The inverse form is
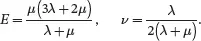 (2.206)
(2.206)
It is sometimes convenient to characterise an isotropic material using the two elastic constants μ and ν in which case, in addition to the relation ( 2.204),
 (2.207)
(2.207)
More frequently, and as required for Chapter 3, it is useful to express Young’s modulus E and Poisson’s ratio ν in terms of the bulk modulus k and the shear modulus μ. On using ( 2.204) and ( 2.205)
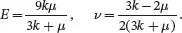 (2.208)
(2.208)
2.18 Analysis of Bend Deformation
For most engineering applications of composite components, the deformation experienced in service conditions will involve some degree of bending. As the effect of bending on ply crack formation in composite laminates is considered in Chapters 11and 19, it is useful to describe here the essential fundamental aspects of an analysis of bend deformation for a uniform orthotropic plate.
2.18.1 Geometry and Basic Equations
A beam of rectangular cross section of length 2 L , width 2 W and depth h is considered within a Cartesian coordinate system such that the x 1-axis is in the axial direction and the x 2-axis is in the in-plane transverse direction whereas the x 3-axis is in the through-thickness direction, as shown in Figure 2.2. The origin is selected to lie at the mid-point of the upper surface of the beam.

Figure 2.2 Schematic diagram of part of a rectangular orthotropic plate of length 2 L and depth h , and coordinate system. The x 2-axis and u 2displacement are directed out of the plane of the page, and the width is denoted by 2 W .
The modelling assumes that the beam is in equilibrium such that the equilibrium equations ( 2.120)–( 2.122) are satisfied where the stress tensor is symmetric as in ( 2.123). The displacement components are denoted by ui . The infinitesimal strains are then given by the relations ( 2.143). The stress-strain relations are assumed to be of the orthotropic form ( 2.196), namely,
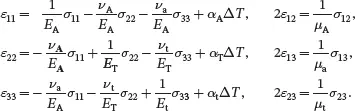 (2.209)
(2.209)
The beam is assumed to be in a state of orthogonal bending combined with uniform through-thickness loading such that
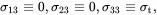 (2.210)
(2.210)
and
 (2.211)
(2.211)
where the strain parameters ε¯A, ε¯T, ε^A and ε^T, the through-thickness stress σt and the temperature difference ΔT are assumed for the moment to be known. From ( 2.143), ( 2.209) and ( 2.211), the in-plane strains and shear stress are given by
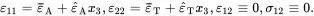 (2.212)
(2.212)
The expression for ε22 in ( 2.209) is first solved for the stress component σ22 so that
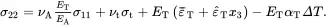 (2.213)
(2.213)
It then follows from ( 2.209) that
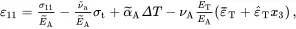 (2.214)
(2.214)
where
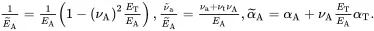 (2.215)
(2.215)
In addition, from ( 2.209)
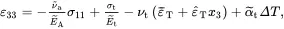 (2.216)
(2.216)
where
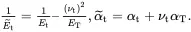 (2.217)
(2.217)
2.18.2 Stress and Displacement Fields
The immediate objective is to determine the displacement component u 3and corresponding stresses σ11, σ12 and σ12 in terms of the mechanical loading parameters ε¯A,ε^A,ε¯T,ε^T,σt and the temperature difference ΔT. From ( 2.209), ( 2.210) and ( 2.212), the in-plane stresses must satisfy the relations
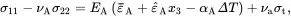 (2.218)
(2.218)
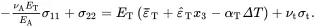 (2.219)
(2.219)
On solving ( 2.218) and ( 2.219) for the stresses, it follows that
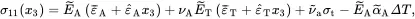 (2.220)
(2.220)
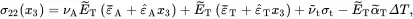 (2.221)
(2.221)
where
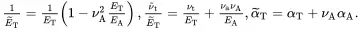 (2.222)
(2.222)
It is noted that the in-plane stresses are only linear functions of x 3. It then follows, on using ( 2.210), that all the equilibrium equations ( 2.120)–( 2.122) are satisfied.
It now only remains to determine the value of the displacement component u 3describing the deflection of the beam. From ( 2.216) and ( 2.220)
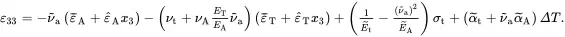 (2.223)
(2.223)
On using ( 2.215) and ( 2.222) it can be shown that
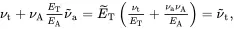 (2.224)
(2.224)
so that ( 2.223) may now be written as
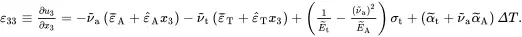 (2.225)
(2.225)
Integration with respect to x 3then leads to
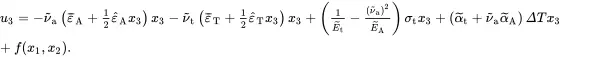 (2.226)
(2.226)
Читать дальше

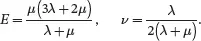 (2.206)
(2.206) (2.207)
(2.207)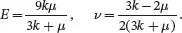 (2.208)
(2.208)
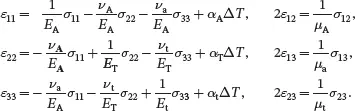 (2.209)
(2.209)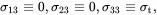 (2.210)
(2.210) (2.211)
(2.211)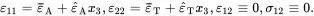 (2.212)
(2.212)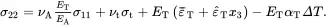 (2.213)
(2.213)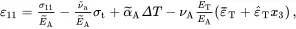 (2.214)
(2.214)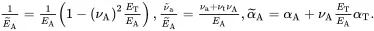 (2.215)
(2.215)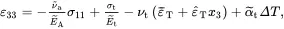 (2.216)
(2.216)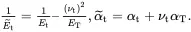 (2.217)
(2.217)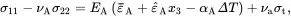 (2.218)
(2.218)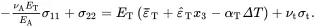 (2.219)
(2.219)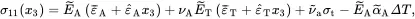 (2.220)
(2.220)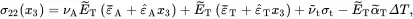 (2.221)
(2.221)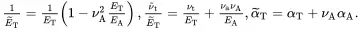 (2.222)
(2.222)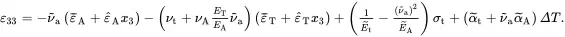 (2.223)
(2.223)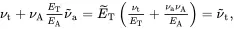 (2.224)
(2.224)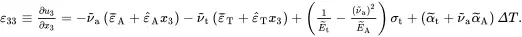 (2.225)
(2.225)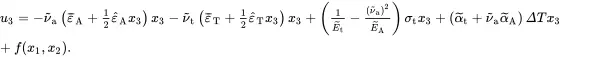 (2.226)
(2.226)










