Amyris balsamifera
FAMILYRutaceae
SYNONYMS Schimmelia oleifera, West Indian sandalwood, West Indian rosewood.
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONA small bushy tree with compound leaves and white flowers which grows wild in thickets all over the island of Haiti.
DISTRIBUTIONMainly Haiti, it has now been introduced to tropical zones all over the world, e.g. Jamaica, South and Central America.
OTHER SPECIESNot to be confused with East Indian or Mysore sandalwood ( Santalum album ), to which it bears no relation.
HERBAL/FOLK TRADITIONThe locals call it ‘candle wood’ because of its high oil content; it burns like a candle. It is used as a torch by fishermen and traders. It also makes excellent furniture wood.
ACTIONSAntiseptic, balsamic, sedative.
EXTRACTIONEssential oil by steam distillation from the broken-up wood and branches. Best if the wood is seasoned first. It provides a very plentiful yield.
CHARACTERISTICSA pale yellow, slightly viscous liquid with a musty, faintly woody scent, quickly fading away. It blends well with lavandin, citronella, oakmoss, sassafras, cedarwood and other wood oils.
PRINCIPAL CONSTITUENTSCaryophyllene, cadinene and cadinol.
SAFETY DATAGenerally non-irritant; no other information available at present.
AROMATHERAPY/HOME USEPerfume.
OTHER USESAs a cheap substitute for East Indian sandalwood in perfumes and cosmetics, although it does not have the same rich tenacity; chiefly employed as a fixative in soaps. Limited application in flavouring work, especially liqueurs.
Angelica archangelica
FAMILYApiaceae (Umbelliferae)
SYNONYMS A. officinalis , European angelica, garden angelica.
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONA large hairy plant with ferny leaves and umbels of white flowers. It has a strong aromatic scent and a large rhizome.
DISTRIBUTIONNative to Europe and Siberia, cultivated mainly in Belgium, Hungary and Germany.
OTHER SPECIESThere are over thirty different types of angelica but this is the most commonly used medicinally. see Botanical Classificationsection.
HERBAL/FOLK TRADITIONThis herb has been praised for its virtues since antiquity.
Angelica
It strengthens the heart, stimulates the circulation and the immune system in general. It has been used for centuries in Europe for bronchial ailments, colds, coughs, indigestion, wind and to stimulate the appetite. As a urinary antiseptic it is helpful in cystitis and is also used for rheumatic inflammation. The Chinese employ at least ten kinds of angelica, well known for promoting fertility, fortifying the spirit and for treating female disorders generally; it has a reputation second only to ginseng. It is current in the British Herbal Pharmacopoeia as a specific for bronchitis associated with vascular deficiency. Candied Angelica stalks are popular in France and Spain.
ACTIONSAntispasmodic, carminative, depurative, diaphoretic, digestive, diuretic, emmenagogue, expectorant, febrifuge, nervine, stimulant, stomachic, tonic. Reported to have bactericidal and fungicidal properties.
EXTRACTIONEssential oil produced by steam distillation from the 1. roots and rhizomes, and, 2. fruit or seed. An absolute is also produced on a small scale, from the roots.
CHARACTERISTICS1. A colourless or pale yellow oil which turns yellowy-brown with age, with a rich herbaceous-earthy bodynote. 2. The seed oil is a colourless liquid with a fresher, spicy top note. It blends well with patchouli, opopanax, costus, clary sage, oakmoss, vetiver and with citrus oils.
PRINCIPAL CONSTITUENTSRoot and seed oil contain phellandrene, pinene, limonene, linalol and borneol; rich in coumarins including osthol, angelicin, bergapten and imperatorin; also contains plant acids.
SAFETY DATABoth root and seed oil are non toxic and non-irritant. The root oil (not the seed oil) is phototoxic, probably due to higher levels of bergapten. Not to be used during pregnancy or by diabetics.
AROMATHERAPY/HOME USE
Skin Care: Dull and congested skin, irritated conditions, psoriasis.
Circulation Muscles And Joints: Accumulation of toxins, arthritis, gout, rheumatism, water retention.
Respiratory System : Bronchitis, coughs.
Digestive System : Anaemia, anorexia, flatulence, indigestion.
Nervous System : Fatigue, migraine, nervous tension and stress-related disorders.
Immune system : Colds.
OTHER USESHighly valued as a fragrance component in soaps, lotions and perfumes especially colognes, oriental and heavy chypres fragrances. It is employed in some cosmetics for its soothing effect on skin complaints. Used extensively as a flavouring agent in most food categories, and in alcoholic and soft drinks, especially liqueurs.
Illicium verum
FAMILYIlliciaceae
SYNONYMSChinese anise, illicium, Chinese star anise.
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONEvergreen tree up to 12 metres high with a tall, slender white trunk. It bears fruit which consist of five to thirteen seed-bearing follicles attached to a central axis in the shape of a star.
DISTRIBUTIONNative to south east China, also Vietnam, India and Japan. Mainly produced in China.
OTHER SPECIESSeveral other related species, e.g. Japanese star anise which is highly poisonous!
HERBAL/FOLK TRADITIONUsed in Chinese medicine for over 1300 years for its stimulating effect on the digestive system and for respiratory disorders such as bronchitis and unproductive coughs. In the East generally, it is used as a remedy for colic and rheumatism, and often chewed after meals to sweeten the breath and promote digestion. A common oriental domestic spice.
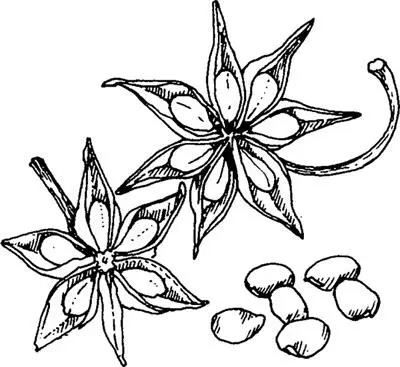
Star Anise
ACTIONSAntiseptic, carminative, expectorant, insect repellent, stimulant.
EXTRACTIONEssential oil by steam distillation from the fruits, fresh or partially dried. An oil is also produced from the leaves in small quantities.
CHARACTERISTICSA pale yellow liquid with a warm, spicy, extremely sweet, liquorice like scent. It blends well with rose, lavender, orange, pine and other spice oils, and has excellent masking properties.
PRINCIPAL CONSTITUENTSTrans-anethole (80–90 per cent).
SAFETY DATADespite the anethole content, it does not appear to be a dermal irritant, unlike aniseed. In large doses it is narcotic and slows down the circulation; it can lead to cerebral disorders. Use in moderation only.
AROMATHERAPY/HOME USE
Circulation Muscles And Joints: Muscular aches and pains, rheumatism.
Respiratory System: Bronchitis, coughs.
Digestive System: Colic, cramp, flatulence, indigestion.
Immune system: Colds.
OTHER USESBy the pharmaceutical industry in cough mixtures, lozenges, etc. and to mask undesirable odours and flavours in drugs. As a fragrance component in soaps, toothpaste and detergents as well as cosmetics and perfumes. Widely used for flavouring food, especially confectionery, alcoholic and soft drinks.
Читать дальше













