Alvaro Meseguer - Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and Engineers
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Alvaro Meseguer - Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and Engineers» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and Engineers
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and Engineers: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and Engineers»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and
Engineers
Provides a modern perspective of numerical mathematics by introducing top-notch techniques currently used by numerical analysts Contains two parts, each of which has been designed as a one-semester course Includes computational practicals in Matlab (with solutions) at the end of each section for the instructor to monitor the student's progress through potential exams or short projects Contains problem and exercise sets (also with solutions) at the end of each section is an excellent book for advanced undergraduate or graduate students in physics, mathematics, or engineering. It will also benefit students in other scientific fields in which numerical methods may be required such as chemistry or biology.

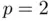
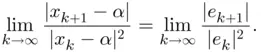
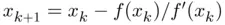 can be expressed in terms of the errors
can be expressed in terms of the errors 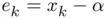 . Since
. Since 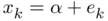 we may write
we may write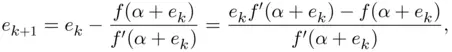
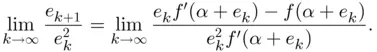
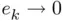 when
when 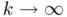 , we may define
, we may define 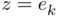 as a continuous variable that approaches zero so that we can rewrite the previous limit as
as a continuous variable that approaches zero so that we can rewrite the previous limit as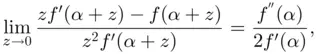
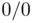 . Therefore we conclude that Newton's method has quadratic convergence with asymptotic error constant
. Therefore we conclude that Newton's method has quadratic convergence with asymptotic error constant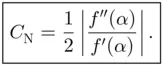
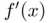 . Either in the exact or approximate version of Newton's method, we need two function evaluations per iteration. There are situations where two or more evaluations per iteration may be computationally expensive, such as in the case of extending Newton's method to solve systems of nonlinear equations, as we will address in Part II. Now, let us assume that we have to provide a Newton‐like iteration without explicitly appealing to the derivative of
. Either in the exact or approximate version of Newton's method, we need two function evaluations per iteration. There are situations where two or more evaluations per iteration may be computationally expensive, such as in the case of extending Newton's method to solve systems of nonlinear equations, as we will address in Part II. Now, let us assume that we have to provide a Newton‐like iteration without explicitly appealing to the derivative of 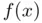 and with just one evaluation of
and with just one evaluation of 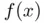 per iteration.
per iteration.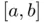 such that
such that 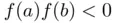 . The key point is to provide an estimation
. The key point is to provide an estimation  of the slope
of the slope 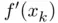 of the function at the
of the function at the 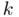 th iterate and substitute Newton's iteration by
th iterate and substitute Newton's iteration by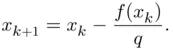
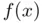 does not oscillate very much within
does not oscillate very much within 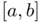 , a reasonable estimation of
, a reasonable estimation of 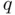 is the slope
is the slope 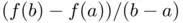 provided by the mean value theorem. In this case, the expression ( 1.17) leads to what is usually termed as the chord method :
provided by the mean value theorem. In this case, the expression ( 1.17) leads to what is usually termed as the chord method :
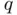 at every iteration with a new quantity
at every iteration with a new quantity 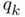 obtained from the values of the
obtained from the values of the 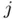 th iterates
th iterates 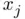 and their images
and their images 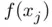 obtained at the previous stages
obtained at the previous stages 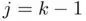 and
and 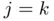 :
:










