Yang Xia - Essential Concepts in MRI
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Yang Xia - Essential Concepts in MRI» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Essential Concepts in MRI
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Essential Concepts in MRI: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Essential Concepts in MRI»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A concise and complete introductory treatment of NMR and MRI Essential Concepts in MRI
Essential Concepts in MRI
Essential Concepts in MRI — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Essential Concepts in MRI», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
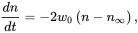 (3.33)
(3.33)
where d n /d t goes to zero as n (a variable) goes to n∞ (a constant given by the population difference in the presence of B 0but in the absence of another rf field). If we define
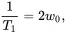 (3.34)
(3.34)
and multiplying Eq. ( 3.33) with (1/2)γℏ, we can derive
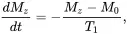 (3.35)
(3.35)
which has been defined previously as Eq. (2.15a). Therefore, we can interpret T 1in terms of quantum transitions between the states.
The process of transverse relaxation may also be viewed as the result of quantum transitions. By defining the probability of transition between the states of operators Ix ′and Iy ′as w 0x′and w 0y′, and recognizing at w0x′=w0y′=w0⊥, we can derive
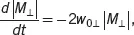 (3.36)
(3.36)
where |M⊥|=(Mx′2+My′2)1/2. Hence,
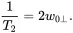 (3.37)
(3.37)
3.7.2 Relaxation Mechanisms in the Random Field Model
More complicated explanation of relaxation mechanisms employs time-dependent Hamiltonians of the nuclear interactions. While in higher spin systems quadrupole interactions are significant, the dominant interaction in the spin-1/2 nuclei arises from the dipolar Hamiltonian, where the random field model of relaxation contains a very useful parameter ( τ c) that relates to the motional properties of the molecules. A full account of this model is too lengthy for this introductory book; here we quote some arguments and conclusions of this so-called Bloembergen–Purcell–Pound theory (BPP theory) [11].
The random field model of relaxation is simplified by restricting consideration to a pair of like spins under the influence of the dipolar interaction. The arguments for the spin-lattice relaxation in this model consider the fact that each spin is not completely isolated from the rest of the molecular ensemble (the lattice). There is an interaction between the spin and the lattice, due to the molecular motions, that enables the exchange of the thermal energy. Each nucleus is influenced by a number of nearby nuclei. These neighboring nuclei, in the same and other molecules, are in thermal motion with respect to the observed nucleus. This collection of motions gives rise to a fluctuating magnetic field, which disturbs the applied external field B 0. Consequently, the magnetic moment will also experience the fluctuating local fields of its neighbors. Given the random nature for the motions of each molecule and of its neighbors, the motion would have a broad distribution of the frequencies. When the fluctuating local fields have components in the direction of B 1and at the precessing frequency ω 0, these field components will induce transitions between energy levels, just like a purposefully applied B 1field.
The model defines a spectral density function Jq(ω) , which is the Fourier transform of the auto-correlation function of the spatial tensor component q(t) . Jq(ω) represents the relative intensity of the motional frequency ω . The auto-correlation function has some characteristic time τc where the function goes to zero when t ≫ τc . Hence, Jq(ω) has a characteristic frequency ( τc -1), with which Jq(ω) goes to zero when ω ≫ τc -1. The correlation time τc is the characteristic time of the signal decay, which can be defined as the average time between molecular collisions for translational motion. The value of τc depends upon many factors of the sample, such as molecular size, molecular symmetry, and solution viscosity. For random molecular tumbling, τc corresponds approximately to the average time for a molecule to rotate through one radian. A shorter/longer τc corresponds to samples with more/less mobile molecules.
Figure 3.3 shows schematically the variations of the spectral density function Jq(ω) in three different cases. Since the area under each curve represents the total energy available for the motion, the area under any curve stays constant among the curves. If τc is long (case a in Figure 3.3), as in solids or viscous liquids, the low motional frequencies have a higher chance of occurring, and consequently Jq(ω) has weaker components at ω 0. At the other extreme, if τc is short (case c in Figure 3.3), as in liquids of low viscosity, molecular motions are distributed over a wide frequency range, and all motional frequencies within that range have equally probable chance of occurring; however, no one component, in particular that at ω 0, can be very intense. An optimum efficiency for thermal relaxation of the spins can be expected when Jq(ω) reaches a maximum at ω 0, when ωτc ~ 1 (case b in Figure 3.3).
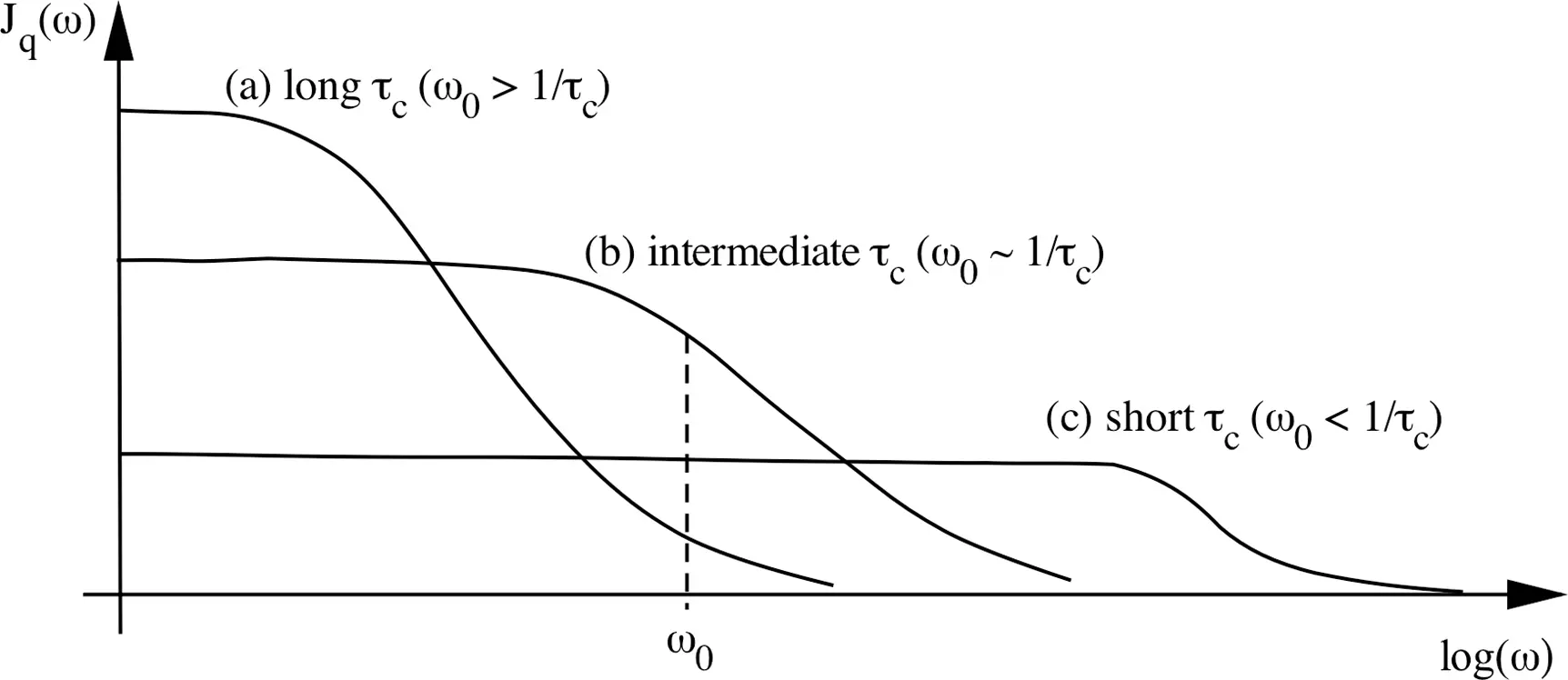
Figure 3.3 Schematic power spectra of the spectral density function Jq(ω) , as the function of the frequency log( ω ). (Case a) Specimens having high viscosities or rigid lattice have long τc ( ω 0> 1/ τ c), which leads to weak Jq(ω) at ω 0. (Case b) Specimens having intermediate viscosities have shorter τ c( ω 0~ 1/ τ c), which leads to a maximum Jq(ω) at ω 0, hence optimum relaxation. (Case c) Specimens having low viscosities have short τc ( ω 0< 1/ τ c), which leads to a broad spectrum of Jq(ω) with no component having a high value.
This model shows that the spin-lattice relaxation will depend on Jq ( ω 0), which has a line shape of a Lorentzian. We can also show that, by similar arguments or using the density operator formalism, the spin-spin relaxation will depend on Jq (0), because it involves no energy exchange. Figure 3.4 shows schematically the plots of relaxation times as the function of log( τc ). On the left of the condition when ω 0 τ c= 1, T 1is approximately equal to T 2, a regime that is called the extreme narrowing regime. When the molecules become less mobile [towards the right along the log( τc ) axis], differences between T 1and T 2become significant, where T 1becomes long (tens of minutes or much longer) while T 2becomes short (tens of milliseconds or much shorter). This random field model is valid in the “weak collision” case where τc < T 2; the theory will fail at the situation in relatively rigid materials. Some of the longest T 1are commonly found in solids, on the order of tens of minutes; some of the shortest T 2are on the order of 10 µs, which occurs in solids as well as well-organized connective tissues such as tendon and ligaments. Typical ranges of T 1and T 2for biological tissues are marked in Figure 3.4.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Essential Concepts in MRI»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Essential Concepts in MRI» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Essential Concepts in MRI» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












