It has the lowest base MAC address—Assuming the priorities of all the bridges are equal, the bridge with the lowest BIA becomes root.
Here's how the election process works. Initially, each switch assumes it is the root. It places all of its ports into a listening state, and every two seconds, sends a configuration/Hello Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) out of every nonblocking port. The BPDU is addressed to the multicast MAC address 0100.0ccc.cccd and sourced from the interface MAC. The BPDU itself contains a transmitting bridge identifier (ID) that uniquely identifies the sending switch. The transmitting bridge identifier includes
Transmitting bridge priority
Transmitting bridge BIA
VLAN ID
The BPDU also contains a root identifier that includes the following:
Root priority
Root BIA
VLAN ID
Because each switch considers itself the root, the root identifier and transmitting bridge ID information is initially identical. The following is a BPDU from a switch advertising itself as the root bridge:
Spanning Tree Protocol Protocol Identifier: Spanning Tree Protocol (0x0000) Protocol Version Identifier: Rapid Spanning Tree (2) BPDU Type: Rapid/Multiple Spanning Tree (0x02) BPDU flags: 0x3c, Forwarding, Learning, Port Role: Designated Root Identifier: 32768 / 1 / 00:15:f9:fb:1e:80 Root Bridge Priority: 32768 Root Bridge System ID Extension: 1 Root Bridge System ID: Cisco_fb:1e:80 (00:15:f9:fb:1e:80) Root Path Cost: 0 Bridge Identifier: 32768 / 1 / 00:15:f9:fb:1e:80 Bridge Priority: 32768 Bridge System ID Extension: 1 Bridge System ID: Cisco_fb:1e:80 (00:15:f9:fb:1e:80) Port identifier: 0x8001 Message Age: 0 Max Age: 20 Hello Time: 2 Forward Delay: 15 Version 1 Length: 0
Notice that the root ID and the transmitting bridge ID are the same, indicating that the switch believes it's the root. However, if a switch receives a BPDU with a superior root ID, it stops advertising itself as the root. Instead, it begins advertising the bridge with the superior bridge ID as the root. In the end, all switches in the topology will advertise the same switch—the one with the lowest bridge ID—as the root. That bridge wins the election and becomes the root.
 An interesting implication of the election process is that older switches tend to be elected as the root. It's not unheard of for someone to purchase a used replacement switch and plug it into an existing network of newer switches, only to have the used switch take over as root and cause a temporary network outage.
An interesting implication of the election process is that older switches tend to be elected as the root. It's not unheard of for someone to purchase a used replacement switch and plug it into an existing network of newer switches, only to have the used switch take over as root and cause a temporary network outage.
Imagining this process is difficult, so let's look at an example. Consider the switches shown in Figure 2.2. Assuming all switches have equal priority, SW1 would be elected root because it has the lowest base MAC address.
SW1#show spanning-tree vlan 1 VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp Root ID Priority 32769 Address 0015.f9fb.1e80 This bridge is the root Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1) Address 0015.f9fb.1e80 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 300 sec
Because this spanning tree instance is for VLAN 1, the priority for this bridge is 32,769—the default of 32,768 plus the VLAN ID. If you don't want SW1 to be the root, you can increase its priority in increments of 4,096, like so:
SW1#configure t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. SW1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 priority ? <0-61440> bridge priority in increments of 4096 SW1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 36864
Notice that 32,768 + 4,096 = 36,864. IOS won't allow priorities that aren't in increments of 4,096. In short order, SW3 (bridge ID 0015.fa83.e900) takes over as the root:
SW1#show spanning-tree vlan 1 VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp Root ID Priority 32769 Address 0015.fa83.e900 Cost 4 Port 5 (GigabitEthernet1/0) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 36865 (priority 36864 sys-id-ext 1) Address 0015.f9fb.1e80 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 300 sec
Refer to Figure 2.4. Even though SW3's base MAC address is higher—0015.fa83.e900 is greater than 0015.f9fb.1e80—it's elected because it has a lower priority than SW1, and a lower base MAC address than SW2 and SW4.
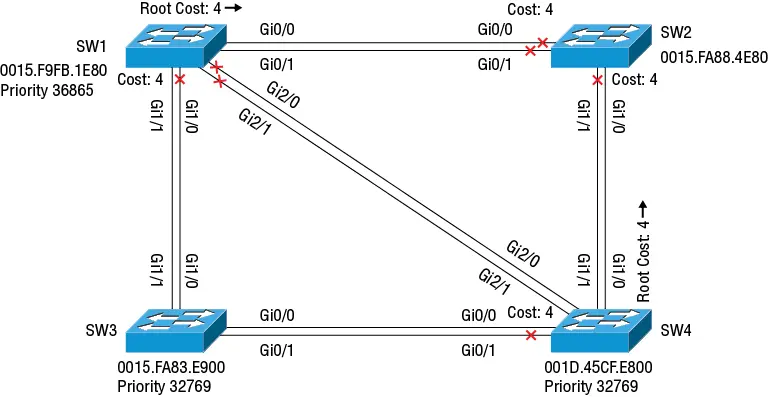
Figure 2.4 Converged STP topology with SW3 as the new root
Alternatively, you could select the root bridge you want by decreasing its priority to less than that of the other bridges. For example, if you wanted to specifically choose SW3 as the root bridge, you could decrease its priority to 28,672 (32,768 – 4,096).
 The bridge with the next lowest bridge ID to the root gets the status of the designated bridge and is also called the secondary root bridge . The designated bridge stands by, waiting to take over in case the primary root bridge fails or ceases to have the best bridge ID, for example, if you were to increase its priority.
The bridge with the next lowest bridge ID to the root gets the status of the designated bridge and is also called the secondary root bridge . The designated bridge stands by, waiting to take over in case the primary root bridge fails or ceases to have the best bridge ID, for example, if you were to increase its priority.
Calculating the Root Ports
The root bridge always has all of its ports in a forwarding state, so it's up to the non-root bridges to prevent bridging loops. Each non-root bridge must determine its root port—the port that has the lowest-cost path to the root bridge. For switches connected directly to the root, this is easy. If a non-root bridge has only one interface to the root, that interface becomes the root port. On the other hand, if a bridge has multiple connections to the root, only the one with the lowest cost to the root will become the root port. All other ports leading back to the root bridge are blocked, thus preventing a loop.
For a switch connected directly to the root, the root port will be the port with the lowest cost. If the costs are equal, the root port will be the one with the lowest designated port ID. To see how this works, refer to Figure 2.5. SW3 is the root for VLAN 1. SW1 has two direct links to the root: Gi1/0 and Gi1/1. The port with the lowest cost to the root will become the root port. The port cost is based on interface bandwidth, as shown in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1 STP port costs by speed
| Speed |
Cost |
| 10 Mbps |
100 |
| 100 Mbps |
19 |
| 1 Gbps |
4 |
| 10 Gbps |
2 |
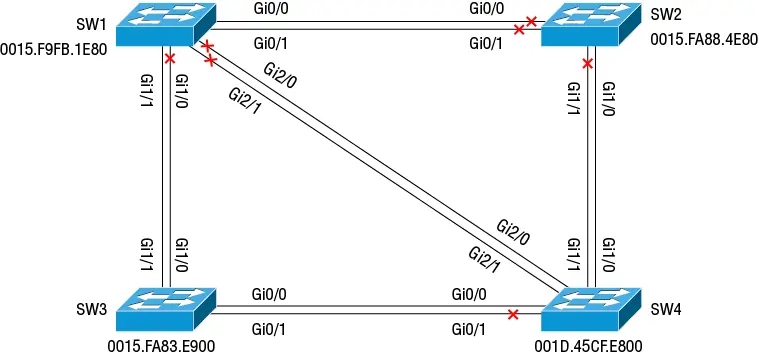
Figure 2.5 VLAN 1 topology with SW3 as root
Because Both of SW1's interfaces facing SW3 are 1 Gbps interfaces, they each have a cost of 4, as shown in the following output from SW1:
SW1#show spanning-tree vlan 1 VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp Root ID Priority 32769 Address 0015.fa83.e900 Cost 4 Port 5 (GigabitEthernet1/0) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 36865 (priority 36864 sys-id-ext 1) Address 0015.f9fb.1e80 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 300 sec Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type ------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- -------------------------------- Gi0/0 Desg FWD 4 128.1 P2p Gi0/1 Desg FWD 4 128.2 P2p Gi0/2 Desg FWD 4 128.3 P2p Gi0/3 Desg FWD 4 128.4 P2p Gi1/0 Root FWD 4 128.5 P2p Gi1/1 Altn BLK 4 128.6 P2p ! Output truncated
Читать дальше

 An interesting implication of the election process is that older switches tend to be elected as the root. It's not unheard of for someone to purchase a used replacement switch and plug it into an existing network of newer switches, only to have the used switch take over as root and cause a temporary network outage.
An interesting implication of the election process is that older switches tend to be elected as the root. It's not unheard of for someone to purchase a used replacement switch and plug it into an existing network of newer switches, only to have the used switch take over as root and cause a temporary network outage.












