Allan T. Kirkpatrick - Internal Combustion Engines
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Allan T. Kirkpatrick - Internal Combustion Engines» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Internal Combustion Engines
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Internal Combustion Engines: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Internal Combustion Engines»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
New engine technologies and concepts Effects of engine speed on performance and emissions Fluid mechanics of intake and exhaust flow in engines Turbocharger and supercharger performance analysis Chemical kinetic modeling, reaction mechanisms, and emissions Advanced combustion processes including low temperature combustion Piston, ring and journal bearing friction analysis The
expands on the combined analytical and numerical approaches used successfully in previous editions. Students and engineers are provided with several new tools for applying the fundamental principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer to internal combustion engines.
Each chapter includes MATLAB programs and examples showing how to perform detailed engineering computations. The chapters also have an increased number of homework problems with which the reader can gauge their progress and retention. All the software is ‘open source’ so that readers can see in detail how computational analysis and the design of engines is performed. A companion website is also provided, offering access to the MATLAB computer programs.

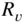 and
and 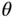 . (Adap...Figure 6.18 Steady‐state flow and swirl system. (Adapted from Uzhan et al. 1...Figure 6.19 Effect of inlet port orientation angle
. (Adap...Figure 6.18 Steady‐state flow and swirl system. (Adapted from Uzhan et al. 1...Figure 6.19 Effect of inlet port orientation angle 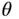 and valve lift
and valve lift 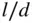 on swi...Figure 6.20 Schematic of bowl in piston crown for production of swirl and sq...Figure 6.21 Instantaneous swirl ratio as a function of piston geometry.Figure 6.22 Swirl ratio and squish versus crank angle. (Adapted from Belaire...Figure 6.23 Squish velocity and turbulent velocity as a function of piston g...Figure 6.24 Laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV) steady‐ flow test rig.Figure 6.25 CFD grid for in‐cylinder flow of a four‐ valve cylinder. (Courte...Figure 6.26 Close‐up of CFD grid. (Courtesy Adapco.)Figure 6.27 CFD flow field. (Courtesy Adapco.)
on swi...Figure 6.20 Schematic of bowl in piston crown for production of swirl and sq...Figure 6.21 Instantaneous swirl ratio as a function of piston geometry.Figure 6.22 Swirl ratio and squish versus crank angle. (Adapted from Belaire...Figure 6.23 Squish velocity and turbulent velocity as a function of piston g...Figure 6.24 Laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV) steady‐ flow test rig.Figure 6.25 CFD grid for in‐cylinder flow of a four‐ valve cylinder. (Courte...Figure 6.26 Close‐up of CFD grid. (Courtesy Adapco.)Figure 6.27 CFD flow field. (Courtesy Adapco.)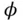 = 0.55 (left) and rich
= 0.55 (left) and rich 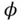 = 1.1 (right...Figure 7.2 Pressure profiles for Figure 7.1. (Adapted from Witze and Vilchis...Figure 7.3 Representative mass fraction burned curves.
= 1.1 (right...Figure 7.2 Pressure profiles for Figure 7.1. (Adapted from Witze and Vilchis...Figure 7.3 Representative mass fraction burned curves.  For varying equival...Figure 7.4 Ignition delay versus equivalence ratio and residual fraction. (A...Figure 7.5 Combustion duration versus equivalence ratio and residual fractio...Figure 7.6 Effect of combustion chamber geometry on combustion duration and ...Figure 7.7 Temperature and species concentration profiles during flame propa...Figure 7.8 Dependence of laminar flame speed
For varying equival...Figure 7.4 Ignition delay versus equivalence ratio and residual fraction. (A...Figure 7.5 Combustion duration versus equivalence ratio and residual fractio...Figure 7.6 Effect of combustion chamber geometry on combustion duration and ...Figure 7.7 Temperature and species concentration profiles during flame propa...Figure 7.8 Dependence of laminar flame speed 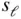 on equivalence ratio
on equivalence ratio 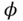 (
( 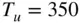 K, Figure 7.9 Dependence of laminar flame speed
K, Figure 7.9 Dependence of laminar flame speed 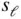 on unburned gas temperature
on unburned gas temperature 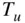 Figure 7.10 Ink roller model of turbulent combustion.Figure 7.11 Pressure profiles for knocking conditions. (Adapted from Douaud ...Figure 7.12 Schlieren photographs of knock process. (Adapted from Smith et a...Figure 7.13 Temperature history of the end gas in Figure 7.12 as determined ...Figure 7.14 High‐speed photographic sequence of the luminosity of a diesel f...Figure 7.15 Simple model of diesel combustion.Figure 7.16 Detailed model of diesel combustion. (Adapted from Dec 1997.)Figure 7.17 Energy release profiles for short‐ and long‐duration fuel inject...Figure 7.18 The effective fuel injection rate versus crank angle. (Adapted f...Figure 7.19 Evolution of a fuel parcel from liquid fuel to combustion produc...Figure 7.20 Spray parcel entrainment and mixing.Figure 7.21 Instantaneous fractions of injected, vaporized, and burned fuel ...Figure 7.22 Predicted energy release versus crank angle for two different ch...Figure 7.23 Representative PPCI dual injection strategy.Figure 7.24 Representative RCCI dual fuel operation.Figure 7.25 Temperature and concentration profiles for
Figure 7.10 Ink roller model of turbulent combustion.Figure 7.11 Pressure profiles for knocking conditions. (Adapted from Douaud ...Figure 7.12 Schlieren photographs of knock process. (Adapted from Smith et a...Figure 7.13 Temperature history of the end gas in Figure 7.12 as determined ...Figure 7.14 High‐speed photographic sequence of the luminosity of a diesel f...Figure 7.15 Simple model of diesel combustion.Figure 7.16 Detailed model of diesel combustion. (Adapted from Dec 1997.)Figure 7.17 Energy release profiles for short‐ and long‐duration fuel inject...Figure 7.18 The effective fuel injection rate versus crank angle. (Adapted f...Figure 7.19 Evolution of a fuel parcel from liquid fuel to combustion produc...Figure 7.20 Spray parcel entrainment and mixing.Figure 7.21 Instantaneous fractions of injected, vaporized, and burned fuel ...Figure 7.22 Predicted energy release versus crank angle for two different ch...Figure 7.23 Representative PPCI dual injection strategy.Figure 7.24 Representative RCCI dual fuel operation.Figure 7.25 Temperature and concentration profiles for 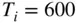 K (iso‐octane).Figure 7.26 Temperature and concentration profiles for
K (iso‐octane).Figure 7.26 Temperature and concentration profiles for 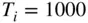 K (iso‐octane).Figure 7.27 Ignition delay as a function of initial temperature
K (iso‐octane).Figure 7.27 Ignition delay as a function of initial temperature 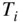 and octane...
and octane...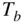 and unburned gas
and unburned gas 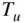 (Exampl...Figure 8.4 Predicted equilibrium and rate limited NO concentrations (Example...Figure 8.5 Predicted equilibrium and rate limited NO concentrations (Example...Figure 8.6 Calculated exhaust NO concentration versus equivalence ratio and ...Figure 8.7 NO concentration versus cylinder wall temperature (Example 8.1)....Figure 8.8 NO concentration versus start of heat release (Example 8.1).Figure 8.9 NO concentration versus engine speed (Example 8.1).Figure 8.10 NO concentration versus IMEP (Example 8.1).Figure 8.11 Advanced timing increases NO. (Adapted from Huls and Nickol 1967...Figure 8.12 Ensemble of fluid elements during compression and combustion.Figure 8.13 Exhaust gas composition versus fuel–air ratio for supercharged e...Figure 8.14 CO concentration in two elements of the charge the burned at dif...Figure 8.15 Wall vortex formed by exhaust stroke. (Adapted from Tabaczynski ...Figure 8.16 Variation of HC concentration at the exhaust valve during the ex...Figure 8.17 HC concentrations as a function of load for direct injection and...Figure 8.18 Two‐ and three‐ring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) struct...Figure 8.19 Soot formation and oxidation versus temperature (Example 8.2).Figure 8.20 Soot and
(Exampl...Figure 8.4 Predicted equilibrium and rate limited NO concentrations (Example...Figure 8.5 Predicted equilibrium and rate limited NO concentrations (Example...Figure 8.6 Calculated exhaust NO concentration versus equivalence ratio and ...Figure 8.7 NO concentration versus cylinder wall temperature (Example 8.1)....Figure 8.8 NO concentration versus start of heat release (Example 8.1).Figure 8.9 NO concentration versus engine speed (Example 8.1).Figure 8.10 NO concentration versus IMEP (Example 8.1).Figure 8.11 Advanced timing increases NO. (Adapted from Huls and Nickol 1967...Figure 8.12 Ensemble of fluid elements during compression and combustion.Figure 8.13 Exhaust gas composition versus fuel–air ratio for supercharged e...Figure 8.14 CO concentration in two elements of the charge the burned at dif...Figure 8.15 Wall vortex formed by exhaust stroke. (Adapted from Tabaczynski ...Figure 8.16 Variation of HC concentration at the exhaust valve during the ex...Figure 8.17 HC concentrations as a function of load for direct injection and...Figure 8.18 Two‐ and three‐ring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) struct...Figure 8.19 Soot formation and oxidation versus temperature (Example 8.2).Figure 8.20 Soot and 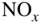 formation on a
formation on a  diagram.Figure 8.21 Representative plot of soot and
diagram.Figure 8.21 Representative plot of soot and 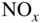 tradeoff versus injection timi...Figure 8.22 Representative plot of soot and
tradeoff versus injection timi...Figure 8.22 Representative plot of soot and  tradeoff versus EGR.Figure 8.23 Engine emission control methods. (Courtesy Englehard Corporation...Figure 8.24 Catalytic converter. (Courtesy Englehard Corporation.)Figure 8.25 Catalytic converter components. (Courtesy Englehard Corporation....Figure 8.26 Conversion efficiencies for oxidizing catalysts. (Adapted from M...Figure 8.27 Conversion efficiencies for three‐way catalyst versus air–fuel r...Figure 8.28 Illustration for Homework Problem 8.3.Figure 8.29 Illustration for Homework Problem 8.14.
tradeoff versus EGR.Figure 8.23 Engine emission control methods. (Courtesy Englehard Corporation...Figure 8.24 Catalytic converter. (Courtesy Englehard Corporation.)Figure 8.25 Catalytic converter components. (Courtesy Englehard Corporation....Figure 8.26 Conversion efficiencies for oxidizing catalysts. (Adapted from M...Figure 8.27 Conversion efficiencies for three‐way catalyst versus air–fuel r...Figure 8.28 Illustration for Homework Problem 8.3.Figure 8.29 Illustration for Homework Problem 8.14.










