where the numerators are individual populations and the denominator is the total population.
Note that k B T is the Boltzmann energy and ħγB 0is the Zeeman energy difference. For example, for protons in a magnetic field of strength B 0= 7 Tesla and at room temperature (T = 300 K), we have
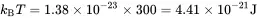
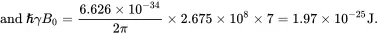
Since k B T is over four orders of magnitude bigger than ħγB 0, the ratio ħγB 0/ k B T is tiny. This is a good news and bad news situation: the good news is that the exponentials in Eq. ( 3.14) can be simplified using the Taylor expansion since the high-order terms would be very small, while the bad news means that our signal will be very small, since the signal is proportional to the population difference.
Due to this tiny ratio between the Zeeman energy and the Boltzmann energy, we can apply the Taylor expansion (Appendix A1.1.4) to simplify the expression in Eq. ( 3.14) by keeping only the first two terms, as
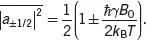 (3.15)
(3.15)
This equation at the room temperature and a 7 Tesla B 0equals approximately 0.5 ± 1.12 × 10 -5, which is almost a half and half situation between the two populations. This approximation is known as the “high-temperature approximation” in the NMR literature, except the “high temperature” in this estimation actually means the room temperature.
3.4 MEASUREMENT OF THE X COMPONENT OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM
In Appendix A2.6, we introduce the concept of density matrix operator ρ , which relates the expectation value of any operator Ato the trace of the matrix product A ρ , via Eq. (A2.33). Since Ix=12[0110] in the formalism of Pauli’s spin matrices (cf. Appendix A2.5), we have, from Eq. ( 3.12),
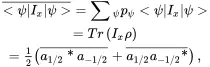 (3.16)
(3.16)
where Tr represents the trace of the matrix (the sum of the diagonal elements) – see Eqs. (A2.32) and (A2.33), and the two examples at the end of Appendix A2.6. The term in brackets describes the degree of “single quantum coherence” of the ensemble, while the average (the bars) reflects the phase coherence between the +1/2 and –1/2 states. At thermal equilibrium, both a1/2*a−1/2¯ and a1/2a−1/2*¯ are zero (no transverse component), while the term (|a1/2|2¯−|a−1/2|2¯) has a stable value (the longitudinal magnetization along the z axis).
3.5 MACROSCOPIC MAGNETIZATION FOR SPIN 1/2
In the current context, the observable quantity is just the (macroscopic) magnetization M, given by
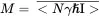 (3.17a)
(3.17a)
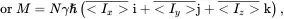 (3.17b)
(3.17b)
where N is the number of spins, and i, j,and kare the unit vectors in the Cartesian coordinates. Equation (3.17) is important because it may be shown that any state of the density matrix (defined in Appendix A2.6) for an ensemble of non-interacting spin-1/2 particles can be described using the macroscopic magnetization defined in this manner, thus permitting a classical description of simple spin systems.
In the absence of an external magnetic field, the ensemble average of the magnetization vector should be zero due to the random directions of the magnetic dipoles of the nuclei.
If a sample is immersed in an external field and in thermal equilibrium, the density operator associated with this magnetization vector is given by
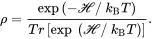 (3.18)
(3.18)
The transverse component of Mis zero due to the even distribution of the azimuthal phase angles of the precessing nuclei in the transverse plane. This corresponds to phase incoherence leading to the zero value of the off-diagonal elements of ρ ,
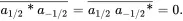 (3.19)
(3.19)
The z component of the magnetization Marises from the difference in populations between the upper and lower energy states. At room temperature, the magnitude of this magnetization in the equilibrium state, M 0, can be derived as
 (3.20)
(3.20)
For a spin-1/2 system at room temperature, the population difference between the spin-up (m=+1/2) state and the spin-down (m=−1/2) state can be calculated from the diagonal elements of ρ , as
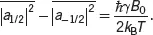 (3.21)
(3.21)
For protons at B 0= 1.4 T (60 MHz), it is equal to about 5 × 10 -6, a small value resulting from the small value of γħB 0(Zeeman splitting) compared to k B T (Boltzmann energy). It is this small magnetization of nuclei at room temperature that limits NMR detection sensitivity and leads to resolution limitations in MRI experiments [7, 8].
When both B 0and B 1( t ) are present and perpendicular to each other ( B 1in the transverse plane), we can write down the Hamiltonian in the laboratory frame as
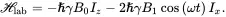 (3.22)
(3.22)
In the rotating frame, the Hamiltonian becomes
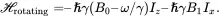 (3.23)
(3.23)
At ω = ω 0, we have
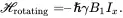 (3.24)
(3.24)
Since Ix=12(I++I−), where I +and I -are the raising and lowering operators defined in Appendix A2.4, the time evolution of the spin system corresponds to an inter-conversion of each spin between |1/2> and | – 1/2> at a rate of γB 1(an oscillation).
3.7 MECHANISMS OF SPIN RELAXATION
Spin relaxation is truly fundamental and central to the theory of NMR and MRI; the influence of spin relaxation on both NMR and MRI measurements is wide, deep, and quite often subtle. It is therefore worth taking some time to learn to appreciate the subtleties of spin relaxation.
Читать дальше

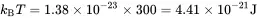
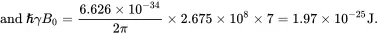
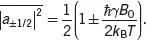 (3.15)
(3.15)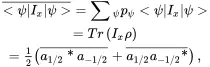 (3.16)
(3.16)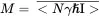 (3.17a)
(3.17a)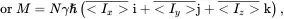 (3.17b)
(3.17b)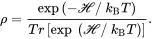 (3.18)
(3.18)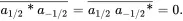 (3.19)
(3.19) (3.20)
(3.20)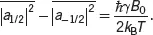 (3.21)
(3.21)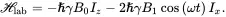 (3.22)
(3.22)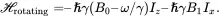 (3.23)
(3.23)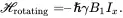 (3.24)
(3.24)










