vectors associated with this coordinates system are denoted eρ , eθ , and ey .
We start with the Helmholtz equation, in a source-free, linear, homogeneous, and isotropic medium, verified by the electric E and magnetic H fields denoted indifferently U [20, p. 16]. ω is the angular frequency, μ the medium permeability, 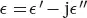 the medium complex permittivity (with j the unit imaginary number), and k is the complex wavenumber such that
the medium complex permittivity (with j the unit imaginary number), and k is the complex wavenumber such that 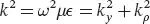 with ky and kρ the wavenumber components along the y - and the ρ -directions, respectively. The method of longitudinal components [17] uses the decomposition of the vector field U into its longitudinal Uyey and transverse UT = U − Uyey components. These components are solutions of the scalar and vector Helmholtz equations, respectively.
with ky and kρ the wavenumber components along the y - and the ρ -directions, respectively. The method of longitudinal components [17] uses the decomposition of the vector field U into its longitudinal Uyey and transverse UT = U − Uyey components. These components are solutions of the scalar and vector Helmholtz equations, respectively.
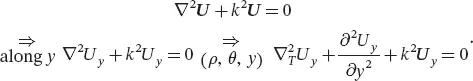 (2.1)
(2.1)
Assuming that the longitudinal component Uy can be written as the product of three functions, one for each space coordinate (in a cylindrical coordinates system in this case), the method of separation of variables allows the partial differential equation to be transformed into three independent ordinary differential equations [18]. The boundary conditions of the cavity, imposing the continuity of the tangential field components at interfaces, are then used to solve these new equations. The contributions of the axial components Uy are then separated from the transverse ones UT . The last equation for which Uy is the solution can then be solved independently in Ey , Hy , ky , and kρ . The expressions for the other field components are deduced by applying the Maxwell equations, with the resulting expressions in Equation 2.2.
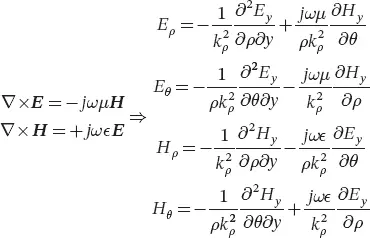 (2.2)
(2.2)
Here we add another simplification and consider only TE modes, meaning that the axial electric field component, Ey , is equal to zero everywhere. In this case, the mode field distribution is deduced from the solution Hy of Equation 2.1.
As an example, let us consider the TE modes of a disk resonator with radius r , height L , and its symmetry axis corresponding to the y -axis. Solving the above-mentioned problem leads to a solution inside the resonator of the form described in Equation 2.3(magnetic field axial component inside the disk resonator for the TE modes) with A the amplitude coefficient, n an integer describing the azimuthal mode order, ϕ and ψ constant phase shifts deduced from the boundary conditions, and Jn the Bessel function of the first kind and order n .
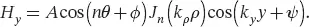 (2.3)
(2.3)
If the resonant structure has metallic borders, boundary conditions impose the field cancellation at the interfaces:
In ρ = r, the tangential components of the magnetic field vanish, for example Hy, which quantifies the radial wavenumber: (2.4)with xnm the m-th zeros of the n-th order Bessel function. This boundary condition gives the radial variation order m, which is an integer.
In the magnetic field tangential components vanish, for example Hρ, which quantifies the axial wavenumber:
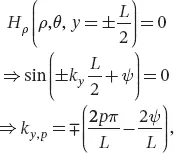 (2.5)
(2.5)
with p an integer defining the axial variation order.
For a metallic cavity, the mode variations are quantified by three integers, n , m , and p , and is therefore named TE nmp. It is the same principle for transverse magnetic (TM) and hybrid (HEM) mode types.
When the resonant structure has dielectric/dielectric or dielectric/air interfaces with the surrounding medium, this quantification with integer numbers is no longer valid since the electromagnetic (EM) field does not vanish at the boundaries. In such situations, the EM field outside the resonator must be explicitly expressed. An approximation consists of writing the field outside with similar variations as inside the resonator with evanescent terms, neglecting the contribution of other modes to the decaying part. This can be made part by part, as developed in [4,7] and as shown in Figure 2.2 for the disk resonator.
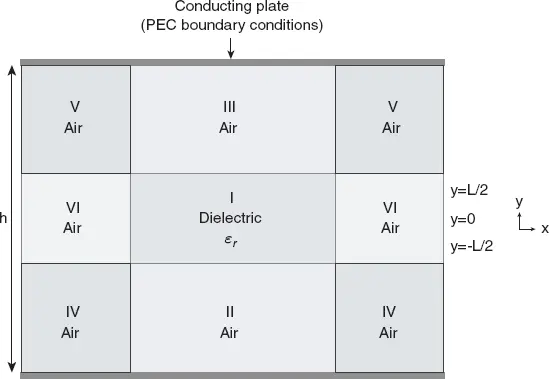
Figure 2.2 Resonant mode field estimation: part-by-part decomposition of the computation volume, case of the disk resonator.
Читать дальше


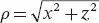 and θ = arctan z / x . The unit vectors associated with this coordinates system are denoted eρ , eθ , and ey .
and θ = arctan z / x . The unit vectors associated with this coordinates system are denoted eρ , eθ , and ey .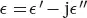 the medium complex permittivity (with j the unit imaginary number), and k is the complex wavenumber such that
the medium complex permittivity (with j the unit imaginary number), and k is the complex wavenumber such that 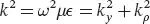 with ky and kρ the wavenumber components along the y - and the ρ -directions, respectively. The method of longitudinal components [17] uses the decomposition of the vector field U into its longitudinal Uyey and transverse UT = U − Uyey components. These components are solutions of the scalar and vector Helmholtz equations, respectively.
with ky and kρ the wavenumber components along the y - and the ρ -directions, respectively. The method of longitudinal components [17] uses the decomposition of the vector field U into its longitudinal Uyey and transverse UT = U − Uyey components. These components are solutions of the scalar and vector Helmholtz equations, respectively.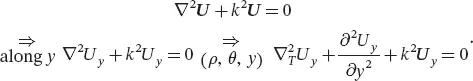 (2.1)
(2.1)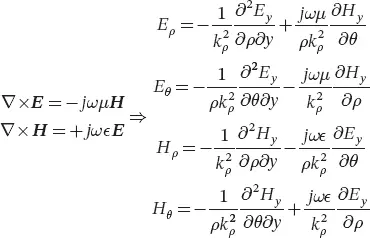 (2.2)
(2.2)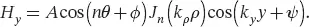 (2.3)
(2.3)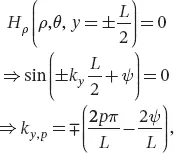 (2.5)
(2.5)





