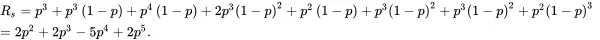Calculate the reliability of the bridge system in Figure 1.11, if the reliability of each component is p.
The block decision diagram of the bridge system is shown in Figure 1.12.

Figure 1.12 Block decision diagram of the bridge system.
The reliability of the system is
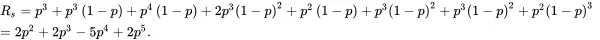
1 Consider an electrical generating system with two engines, E1, E2, and three generators, G1, G2, G3, each one with rate equal to 30 kVA. The system fails when the generators fail to supply at least 60 kVA. The structure of the system is shown in Figure 1.13. Figure 1.13 Electrical generating system.Find the minimal cut sets of the system.Estimate the unreliability of the system for one-month operation, given that the failure rate for each engine is 5×10−6h−1 and that for each generator is 10−5h−1.
2 Consider the reliability of the following system consisting of five components in Figure 1.14. All the components are identical and independent from each other. The reliability of components i is Ri. Let Rs be the reliability of the system. Give the reliability formulation of the system. Figure 1.14 Reliability block diagram of the system.
3 The system has N = 4 components. Each component has three states: (M∈{0,1,2}). Let xi denote the state of component i: then, we have the probability P(xi≥1)=0.7, P(xi=2)=0.5, for i =1,2,3,4. Give the following system structure function,ϕ(x)=min(x1,(x2+x3),x4).Find all minimal path and cut vectors (MPVs and MCVs) of the system.Calculate system reliability R=Pr(ϕ(x)≥1).
4 The power grid structure is shown in Figure 1.15 below. There are three substations: A is the power supplier that generates electric power to be transmitted to the substations B and C, which are the power consumers. Assume that the substations are always working but the power transmission lines may fail. The overall power grid works only if all the following conditions are satisfied: Figure 1.15 Diagram of the power grid structure.Both substations B and C have power input.At least two outgoing transmission lines of A are working.
Then
1 Build a BDD for the power grid system.
2 Estimate the unreliability of the system for one-month operation by BDD, given that the failure rate for lines 1, 2, 3 is λ1=510−6 h-1 and for lines 4, 5 is λ2=10−5 h-1.
1 Consider the series-parallel system in Figure 1.16. The components 1, 2, 3, and 4 are independent from each other and have exponential reliabilities with failure rates λ1, λ2, λ3 and λ4, respectively. Assuming that λ1=2λ3 and λ4=λ2/2, calculate the system mean time to failure (MTTF) expression in terms of λ2 and λ3.
2 A manufacturer performs a test on a ceramic capacitor and finds that it experiences failures exponentially distributed in time, with rate λ=510−4 failures per hour. To retain operation performance of the ceramic capacitor, an instantaneous and imperfect maintenance activity is performed at an interval of 103 hours. The reliability after maintenance is 0.98. Calculate the average availability and the instantaneous availability at time 1.2103 hours.
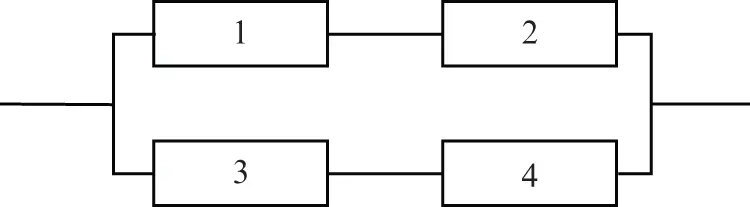
Figure 1.16 Reliability block diagram of the system.
1 1 Zio, E. (2007). An Introduction to the Basics of Reliability and Risk Analysis, Vol. 13. World scientific.
2 2 Matic, Z. and Sruk, V. (2008, June). The physics-of-failure approach in reliability engineering. In ITI 2008-30th International Conference on Information Technology Interfaces (pp. 745–750). IEEE.
3 3 Paris, P. and Erdogan, F. (1963). A critical analysis of crack propagation laws.
4 4 Magnee, A. (1995). Generalized law of erosion: Application to various alloys and intermetallics. Wear 181: 500–510.
5 5 Barlow, R.E. and Proschan, F. (1975). Statistical Theory of Reliability and Life Testing: Probability Models. Florida State Univ Tallahassee.
6 6 Rauzy, A. (2008). Binary decision diagrams for reliability studies. In: Handbook of Performability Engineering, (ed. K.B. Misra) 381–396. London: Springer.
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.