Alvaro Meseguer - Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and Engineers
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Alvaro Meseguer - Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and Engineers» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and Engineers
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and Engineers: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and Engineers»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Fundamentals of Numerical Mathematics for Physicists and
Engineers
Provides a modern perspective of numerical mathematics by introducing top-notch techniques currently used by numerical analysts Contains two parts, each of which has been designed as a one-semester course Includes computational practicals in Matlab (with solutions) at the end of each section for the instructor to monitor the student's progress through potential exams or short projects Contains problem and exercise sets (also with solutions) at the end of each section is an excellent book for advanced undergraduate or graduate students in physics, mathematics, or engineering. It will also benefit students in other scientific fields in which numerical methods may be required such as chemistry or biology.

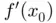 is the value of the derivative of
is the value of the derivative of 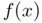 at
at 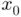 . The motivation for approximating
. The motivation for approximating 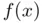 by
by 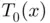 is simple: if
is simple: if 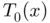 is a reasonably good approximation of
is a reasonably good approximation of 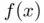 , then the solution of
, then the solution of  should be a reasonable good estimation of the solution of
should be a reasonable good estimation of the solution of 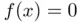 . Let
. Let 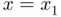 be the solution of
be the solution of 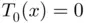 satisfying
satisfying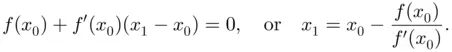
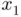 where
where 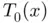 intercepts the
intercepts the 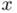 ‐axis is the new (hopefully more accurate) estimation of the root. The process can be repeated approximating
‐axis is the new (hopefully more accurate) estimation of the root. The process can be repeated approximating 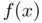 by its Taylor expansion
by its Taylor expansion 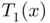 at
at 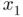 (straight gray line below the curve) in order to obtain an even better estimation
(straight gray line below the curve) in order to obtain an even better estimation 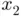 satisfying
satisfying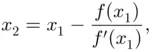
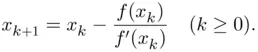
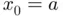 as starting point, instead of an interval. Second, in addition to the string name corresponding to the M‐file function
as starting point, instead of an interval. Second, in addition to the string name corresponding to the M‐file function 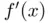 in the argument
in the argument 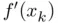 by the ratio
by the ratio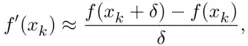
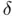 is a small increment (
is a small increment ( 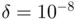 in our code). This approximation of the derivative, along with the suitability of the chosen
in our code). This approximation of the derivative, along with the suitability of the chosen 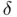 , will be properly justified later in the chapter devoted to numerical differentiation. 9 The reader may check that there are no noticeable differences when using either the exact or the approximate derivative ( 1.10).
, will be properly justified later in the chapter devoted to numerical differentiation. 9 The reader may check that there are no noticeable differences when using either the exact or the approximate derivative ( 1.10).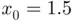 . The first two columns of Table 1.1outline the sequences
. The first two columns of Table 1.1outline the sequences 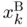 and
and 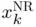 resulting from the bisection and Newton–Raphson methods, respectively. While the bisection method requires almost 50 iterations to achieve full accuracy, Newton's method does the same job in just 5. In fact, Newton–Raphson's sequence nearly doubles the number of converged digits from one iterate to the next, whereas in the bisection sequence this number grows very slowly (and sometimes even decreases, as seen from
resulting from the bisection and Newton–Raphson methods, respectively. While the bisection method requires almost 50 iterations to achieve full accuracy, Newton's method does the same job in just 5. In fact, Newton–Raphson's sequence nearly doubles the number of converged digits from one iterate to the next, whereas in the bisection sequence this number grows very slowly (and sometimes even decreases, as seen from 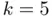 to 6). This is better understood when looking at the third and fourth columns of Table 1.1, where we have included the absolute error corresponding to both methods
to 6). This is better understood when looking at the third and fourth columns of Table 1.1, where we have included the absolute error corresponding to both methods 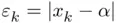 , where
, where 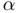 is the reference value given in the exact expression ( 1.3), and whose numerical evaluation with Matlab is
is the reference value given in the exact expression ( 1.3), and whose numerical evaluation with Matlab is 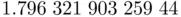 .
.










