Ultra-High-Throughput, Massively Parallel DNA Sequencing. A revolution has occurred within the last decade that has had a lasting and profound impact on profiling of microbial communities and on microbial functional genetics in general. Technological advances in ultra-high-throughput, massively parallel sequencing have taken place, which allow the simultaneous determination of multiple millions of base pairs of DNA sequences in single reaction runs (hence the term “massively parallel”) at very reasonable costs. New bioinformatic methods now also allow the rapid and accurate assembly of these sequences into large regions of overlapping sequences (called contigs) that can be mapped into a complete genome.
At this writing, Illumina sequencing technology is the prevailing platform for massively parallel sequencing ( Figure 5-6A). Despite the limitation of generating rather short read lengths of 50–300 contiguous bases, this method is extremely powerful and inexpensive in terms of capacity and time per sequencing run. At the time of this writing, the Illumina chemistry yields robust sequence determinations, even of long stretches of repeated bases, in as little as 6 hours for data outputs of 0.5–15 gigabases (1–25 million reads) to a few days for outputs of 7.5–35 GB (100–200 million reads). Meanwhile, improvements in DNA sequencing reagents and read detection technologies ( Figure 5-6B) are appearing at an astounding pace. Modification to the original Illumina process for library preparation now enables paired-end sequencing ( Figure 5-6C), which significantly improves alignment of reads to produce longer high-quality contigs that can be used for genome assembly.
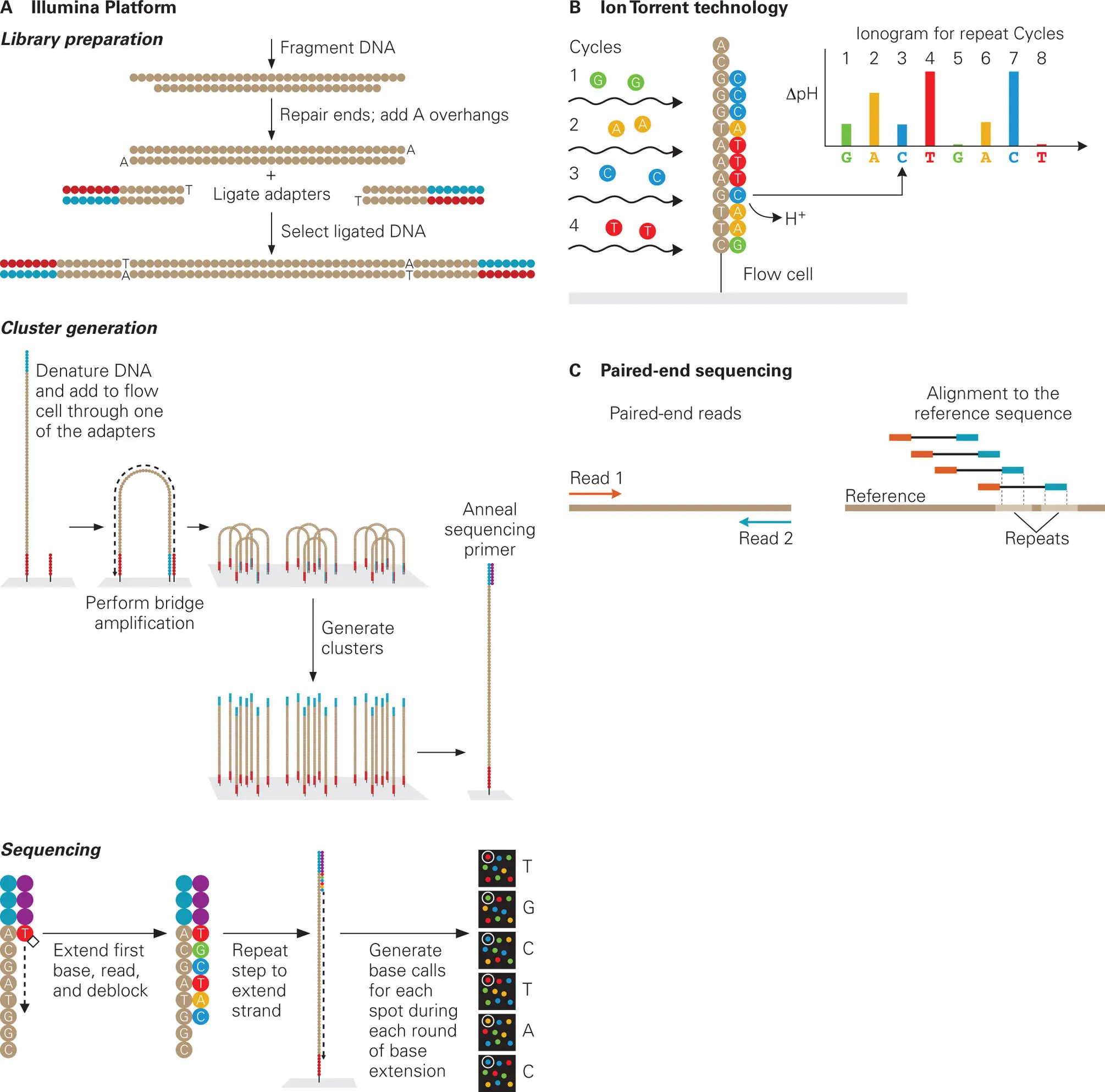
Figure 5-6. Illumina method of massively parallel DNA sequence determination. (A) Shown are the steps in the Illumina platform. (B) Alternative sequence readout can be performed using the less expensive Ion Torrent technology, which detects protons (H+) released during the nucleotide incorporation reaction step as a change in pH for each H+ released during the cycle. (C) Paired-end sequencing entails sequencing both ends of a DNA fragment of defined length (which can be longer than the sequence read), allowing improved sequence alignment of reads during genome assembly. With a small modification of the library preparation process, it is possible to read both the forward and reverse template strands of each cluster (spot), which provides positional information and improved alignment of the paired-end reads with a reference sequence during assembly. Adapted from copyrighted publications from Illumina, with permission.
An alternative sequencing platform that generates much longer sequence reads and is ideal for de novo genome sequencing is the single-molecule, real-time (SMRT) sequencing platform developed by Pacific BioSciences (PacBio). The PacBio SMRT system takes advantage of the intrinsic speed, fidelity (3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity), and importantly the high processivity of a single molecule of a special strand-displacing DNA polymerase, originally obtained from Bacillus subtilis phage phi29, to generate very long reads from a single molecule of DNA template ( Figure 5-7). At this writing, each SMRT cell reaction run yields up to 5 GB of sequencing data in about 12 hours. Current chemistry and library preparation advances have pushed the limits of sequence read lengths up to 60 kB (with average read lengths of 10–20 kB), which can yield large overlapping contigs of up to 15 MB in length, enabling the complete assembly of most microbial genomes, including plasmids, without gaps.
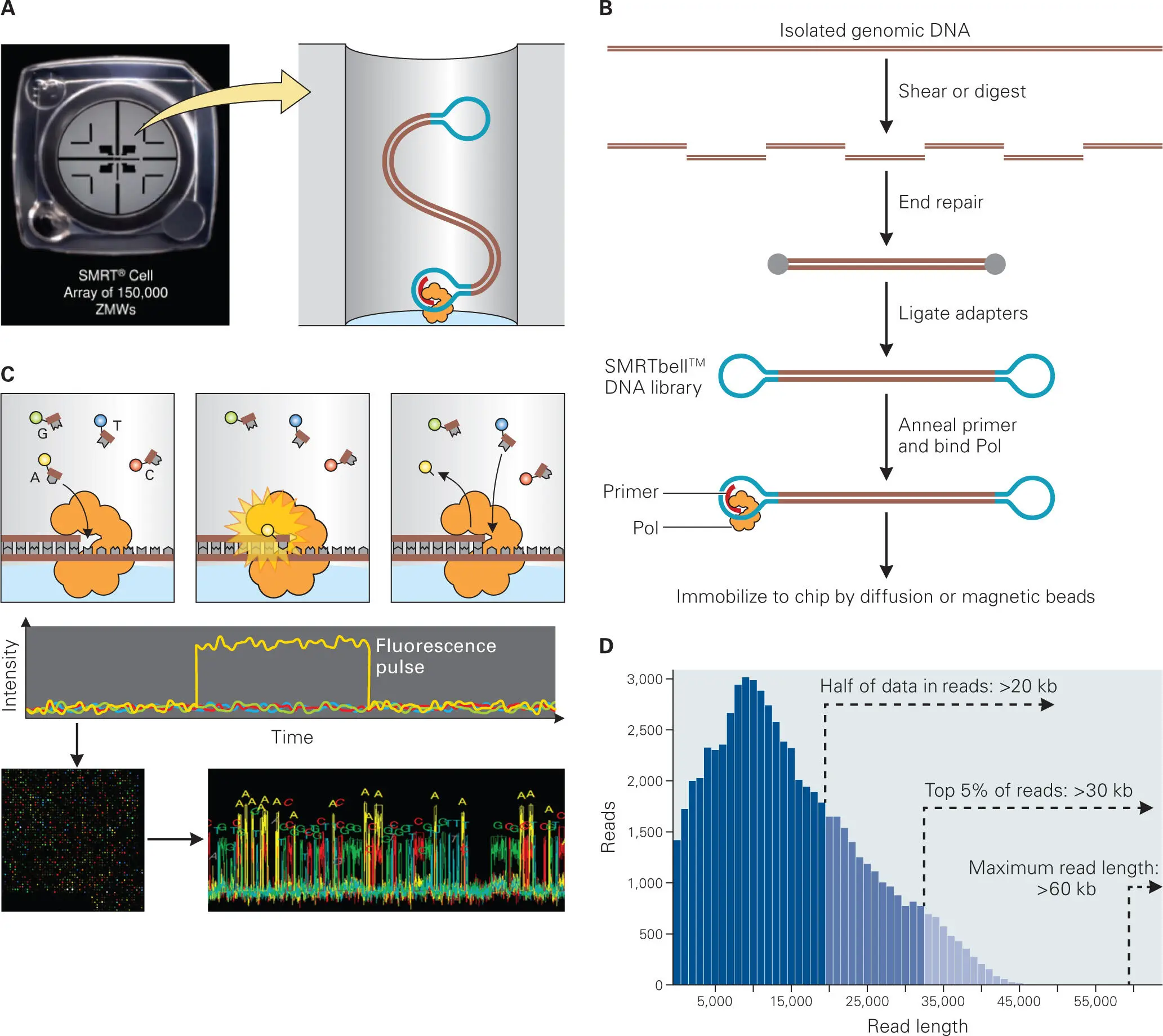
Figure 5-7. The PacBio SMRT sequencing platform. The Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) single-molecule, real-time (SMRT) sequencing technology uses a single highly processive, strand-displacing DNA polymerase that is immobilized to the base of a matrix in a fluorescence-detection well. (A) Each SMRT reaction cell contains 150,000 zero-mode waveguides (ZMWs), which are nanophotonic confinement wells that are illuminated from below and have a detection volume of 20 zeptoliters (10-21 liters). The technology uses ZMWs to observe the base incorporations of an anchored polymerase molecule, which allows light to illuminate only the bottom of the well, in which a single DNA polymerase plus DNA template complex is immobilized. (B) The current version of the SMRT technology uses SMRTbell template preparation to generate a circularized, double-stranded DNA template from appropriately sized fragments of the genomic DNA, generated either by random shearing or by amplification of target regions of interest. Universal hairpin adaptors are then ligated onto the ends of the DNA fragment to generate the SMRTbell library. These hairpin dimer sequences are removed at the end of the library preparation protocol. The sequencing primer is then annealed to the SMRTbell template, followed by binding of the DNA polymerase, to form a complex, which is then immobilized to the bottom of the ZMW well. (C) In each ZMW well, a single molecule of the DNA polymerase sequences a single nucleotide at a time of a single molecule of DNA template. Phospholinked nucleotides, each labeled with a different fluorescently linked dye, are introduced into the ZMW well. As a nucleotide binds the polymerase-DNA complex in the ZMW well, the fluorescently labeled phospholinked nucleotide emits a light pulse that is detected. When the phosphodiester bond is cleaved during the DNA elongation reaction, the fluorescent dye is released and diffuses away from the ZMW detection zone and the light emitted by that nucleotide is no longer detected. The fluorescent read output from incorporation of the four different fluorescent dyes is captured for the entire SMRT cell over time and processed by a computer into sequence reads (one read per ZMW well). (D) With the latest chemical reagent kits, SMRT technology can provide real-time sequence reads of 5–60 kB in length. Adapted from copyrighted publications from PacBio, with permission.
Currently, the Illumina and PacBio sequencing platforms are often used in combination to determine the complete genome sequence of a new bacterial isolate. If a complete genome is already available for a closely related bacterium such that that genome can be used as a template, then sequence assembly of overlapping contigs from a new bacterial isolate can readily be completed without any or only a few gaps remaining to be filled. For this, the shorter reads obtained by the Illumina platform are sufficient. For de novo genome sequencing (where no existing complete genome is available for a related bacterium), the longer reads of the PacBio platform provide a scaffold and high-quality draft sequence that can be rapidly polished by the high accuracy and coverage (i.e., the large number of overlapping sequence reads used to accurately call a sequence) provided by the Illumina sequencing. As these DNA sequencing methods develop, it will become increasingly quick and cost-effective to not only take the census of bacterial species in complex microbial communities, but also to sequence parts or entire genomes directly from the mixture of genomic DNA isolated from these populations.
To understand the power of current whole-genome sequencing technologies, let us consider a common, recurring problem in bacterial genetics. Interesting mutations often arise spontaneously in bacteria whose complete genomes have already been determined. Researchers are often interested in knowing what these mutations are, particularly if the bacterium is a pathogen. Classical bacterial genetics provides exceedingly clever ways to map mutations so that they can be located by conventional sequencing of a limited region of the chromosome of the mutant strain. However, these classical methods are often time-consuming and are far from foolproof, especially in bacterial species lacking powerful genetic systems, such as many bacterial pathogens.
Читать дальше














