Root Bridges and Port Priority
Each MST instance has its own root bridge. By having multiple instances with different root bridges, you can distribute the traffic load across all the links. Using Figure 2.7as an example, you could make SW1 the root for MST1 and SW4 the root for MST2.
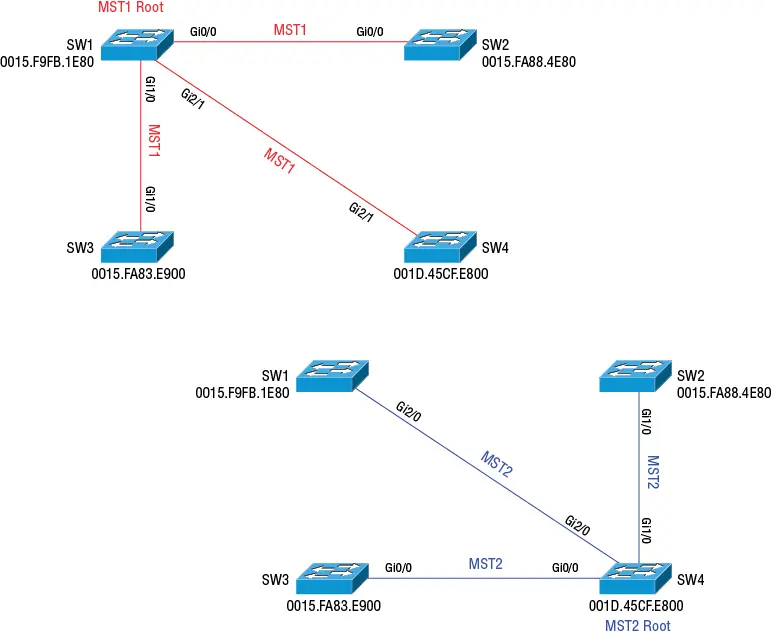
Figure 2.7 Multiple Spanning Tree
The command for adjusting the MST bridge priority is almost identical for (R)PVST+. The difference is that instead of specifying a VLAN, you specify the MST instance. For example, to make SW1 the root for MST1, you would do the following:
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. SW1(config)#spanning-tree mst 1 priority 0 SW1(config)#exit SW1#show spanning-tree mst 1 ##### MST1 vlans mapped: 1,3,5 Bridge address 0015.f9fb.1e80 priority 1 (0 sysid 1) Root this switch for MST1 ! Output truncated
In Figure 2.8, SW1 and SW4 are directly connected via two links. To ensure that both links are used, we'll lower the MST1 port priority for Gi2/1 on SW1. This will cause SW4 to use the link for MST1 instead of blocking it. The command for adjusting the port priority is also much the same as in (R)PVST+:
SW1(config)#interface gi2/1 SW1(config-if)#spanning-tree mst 1 port-priority 32
MST can interoperate with other Spanning Tree protocols and even other MST regions. When an MST region is connected to switches in another MST region, or simply not running MST at all, it will make the MST region appear as a single RPVST+ or PVST+ topology, depending on what the peer switch is running. This is called PVST simulation . To illustrate, let's change SW2 back to RPVST+ mode:
SW2(config)#spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst SW2(config)#do show spanning-tree vlan 1-10 summary Switch is in rapid-pvst mode Root bridge for VLAN0001 is 32768.0015.f9fb.1e80. Root bridge for VLAN0002 is 32768.0015.f9fb.1e80. Root bridge for VLAN0003 is 32768.0015.f9fb.1e80. Root bridge for VLAN0004 is 32768.0015.f9fb.1e80. Root bridge for VLAN0005 is 32768.0015.f9fb.1e80. Root bridge for VLAN0006 is 32768.0015.f9fb.1e80. Root bridge for VLAN0007 is 32768.0015.f9fb.1e80. Root bridge for VLAN0008 is 32768.0015.f9fb.1e80. Root bridge for VLAN0009 is 32768.0015.f9fb.1e80. Root bridge for VLAN0010 is 32768.0015.f9fb.1e80. ! Output truncated
SW1 advertises itself as the root for all VLANs, even though in the MST topology it's only the root for the MST1 instance. If a switch outside of the MST topology attempts to become root, the MST switches will block the ports, placing them into a PVST Simulation Inconsistent state. For example, let's try to make SW2 the root for VLAN 1:
SW2(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 0 ! SW1 will block the port that's connected to SW2 and place it into a broken state, resulting in no traffic traversing the link: *Sep 15 01:01:21.412: %SPANTREE-2-PVSTSIM_FAIL: Blocking root port Gi0/0: Inconsistent inferior PVST BPDU received on VLAN 7, claiming root 32775:0015.fa88.4e80 SW1#show spanning-tree int gi0/0 Mst Instance Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type ------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- -------------------------------- MST0 Root BKN*20000 128.1 P2p Bound(PVST) *PVST_Inc MST1 Mstr BKN*20000 128.1 P2p Bound(PVST) *PVST_Inc MST2 Mstr BKN*20000 128.1 P2p Bound(PVST) *PVST_Inc SW1#show spanning-tree inconsistentports Name Interface Inconsistency -------------------- ------------------------ ------------------ MST0 GigabitEthernet0/0 PVST Sim. Inconsistent MST1 GigabitEthernet0/0 PVST Sim. Inconsistent MST2 GigabitEthernet0/0 PVST Sim. Inconsistent Number of inconsistent ports (segments) in the system : 3
On any 802.1Q trunk, the native VLAN is the VLAN whose traffic isn't tagged. By default, this is VLAN 1. VLAN 1 is a special VLAN that plays a crucial role in many protocols, including Spanning Tree. If you're using an 802.1Q trunk, by default VLAN 1 traffic is sent untagged. You can force a switch to tag native VLAN traffic using the global configuration command vlan dot1q tag native. This is useful to prevent untagged traffic from inadvertently slipping into VLAN 1, as well as to prevent VLAN hopping attacks.
VLAN 1 always exists on all switches, and you can't disable it. But you can prune it from a trunk. If you prune VLAN 1 from a trunk on a switch running (R)PVST+, the switch won't forward any BPDUs for VLAN 1. However, if the switch is running MST, it will continue to forward BPDUs for VLAN 1—untagged—to maintain compatibility with switches that don't support 802.1Q trunks.
Topology Change Detection
When a non-edge port on a bridge transitions to the forwarding state—something that can happen if a new switch is added, for example—it notifies other bridges in the topology in order to trigger a reconvergence. The bridge flushes any MAC addresses associated with the port and begins sending BPDUs with the topology change (TC) bit set. It also begins a timer called the TC While timer that's twice the value of its Hello time (by default, the Hello time is 2 seconds, so the TC While timer would be 4 seconds). It continues sending BPDUs with the TC bit set until the TC While timer expires.
When another bridge receives a BPDU with the TC bit set, it clears its MAC address table for all ports except the port on which it received the BPDU. It begins its own TC While timer and sends BPDUs with the TC bit set out of all of its designated ports and its root port. Eventually, all bridges become aware of the topology change.
Cisco has added a few extra features to IOS that let you customize Spanning Tree behavior and prevent loops in certain edge cases:
Root Guard
BPDU Guard
BPDU Filter
Unidirectional Link Detection and Loop Guard
Root Guard is a Spanning Tree extension that prevents another switch from becoming root. This can happen if someone adds a new switch with a lower bridge priority. You configure Root Guard on a per-interface basis. If the switch receives a superior BPDU on the port, it will place the port into a Root Inconsistent state and stop forwarding traffic to or from that port. Enable Root Guard by executing the interface command spanning-tree guard root on any ports that you do not want to become root ports.
For an example of how Root Guard works, refer to Figure 2.5from our discussion on RSTP. SW3 is the current root. To prevent SW2 from becoming the root, we can configure Root Guard on the following ports:
SW1:Gi0/0Gi0/1
SW4:Gi1/0Gi1/1
Let's configure Root Guard on SW1:
SW1(config)#int range gi0/0-1 ! Enable root guard on the interfaces SW1(config-if-range)#spanning-tree guard root ! Enable Spanning Tree events debugging SW1(config-if)#do debug spanning-tree events
And on SW4:
SW4(config)#int range gi1/0-1 ! Enable root guard on the interfaces SW4(config-if-range)#spanning-tree guard root SW4(config-if-range)# *Sep 13 21:40:28.908: %SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARD_CONFIG_CHANGE: Root guard enabled on port GigabitEthernet1/0. *Sep 13 21:40:28.921: %SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARD_CONFIG_CHANGE: Root guard enabled on port GigabitEthernet1/1.do SW4(config-if-range)#do debug spanning-tree events Spanning Tree event debugging is on
SW3 is the current root. Let's attempt to make SW2 the root:
SW2(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 0
SW1 marks its ports facing SW2—Gi0/0 and Gi0/1—as Root Inconsistent:
SW1(config-if)# *Sep 13 21:46:17.848: %SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARD_BLOCK: Root guard blocking port GigabitEthernet0/0 on VLAN0001. SW1(config-if)#do show spanning-tree inconsistentports Name Interface Inconsistency -------------------- ------------------------ ------------------ VLAN0001 GigabitEthernet0/0 Root Inconsistent VLAN0001 GigabitEthernet0/1 Root Inconsistent Number of inconsistent ports (segments) in the system : 2
Читать дальше













