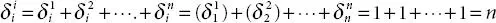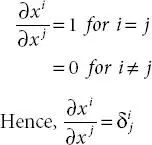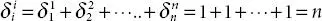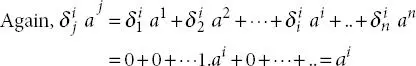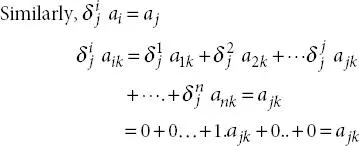1.2 Systems of Different Orders
Let us consider the two quantities, a 1, a 1 or a 1, a 2, which are represented by ai or ai , respectively, for i = 1, 2. In such cases, the expressions ai , ai , ai j , ai j , and 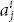 are called systems . In each value of ai and ai are called systems of first order and each value of ai j , ai j , and
are called systems . In each value of ai and ai are called systems of first order and each value of ai j , ai j , and 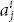 is called a double system or system of second order , of which a 12, a 22 a 23, a 13, and
is called a double system or system of second order , of which a 12, a 22 a 23, a 13, and 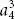 are called their respective components . Similarly, we have systems of the third order that depend on three indices shown as ai jk , aikl , ai jm , ai jn , and
are called their respective components . Similarly, we have systems of the third order that depend on three indices shown as ai jk , aikl , ai jm , ai jn , and 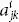 and each number of their respective components are 8.
and each number of their respective components are 8.
In a system of order zero, it is shown that the quantity has no index, such as a . The upper and lower indices of a system are called its indices of contravariance and covariance , respectively. For a system of 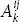 , i and j are indices of a contravariant and k is of covariance . Accordingly, the system Aij is called a contravariant system, Aklm is called a covariant system, and is
, i and j are indices of a contravariant and k is of covariance . Accordingly, the system Aij is called a contravariant system, Aklm is called a covariant system, and is 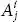 called a mixed system .
called a mixed system .
1.3 Summation Convention Certain Index
If in some expressions a certain index occurs twice, this means that this expression is summed with respect to that index for all admissible values of the index.
Thus, the linear form 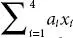 has an index, i, occurring in it twice. We will omit the summation symbol Σ and write aixi to mean a 1 x 1+ a 2 x 2+ a 3 x 3+ a 4 x 4. In order to avoid Σ, we shall make use of a convention used by A. Einstein which is accordingly called the Einstein Summation Convention or Summation Convention .
has an index, i, occurring in it twice. We will omit the summation symbol Σ and write aixi to mean a 1 x 1+ a 2 x 2+ a 3 x 3+ a 4 x 4. In order to avoid Σ, we shall make use of a convention used by A. Einstein which is accordingly called the Einstein Summation Convention or Summation Convention .
Of course, the range of admissible values of the index, 1 to 4 in this case, must be specified. If the symbol i has a range of values from 1 to 3 and j ranges from 1 to 4, the expression
(1.1)
represents three linear forms:
(1.2) 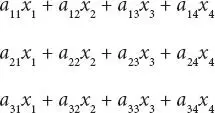
Here, index i is the identifying (free) index and since index j , occurs twice, it is the summation index.
We shall adopt this convention throughout the chapters and take the sum whenever a letter appears in a term once in a subscript and once in superscript or if the same two indices are in subscript or are in superscript.
Example 1.3.1.Express the sum 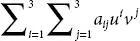 .
.
Solution: 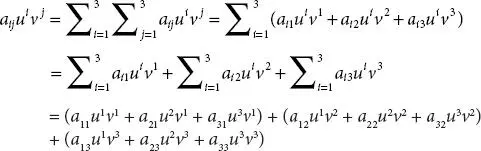
The summation (or dummy) index can be changed at will. Thus, Equation (1.1)can be written in the form a ikx kif k has the same range of values as j.
We will assume that the summation and identifying indices have ranges of value from 1 to n.
Thus, aixi will represent a linear form
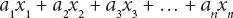
For example, 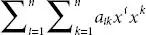 can be written as aikxixk and here, i and k both are dummy indexes.
can be written as aikxixk and here, i and k both are dummy indexes.
So, any dummy index can be replaced by any other index with a range of the same numbers.
If in an expression an index is not a dummy, i.e., it is not repeated twice, then it is called a free index . For example, for ai jxj , the index j is dummy, but index i is free.
A particular system of second order denoted by 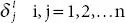 , is defined as
, is defined as
(1.3) 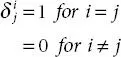
Such a system is called a Kronecker symbol or Kronecker delta .
For example, 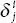 , by summation convention is expressed as
, by summation convention is expressed as
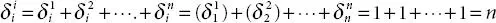
We shall now consider some properties of this system.
Property 1.4.1.If x 1, x 2, … xn are independent variables, then
(1.4) 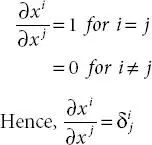
Property 1.4.2.From the summation convention, we get
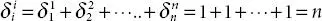
Similarly, δ ii= δ ii= n
Property 1.4.3.From the definition of δ i j, taken as an element of unit matrix I, we have

Property 1.4.4.
(1.5) 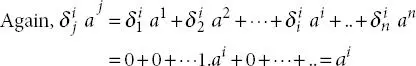
(1.6) 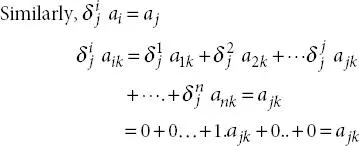
Читать дальше

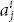 are called systems . In each value of ai and ai are called systems of first order and each value of ai j , ai j , and
are called systems . In each value of ai and ai are called systems of first order and each value of ai j , ai j , and 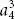 are called their respective components . Similarly, we have systems of the third order that depend on three indices shown as ai jk , aikl , ai jm , ai jn , and
are called their respective components . Similarly, we have systems of the third order that depend on three indices shown as ai jk , aikl , ai jm , ai jn , and 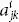 and each number of their respective components are 8.
and each number of their respective components are 8.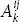 , i and j are indices of a contravariant and k is of covariance . Accordingly, the system Aij is called a contravariant system, Aklm is called a covariant system, and is
, i and j are indices of a contravariant and k is of covariance . Accordingly, the system Aij is called a contravariant system, Aklm is called a covariant system, and is 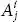 called a mixed system .
called a mixed system .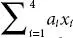 has an index, i, occurring in it twice. We will omit the summation symbol Σ and write aixi to mean a 1 x 1+ a 2 x 2+ a 3 x 3+ a 4 x 4. In order to avoid Σ, we shall make use of a convention used by A. Einstein which is accordingly called the Einstein Summation Convention or Summation Convention .
has an index, i, occurring in it twice. We will omit the summation symbol Σ and write aixi to mean a 1 x 1+ a 2 x 2+ a 3 x 3+ a 4 x 4. In order to avoid Σ, we shall make use of a convention used by A. Einstein which is accordingly called the Einstein Summation Convention or Summation Convention .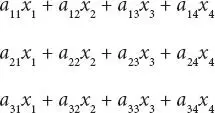
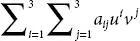 .
.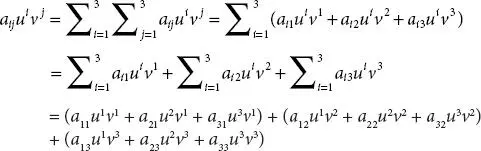
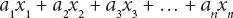
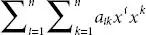 can be written as aikxixk and here, i and k both are dummy indexes.
can be written as aikxixk and here, i and k both are dummy indexes.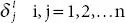 , is defined as
, is defined as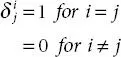
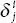 , by summation convention is expressed as
, by summation convention is expressed as