1.3.1 Engineering Design in a Manufacturing System
Design science uses scientific methods to analyse the structure of technical systems and their relationships with the environment. The aim is to derive rules for the development of these systems from system elements and their relationships. Design methodology is a concrete course of action for the design of technical systems that derives its knowledge from design science and cognitive psychology, and from practical experience in different domains.
Designs of products and processes are essential to manufacturing systems. For example, some typical activities to design a product are (i) a functional design to determine functional modules and features and their relations, (ii) a parametric design to determine geometrics and dimensions of parts, (iii) a tolerance analysis of geometric dimensioning and tolerances (GD&Ts) to determine the quality, position, and shape of all parts, and (iv) an assembly design to determine the assembly relations of parts and components.
1.3.2 Importance of Engineering Design
A manufacturing system is understood from the technological and economic perspectives. Technologically, a manufacturing system is to transform raw materials into final products via a set of operations. Economically, a manufacturing system is a process to add values to final products via a set of economic transactions associated with manufacturing processes. Making a profit is always a primary goal to entrepreneurs. The profit can be maximized in two ways: (i) to reduce costs on no value‐added activities and (ii) to increase the sale price by providing a corresponding value to the customer.
Engineering design plays a significant role in implementing these two strategies. Figure 1.7shows the impact of the activities of design, manufacturing processes, raw materials, management, and marketing on the overall product costs. The impacts are measured by the percentages of overall product cost affected by the activities in a certain category. Even though the minimal percentage of the actual cost is related to the design activities, they mainly affect the overall product cost.
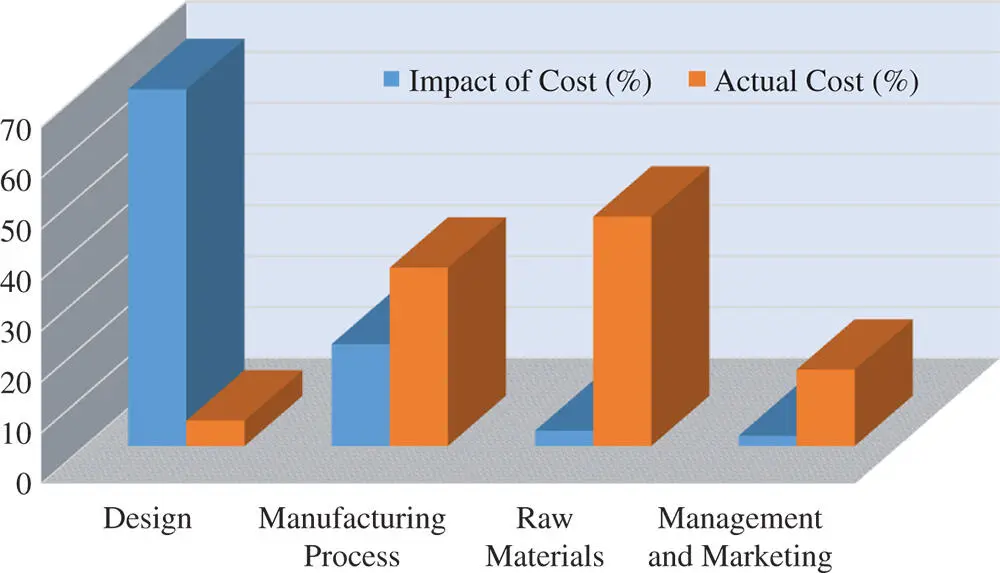
Figure 1.7Significant impact of design activities on overall product cost.
In Figure 1.8, the value‐added chain smile curve by ITC (2019) shows the importance of design effectiveness on the possibility of added values of products in contrast to competitors. Business activities in a manufacturing system can be classified based on its involvement with hardware systems. The more dependence on hardware systems, the less chances a company gains in competitiveness on adding more values to products. Along with the product lifecycle, the more design activities are involved, the better the chances to gain competitiveness by adding more values of products than competitors.
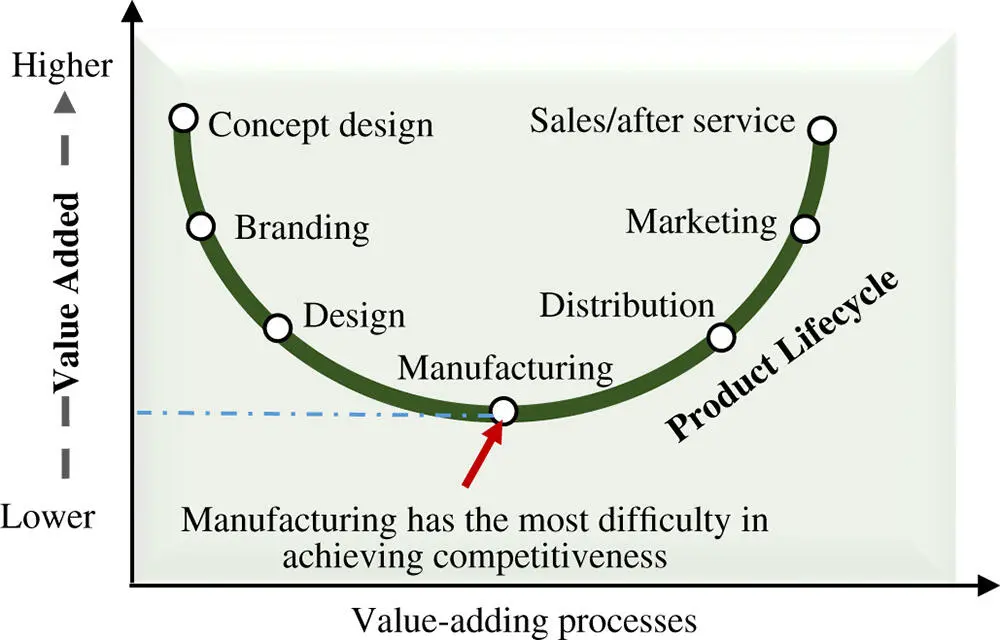
Figure 1.8Value‐added chain smile curve (IEC 2019; ITC 2019).
The importance of engineering design can also be reflected by the additional costs a company may spend to fix some defects and errors occurring to different phases of a product lifecycle. The first‐time correct is an idea goal to make highly diversified products and can only be achieved when CAD tools are capable of eliminating all of the design defects at the design stage. Figure 1.9shows that, conventionally, the errors with a 75% fixing cost are made at the design stage of products, but the errors fixed at the manufacturing stage or later take around 80% of the fixed cost. It is clear that the earlier an error or defect is identified, the less cost is needed to fix it.
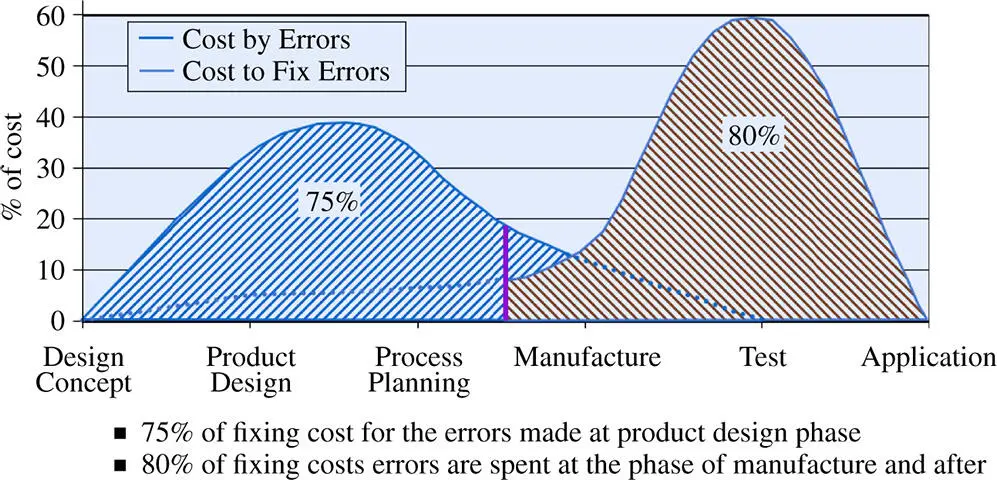
Figure 1.9Relative costs to fix errors at different phases of product lifecycle.
1.3.3 Types of Design Activities
In this section, the role of CATs in the design aspect is analysed, the nature of engineering designs is discussed, and the potential for using CAT technologies for design problems with different creativity levels is explored. Based on the level of creativity, Designwork (2016) classifies the engineering design problems into types: routine design , redesign , selection design , parametric design , integrated design, and new design ( Table 1.2).
Table 1.2Types of design activities.
| Type |
Description |
Example |
| Routine design |
To perform a design by following existing standards and codes that outline the steps and computations for certain products or systems. |
Follow the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Codes to design a pressure vessel. |
| Redesign |
To revise an existing design when FRs have been changed in a dynamic environment. |
Reprogram a robot when the tag points on the motion trajectory are changed. |
| Selection design |
To find a solution by selecting appropriate components from an existing design inventory. |
Select standardized fasteners to join two metal plates. |
| Parametric design |
To determine design variables in a given conceptual structure for an optimized performance. |
Minimize the materials usage of a cylindrical container subject to the given volume. |
| Integrated design |
To design and assemble components as an integrated product or system to meet strongly coupled FRs. |
Design a robotic configuration for a given task in a modular robot system. |
| New design |
To design a product or system from scratch to meet emerging FRs. |
Design a patentable product or system. |
Corresponding to the needs to involve computers, human–machine interaction, and human designers, a rougher classification based on the level of creativity and innovation may facilitate further discussion. To this end, the designs can be regrouped as:
1 New design for a design from scratch to conceptual design, detailed design, and assembly design to the final product to meet specified design requirements.
2 Incremental design for a design subjected to given product structures, change individual parts, and functions to meet additional requirements of products.
3 Routine design for a design subjected to given functionalities, topological relations, layouts, and parametrize dimensions for the design of product families.
The level of creativity and innovation can be characterized based on the types of solution space and design variables . Goel (1997) corresponded routine design, innovative design, and new creative design to different combinations of solution space and design variables ( Table 1.3).
Table 1.3Characteristics of solution spaces and design variables.
| Level of creativity |
Routine design |
Incremental design |
New design |
| Solution space |
Structure |
Known |
Known |
Unknown |
| Search procedure |
Known |
Unknown |
Unknown |
| Design variables |
Types |
Fixed |
Fixed |
Changed |
| Ranges |
Fixed |
Changed |
Changed |
The characteristics of the solution space and design variables determines whether or not an engineering design belongs to a ‘routine’, ‘incremental’, or ‘new’ design. Both humans and computers can compete to accomplish some design activities; however, computers and human designers are good at different things, and it is desirable to synergize the strengths of designers and computers to achieve the effectiveness of engineering designs. Many researchers have discussed the differences between humans and computers. Table 1.4summarizes the role differences of human beings and computers in engineering design processes.
Читать дальше















