1 ...6 7 8 10 11 12 ...17 It is possible to edit data that have been already entered and to edit and invoke commands that have been previously used.
The data you have read and stored may be edited and changed interactively during your R session. Simply click on Edit on the toolbar to get access to the Data Editor , which allows you to bring up any data frame as a spreadsheet. You can edit its entries as you wish.
It is also possible to change particular entries of a data frame. For example,
arch1[7] <- 10
changes the mark for the seventh student in 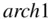 in the data frame
in the data frame 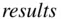 from 100 to 10. It may have been entered as 100 in error.
from 100 to 10. It may have been entered as 100 in error.
The command
history()
brings up the previous 25 commands on a separate screen. These can be edited and/or used again as you wish.
history(max.show = Inf)
retrieves all previous commands that you have used.
As your R session continues, you may find that the set of objects you have used has become unwieldy, and you may want to remove some. To see what the workspace contains write
ls()
or equivalently
objects()
which causes all objects in the workspace to appear on the screen. If you have run the preceding examples in this chapter, the following should appear.
[1] "downtime" "newdata" "prod1" "results" "x" [6] "X" "x2"
The content of the workspace can also be examined from the toolbar; go to Misc and choose List Objects .
To tidy up, you might want to remove some.
rm(x2)
removes the object x2.
To remove the complete workspace, write
rm(list = ls())
1.10 Saving and Retrieving
To save the entire workspace, click  on the tool bar. You will then be given the opportunity to specify the location where you want to save the workspace. The workspace is saved to a file with
on the tool bar. You will then be given the opportunity to specify the location where you want to save the workspace. The workspace is saved to a file with 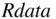 attachment.
attachment.
A saved workspace may be retrieved at File on the toolbar by clicking on Load Workspace , and specifying its location.
In a similar fashion, a file containing the commands may be saved and loaded by clicking on Save History or Load History , and specifying its location. The commands are stored in a file with 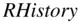 attachment.
attachment.
A key feature of R it that it is a library of packages as much as it is a programming language. Packages are a collection of stored functions, data, and code that can be loaded for specific needs. The base installation of R contains a set of packages, which are sufficient for most users' needs. To see what packages are available with the base installation, type
search()
which gives
[1] ".GlobalEnv" "package:stats" "package:graphics" [4] "package:grDevices" "package:utils" "package:datasets" [7] "package:methods" "Autoloads" "package:base"
The libraryfunction enables you to see what is available in any particular package. For example, by writing
library(help = "stats")
you will get a list of statistical procedures available in the “stats”package.
By clicking on packages on the toolbar, you will be given a list of available packages. If you want to install a specific package, “Matrix” say, just click on “Matrix.”Alternatively, write
install.packages("Matrix")
in the command window.
library(help = "Matrix")
tells us what procedures are in the package “Matrix.”
installed.packages()
details all installed packages.
Currently, there are thousands of packages available. It is unlikely that you will need any of these at this stage of your learning, as the packages available in the base package are usually adequate for the general users' needs.
Over the last decade, many attempts have been made to develop interfaces for R to make it more user‐friendly. Some interfaces are enhanced code editors that interact with R in order to make it easier to use; RStudio and R tools for Visual Studio are two such examples, both of which provide an integrated development environment (IDE) for working with R .
There are also full‐blown GUI such as R Commander (Rcmdr) , Rattle and RKWard , all of which contain menus and dialog boxes with a point‐and‐click approach.
We will look at two of the most popular of these interfaces, RStudio , and R Commander .
RStudio is the most well known of the code editors currently available to interface with R . Written in C++, Version 1 was released in 2016, and since then many updates and revisions have been made. Like R , it is open source, and, after you have installed R, it can be downloaded from the RStudio website at http://www.rstudio.orgby proceeding as follows:
Click “Download RStudio”;
Choose the Desktop version;
Select the setup program suitable to your operating system;
Press the option “Run”.
RStudio is now installed, and you should see an icon on your screen. Clicking on this will start up and launch the RStudio interface. A screen divided into four windows will appear, each window representing a set of integrated tools designed to help you to be more productive in R .
The top left quadrant is the Editor Window.
The lower left quadrant is the Command Window where you write and execute commands after the prompt “>” similar to what you do in the main R. This is where you will first work, and when it is correct, copy it into the Editor Window.
The top right quadrant is the Workspace and History Window. This keeps a record of the commands you have used.
The lower right quadrant is referred to as the File/Plots/Packages Window. Here, you can open files, view plots and load packages. This window also contains the help function.
To see for yourselves, click on the RStudio icon. Similar to R , RStudio can be run on a desktop using Windows, (Mac) OS X, and Linux or in a browser connected to RStudio .
Of the GUI available, R Commander, also known as Rcmdr , is the most popular with a point‐and‐click interface to many statistical tasks. It is called “commander” because every time you make a selection from the menu, the R commands corresponding to the task is listed in the output window. You can save this code to be used again. R cmdr is obtained by going into R , clicking on packages on the tool bar, and downloading Rcmdr .
1 In a class of 50 students of computing, 23 are female and 27 are male. The results of their first‐year Java programming examination are given as follows:Females:57, 59, 78, 79, 60, 65, 68, 71, 75, 48, 51, 55, 56, 41, 43,44, 75, 78, 80, 81, 83, 83, 85Males:48, 49, 49, 30, 30, 31, 32, 35, 37, 41, 86, 42, 51, 53, 56,42, 44, 50, 51, 65, 67, 51, 56, 58, 64, 64, 75Read these data into R by storing them in the following ways:As two vectors, one for the females and one for the males;As one vector, with a factor vector designating the gender.If it was discovered that the mark for the 34th student was entered incorrectly and should have been 46 instead of 86, use an appropriate editing procedure to change this.Save the workspace in a file in a suitable directory for access later.
Читать дальше

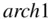 in the data frame
in the data frame 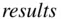 from 100 to 10. It may have been entered as 100 in error.
from 100 to 10. It may have been entered as 100 in error. on the tool bar. You will then be given the opportunity to specify the location where you want to save the workspace. The workspace is saved to a file with
on the tool bar. You will then be given the opportunity to specify the location where you want to save the workspace. The workspace is saved to a file with 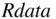 attachment.
attachment.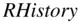 attachment.
attachment.










