Barry Fox - Arthritis For Dummies
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Barry Fox - Arthritis For Dummies» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Arthritis For Dummies
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Arthritis For Dummies: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Arthritis For Dummies»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Arthritis For Dummies
Arthritis For Dummies
Arthritis For Dummies — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Arthritis For Dummies», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Cartilage: The human shock absorber
Cartilage is extremely important for the healthy functioning of a joint, especially if that joint bears weight, like your knee. Imagine for a moment that you’re looking into the inner workings of your left knee as you walk down the street. When you shift your weight from your left leg to your right, the pressure on your left knee is released. The cartilage in your left knee then “drinks in” synovial fluid, in much the same way that a sponge soaks up liquid when immersed in water. When you take another step and transfer the weight back onto your left leg, much of the fluid squeezes out of the cartilage. This squeezing of joint fluid into and out of the cartilage helps it respond to the off-and-on pressure of walking without shattering under the strain.
Can you imagine the results if we didn’t have this watery cushion within our joints? With the rough, porous surfaces of the bone ends pitted against each other, bones would grind each other down in no time. One thing is certain: Nobody would be getting around too easily without joint fluid and cartilage.
Types of joints
To accommodate the bends, twists, and turns that we all perform without even thinking, the skeletal system is made up of different shapes and sizes of bones, which connect to form different kinds of joints. The joints are categorized according to how much motion they allow:
Synarthrodial joints allow no movement at all. You can find these in the skull, where the bones meet to form tough, fibrous joints called sutures. Because they don’t move, arthritis doesn’t affect them.
Amphiarthrodial joints, such as those in the spine or the pelvis, allow limited movement. Generally, these joints aren’t attacked by arthritic conditions as often as others. (A slipped disc is not arthritis.)
Synovial joints allow a wide range of movement; most of our joints fall into this class. Synovial joints come in all kinds of interesting variations including those that glide, hinge, pivot, look like saddles, or have a ball-and-socket type structure. (For more on these joints, take a look at the section “ Looking at the types of synovial joints” later in this chapter.) Because of the synovial joints, you can bend over and pick a flower, kick up your heels while swing dancing, reach for a glass on a high shelf, and turn around to see what’s going on behind you. Unfortunately, these joints are also the ones most likely to be hit with arthritis, precisely because they do move!
STRANGE-BUT-TRUE JOINT POINTS
Here are a couple of things you may not know about your joints:
By the time a fetus is four months old, its joints and limbs are in working order and ready to move.
A newborn baby has 350 bones, many of which fuse to form the 206 bones of the adult body.
Cartilage is 65 percent to 85 percent water. (The amount of water in your cartilage generally decreases as you get older.)
When you run, the pressure on your knees can increase to ten times that of your body weight.
Not a single man-made substance is more resilient, a better shock absorber, or lower in friction than cartilage.
Looking at the types of synovial joints
 Because of their tendency to become arthritic, synovial joints are the ones that we discuss the most throughout this book. Synovial joints come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes to accommodate a wide variety of movements.
Because of their tendency to become arthritic, synovial joints are the ones that we discuss the most throughout this book. Synovial joints come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes to accommodate a wide variety of movements.
Gliding joints
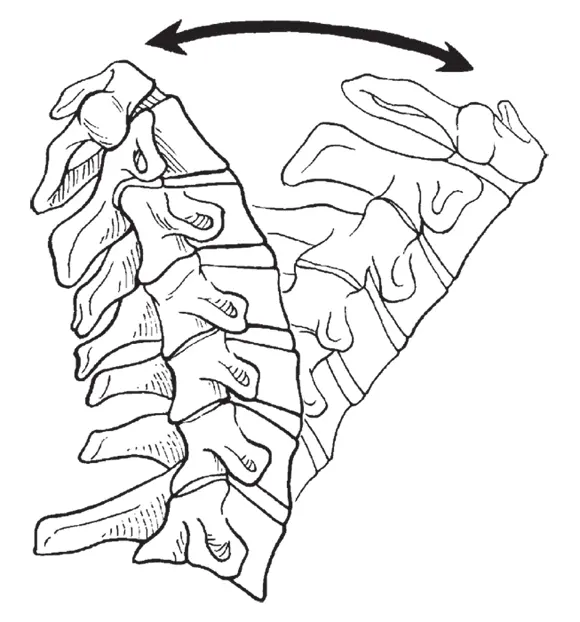
A gliding joint contains two bones with somewhat flat surfaces that can slide over each other. The vertebrae in your spine are connected by gliding joints, allowing you to bend forward to touch your toes and backward to do a backbend (well, maybe!). See Figure 1-2 for an example of a gliding joint.
Hinge joints
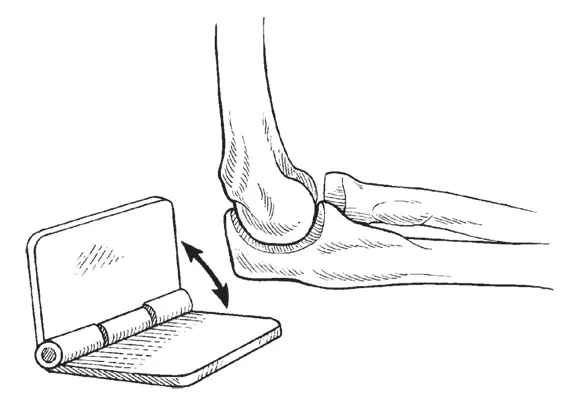
You can find hinge joints in your elbows, knees, and fingers. These joints open and close like a door. But just like a door, hinge joints only go one way — you can’t bend your knee up toward your face, only back toward your rear. See Figure 1-3 for an example of a hinge joint.
© John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
FIGURE 1-2:A gliding joint. The gliding joint helps keep your vertebrae aligned when you bend and stretch.
© John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
FIGURE 1-3:A hinge joint. Hinge joints bend only one way.
Saddle joints
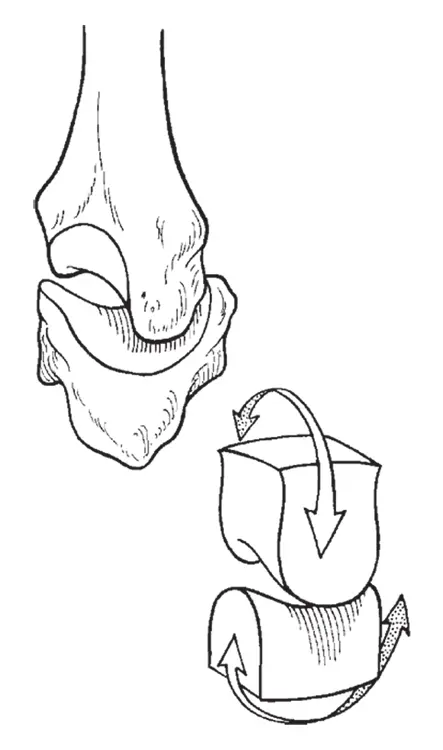
This joint looks like a horse’s back with a saddle resting on it. One bone is rounded ( convex ) and fits neatly into the other bone, which is concave . The saddle joint moves up and down and side to side, but it doesn’t rotate. Your wrist and your thumb have this kind of joint. See Figure 1-4 for an example of a saddle joint.
© John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
FIGURE 1-4:A saddle joint. The saddle joint moves up and down and side to side.
Ball-and-socket joints
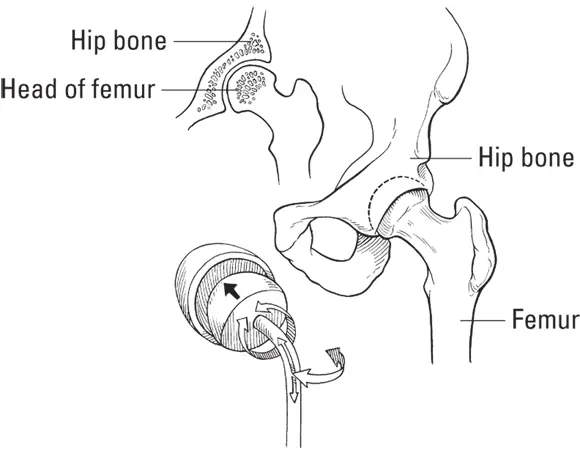
This is truly a freewheeling joint — it’s ready for anything! Up, down, back, forth, or around in circles. The bone attached to a ball-and-socket joint can move in just about any direction. The end of one bone is round, like a ball, whereas the other bone has a neat little cave that the ball fits into. Your shoulders and hips have ball-and-socket joints. Swimming the backstroke is a perfect example of the kind of range of motion made possible by these joints. See Figure 1-5 for an example of a ball-and-socket joint.
© John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
FIGURE 1-5:A ball-and-socket joint. These joints can move just about any direction — up, down, back, forth, or around in circles.
Distinguishing Between Arthritis and Arthritis-Related Conditions
 Some organizations define arthritis as a group of more than 100 related diseases, ranging from bursitis to osteoarthritis. But in this book, we use the following classifications, which conform to those widely accepted by the medical community:
Some organizations define arthritis as a group of more than 100 related diseases, ranging from bursitis to osteoarthritis. But in this book, we use the following classifications, which conform to those widely accepted by the medical community:
“True” arthritis
Arthritis as a “major player”
Arthritis as a “minor player”
Arthritis as a “companion condition”
In the following subsections, we go over the various types of arthritis and arthritis-related diseases and their classifications. We also discuss each disease in greater detail in Chapters 2, 3, 4and 5. (Check out the sidebar titled “Hypersensitive fingers and toes” later in the chapter to find out about Raynaud’s phenomenon, a particularly chilling form of arthritis.)
Defining “true” arthritis
True arthritis isn’t a medical term; it’s just a convenient way of referring to the group of ailments in which arthritis is the primary disease process and is a major part of the syndrome. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the best-known members of this group, which can cause problems ranging from mild joint pain to a permanently bowed spine.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Arthritis For Dummies»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Arthritis For Dummies» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Arthritis For Dummies» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












