16 Chapter 12: Engine Instrumentation and Testing12.1 Introduction 12.2 Instrumentation 12.3 Combustion Analysis 12.4 Exhaust Gas Analysis 12.5 Control Systems in Engines 12.6 Vehicle Emissions Testing 12.7 Further Reading 12.8 References 12.9 Homework
17 Chapter 13: Overall Engine Performance13.1 Introduction 13.2 Effect of Engine Size, Bore, and Stroke 13.3 Effect of Engine Speed 13.4 Effect of Air–Fuel Ratio and Load 13.5 Engine Performance Maps 13.6 Effect of Ignition and Injection Timing 13.7 Effect of Compression Ratio 13.8 Vehicle Performance Simulation 13.9 Further Reading References 13.11 Homework
18 Appendix A Conversion Factors and Physical Constants
19 Appendix B Physical Properties of Air
20 Appendix C Thermodynamic Property Tables for Various Ideal Gases
21 Appendix D Curve‐Fit Coefficients for Thermodynamic Properties of Various Fuels and Ideal Gases
22 Appendix E Detailed Thermodynamic and Fluid Flow AnalysesE.1 Thermodynamic Derivatives E.2 Numerical Solution of Equilibrium Combustion Equations E.3 Isentropic Compression/Expansion with known ΔP E.4 Isentropic Compression/Expansion with known Δv E.5 Constant Volume Combustion E.6 Quality of Exhaust Products E.7 Finite Difference Form of the Reynolds Slider Equation E.8 Reference
23 Appendix F Computer Programs F.1 Volume.m F.2 Velocity.m F.3 BurnFraction.m F.4 FiniteHeatRelease.m F.5 FiniteHeatMassLoss.m F.6 CIHeatRelease.m F.7 FourStrokeOtto.m F.8 RunFarg.m F.9 farg.m F.10 fuel.m F.11 RunEcp.m F.12 ecp.m F.13 AdiabaticFlameTemp.m F.14 OttoFuelAir.m F.15 FourStrokeFuelAir.m F.16 TwoZoneFuelAir.m F.17 Fuel_Injected.m F.18 LimitPressFuelAir.m F.19 ValveFlow.m F.20 Droplet.m F.21 Kinetic.m F.22 Soot.m F.23 TwoZoneNO.m F.24 RingPressure.m F.25 Friction.m F.26 HeatTransfer.m
24 Index
25 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 1 Table 1.1 Performance Comparison of Three Different Four‐Stroke Turbocharged ... Table 1.2 Engine Data for Homework Problems
2 Chapter 2 Table 2.1 Fuel Properties Table 2.2 Input Parameters for Four‐Stroke Gas Cycle Table 2.3 State Variables for Four‐Stroke Example 2.3 Table 2.4 Computed Performance Parameters for Four‐Stroke Example 2.3 Table 2.5 Comparison of Energy Release Models with and without heat/mass tran...
3 Chapter 3 Table 3.1 Ideal Gas Enthalpy of Formation, Enthalpy of Vaporization, Saturati... Table 3.2 Enthalpy of Vaporization, Saturation Vapor Pressure, and Specific V... Table 3.3 Curve‐Fit Coefficients for Antoine's Equation for Saturation Vapor ... Table 3.4 Curve‐Fit Coefficients for Enthalpy of Vaporization 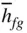 (kJ/mole) Table 3.5 Molecular Mass, Stoichiometric Air–Fuel Ratios, Product Mole Fracti... Table 3.6 Low‐Temperature
(kJ/mole) Table 3.5 Molecular Mass, Stoichiometric Air–Fuel Ratios, Product Mole Fracti... Table 3.6 Low‐Temperature 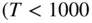 K) Combustion Products Table 3.7 Equilibrium Constant
K) Combustion Products Table 3.7 Equilibrium Constant 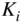 Curve‐Fit CoefficientsTable 3.8 Pre‐exponential Factors, Activation Energies, and Exponents of Some...
Curve‐Fit CoefficientsTable 3.8 Pre‐exponential Factors, Activation Energies, and Exponents of Some...
4 Chapter 4Table 4.1 Enthalpy of Formation, Entropy, Lower/Higher Heat of Combustion, an...Table 4.2 Stoichiometric Adiabatic Flame Temperature of Various FuelsTable 4.3 Effect of Fuel Type on Otto Fuel–Air CycleTable 4.4 Effect of Equivalence Ratio 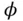 on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.5 Effect of Spark Advance
on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.5 Effect of Spark Advance 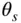 on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.6 Effect of Engine Speed
on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.6 Effect of Engine Speed 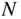 on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.7 Effect of Compression Ratio
on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.7 Effect of Compression Ratio 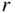 on CFR Engine Performance
on CFR Engine Performance
5 Chapter 5Table 5.1 Valve Lift DataTable 5.2 Representative Valve Timing Angles for Conventional and High Perfor...
6 Chapter 7Table 7.1 Curve‐Fit Parameters for Laminar Flame Speed CorrelationTable 7.2 Turbulent Flame RegimesTable 7.3 Five‐Step Reduced Kinetic Model
7 Chapter 8Table 8.1 Hydrocarbon Emission SourcesTable 8.2 US Passenger Car and Light‐Duty Truck Emission Standards (g/mile)Table 8.3 Low‐Emission Vehicle (LEV) and Ultra‐Low‐Emission Vehicle (ULEV) St...
8 Chapter 9Table 9.1 Specific Heat Curve Fit Coefficients for Fuel ComponentsTable 9.2 Bond Dissociation Energy of Hydrocarbon FuelsTable 9.3 Octane Number Measurement ConditionsTable 9.4 Knock Characteristics of Single Component FuelsTable 9.5 Cetane Number Measurement Conditions (ASTM D613)Table 9.6 Gasoline Property SpecificationsTable 9.7 Properties of Gasoline FuelsTable 9.8 FTP Regulated Emissions (g/mile) from Industry Average and Reformul...Table 9.9 Thermodynamic Properties of Spark‐Ignition FuelsTable 9.10 Critical Compression Ratio vs. Methane NumberTable 9.11 Property Data for Example 9.1Table 9.12 LPG Fueled Vehicle (3.1 L engine) EmissionsTable 9.13 CNG‐Fueled Vehicles (2.2 L engine) Regulated Emissions (g/mile)Table 9.14 CNG‐Fueled Vehicles Toxic Emissions (mg/mile)Table 9.15 Heavy‐Duty Natural Gas Engine Emission Certification Data (g/bhp‐h...Table 9.16 FTP Toxic Emissions (mg/mile) from Ethanol Fueled VehiclesTable 9.17 Toxic Emissions (mg/mile) from Methanol‐Fueled VehiclesTable 9.18 Comparison of Hydrogen Storage MethodsTable 9.19 Diesel Fuel Specifications (ASTM D975)Table 9.20 European Diesel Fuel Specifications (EN 590)Table 9.21 Centane numbers of hydrocarbon fuelsTable 9.22 Comparison of Thermodynamic Properties of Various Compression Igni...Table 9.23 Biodiesel components
9 Chapter 10Table 10.1 SAE Specifications for Engine OilsTable 10.2 SAE Engine Oil Carbon ContentTable 10.3 Viscosity Parameters for Equation (10.4)Table 10.4 Types of Valve TrainsTable 10.5 Coefficients for Valve Train Friction TermsTable 10.6 Coefficients for Auxiliary Friction TermsTable 10.7 FMEP Component EquationsTable 10.8 SOHC Four‐Cylinder in‐line Engine Parameters for Example 10.4
10 Chapter 11Table 11.1 Energy balance on a medium speed, four‐stroke, turbocharged diesel...Table 11.2 Energy Balance on an Air‐Cooled, Spark Ignition Aircraft EngineTable 11.3 Variation of the Mean Combustion Gas Temperature and Heat Transfer...
11 Chapter 12Table 12.1 FID Characteristic Response
12 2 Table B.1 Properties of Air at Atmospheric PressureTable B.2 Physical Properties of Air at Atmospheric Conditions ( 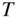 = 298 K,
= 298 K, 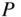 ...
...
1 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Piston and connecting rod. (Courtesy Mahle, Inc.) Figure 1.2 Automobile engine. (Courtesy Mercedes‐Benz Photo Library.) Figure 1.3 Marine engine. (Courtesy Man B&W Diesel.) Figure 1.4 Four‐stroke spark‐ignition engine. Figure 1.5 A cross‐scavenged two‐stroke cycle. Figure 1.6 Engine slider crank geometry. Figure 1.7 Wide‐open throttle (WOT) performance of an automotive four‐stroke... Figure 1.8 Brake mean effective pressure at WOT versus mean piston speed for... Figure 1.9 Effect of engine speed and intake manifold geometry on volumetric... Figure 1.10 Performance map of bmep and bsfc versus mean piston speed for an... Figure 1.11 Cylinder volume vs. crank angle for 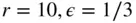 (Equations 1.33 and 1.36).... Figure 1.12 Nondimensional velocity vs. crank angle for
(Equations 1.33 and 1.36).... Figure 1.12 Nondimensional velocity vs. crank angle for 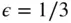 (Equation 1.38). Figure 1.13 Various piston‐cylinder geometries. (Adapted from Obert 1950.) Figure 1.14 Poppet valve assembly. (Adapted from Taylor 1985.) Figure 1.15 Poppet valve timing profile. (Courtesy of Competition Cams, Inc.... Figure 1.16 Turbocharger schematic. (Courtesy of Schwitzer.) Figure 1.17 Liquid cooling system schematic. Figure 1.18 Air cooling of model airplane engine. (Courtesy R. Schroeder.) Figure 1.19 3.2 L V‐6 automobile engine. (Courtesy of Honda Motor Co.) Figure 1.20 Cutaway view of 3.2 L V‐6 automobile engine. (Courtesy of Honda ... Figure 1.21 A variable valve timing mechanism. (Courtesy of Honda Motor Co.)... Figure 1.22 A 5.9 L L6 on‐highway diesel engine. (Courtesy of PriceWebber.)... Figure 1.23 A 94 L L8 stationary natural gas engine. (Courtesy of Cooper Ene... Figure 1.24 Cutaway view of 94 L L8 stationary natural gas engine. (Courtesy... Figure 1.25 Hybrid electric vehicle powertrain configurations.
(Equation 1.38). Figure 1.13 Various piston‐cylinder geometries. (Adapted from Obert 1950.) Figure 1.14 Poppet valve assembly. (Adapted from Taylor 1985.) Figure 1.15 Poppet valve timing profile. (Courtesy of Competition Cams, Inc.... Figure 1.16 Turbocharger schematic. (Courtesy of Schwitzer.) Figure 1.17 Liquid cooling system schematic. Figure 1.18 Air cooling of model airplane engine. (Courtesy R. Schroeder.) Figure 1.19 3.2 L V‐6 automobile engine. (Courtesy of Honda Motor Co.) Figure 1.20 Cutaway view of 3.2 L V‐6 automobile engine. (Courtesy of Honda ... Figure 1.21 A variable valve timing mechanism. (Courtesy of Honda Motor Co.)... Figure 1.22 A 5.9 L L6 on‐highway diesel engine. (Courtesy of PriceWebber.)... Figure 1.23 A 94 L L8 stationary natural gas engine. (Courtesy of Cooper Ene... Figure 1.24 Cutaway view of 94 L L8 stationary natural gas engine. (Courtesy... Figure 1.25 Hybrid electric vehicle powertrain configurations.
Читать дальше

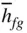 (kJ/mole) Table 3.5 Molecular Mass, Stoichiometric Air–Fuel Ratios, Product Mole Fracti... Table 3.6 Low‐Temperature
(kJ/mole) Table 3.5 Molecular Mass, Stoichiometric Air–Fuel Ratios, Product Mole Fracti... Table 3.6 Low‐Temperature 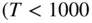 K) Combustion Products Table 3.7 Equilibrium Constant
K) Combustion Products Table 3.7 Equilibrium Constant 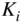 Curve‐Fit CoefficientsTable 3.8 Pre‐exponential Factors, Activation Energies, and Exponents of Some...
Curve‐Fit CoefficientsTable 3.8 Pre‐exponential Factors, Activation Energies, and Exponents of Some...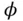 on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.5 Effect of Spark Advance
on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.5 Effect of Spark Advance 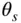 on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.6 Effect of Engine Speed
on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.6 Effect of Engine Speed 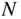 on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.7 Effect of Compression Ratio
on CFR Engine PerformanceTable 4.7 Effect of Compression Ratio 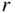 on CFR Engine Performance
on CFR Engine Performance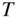 = 298 K,
= 298 K, 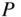 ...
...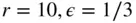 (Equations 1.33 and 1.36).... Figure 1.12 Nondimensional velocity vs. crank angle for
(Equations 1.33 and 1.36).... Figure 1.12 Nondimensional velocity vs. crank angle for 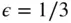 (Equation 1.38). Figure 1.13 Various piston‐cylinder geometries. (Adapted from Obert 1950.) Figure 1.14 Poppet valve assembly. (Adapted from Taylor 1985.) Figure 1.15 Poppet valve timing profile. (Courtesy of Competition Cams, Inc.... Figure 1.16 Turbocharger schematic. (Courtesy of Schwitzer.) Figure 1.17 Liquid cooling system schematic. Figure 1.18 Air cooling of model airplane engine. (Courtesy R. Schroeder.) Figure 1.19 3.2 L V‐6 automobile engine. (Courtesy of Honda Motor Co.) Figure 1.20 Cutaway view of 3.2 L V‐6 automobile engine. (Courtesy of Honda ... Figure 1.21 A variable valve timing mechanism. (Courtesy of Honda Motor Co.)... Figure 1.22 A 5.9 L L6 on‐highway diesel engine. (Courtesy of PriceWebber.)... Figure 1.23 A 94 L L8 stationary natural gas engine. (Courtesy of Cooper Ene... Figure 1.24 Cutaway view of 94 L L8 stationary natural gas engine. (Courtesy... Figure 1.25 Hybrid electric vehicle powertrain configurations.
(Equation 1.38). Figure 1.13 Various piston‐cylinder geometries. (Adapted from Obert 1950.) Figure 1.14 Poppet valve assembly. (Adapted from Taylor 1985.) Figure 1.15 Poppet valve timing profile. (Courtesy of Competition Cams, Inc.... Figure 1.16 Turbocharger schematic. (Courtesy of Schwitzer.) Figure 1.17 Liquid cooling system schematic. Figure 1.18 Air cooling of model airplane engine. (Courtesy R. Schroeder.) Figure 1.19 3.2 L V‐6 automobile engine. (Courtesy of Honda Motor Co.) Figure 1.20 Cutaway view of 3.2 L V‐6 automobile engine. (Courtesy of Honda ... Figure 1.21 A variable valve timing mechanism. (Courtesy of Honda Motor Co.)... Figure 1.22 A 5.9 L L6 on‐highway diesel engine. (Courtesy of PriceWebber.)... Figure 1.23 A 94 L L8 stationary natural gas engine. (Courtesy of Cooper Ene... Figure 1.24 Cutaway view of 94 L L8 stationary natural gas engine. (Courtesy... Figure 1.25 Hybrid electric vehicle powertrain configurations.










