Co-payment: This amount is what you pay as your share of the cost of each service you receive. Strictly speaking, co-pays are fixed dollar amounts (such as $20), whereas coinsurance is the correct term when your share is a percentage of the cost (such as 20 percent). But because coinsurance is too wonky for words, I use co-pays in these pages.
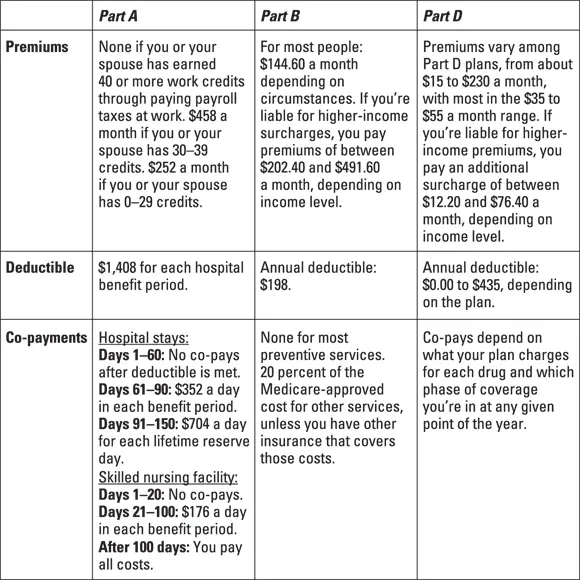
If you had insurance in the past, you probably paid a single premium for all your health care and a single deductible for the whole year (maybe a hefty one if you were in a high-deductible plan), with co-pays for each service. But Medicare, of course, is divided into four parts, each with its own costs and charges. The following sections explain each set of costs under Part A, Part B, Part D, and Medicare Advantage (Part C) plans. Finally, Figure 3-1 shows the costs for Parts A, B, and D at a glance. Note: The costs in the chart are for people enrolled in traditional Medicare plus stand-alone Part D drug plans. Medicare Advantage plan costs are different and vary among plans.
© John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
FIGURE 3-1:2020 premiums, deductibles, and co-payments at a glance.
Part A covers nursing care, room, and meals in a hospital or skilled nursing facility (such as a rehab center or a nursing home); home health services; and hospice care. The following sections describe the possible out-of-pocket costs that you may pay for those services. Note: The costs in the following sections apply if you’re enrolled in the traditional Medicare program. They’ll likely be different if you’re in a Medicare Advantage health plan such as an HMO or a PPO — see the later section “ Medicare Advantage costs.”
You don’t pay premiums for Part A coverage if you or your spouse paid enough in Medicare payroll taxes to earn at least 40 credits (sometimes called quarters ) while working. If you don’t have enough credits through your own or your spouse’s work record, you can buy Part A services by paying premiums for them: in 2020, $458 a month if you have 30 to 39 credits and $252 if you have fewer than 30 credits. These amounts tend to go up or down a little each year. (I explain work credits in more detail in Chapter 5.)
Part A doesn’t have an annual deductible but rather applies a deductible to each hospital benefit period. This unit of time begins when you’re first admitted to a hospital and ends only when you’ve been out of the hospital for 60 days. Huh? Yes, this timeline is a weird concept that I explain thoroughly in Chapter 14. All you need to know here is that the deductible for each hospital benefit period is $1,408 in 2020 (it goes up a little each year) and that after you’ve met it, Medicare picks up the whole tab for up to 60 days.
Co-payments (hospital and skilled nursing facility)
If you stay in the hospital for more than 60 days in any one benefit period, you’re charged a daily co-pay for each day from the 61st to the 90th. In 2020, the co-pay is $352 a day, but this amount increases a little each year. If you still need to remain in the hospital after 90 days, you can choose to draw on some of your lifetime reserve days. These days require a hefty co-pay — $704 a day in 2020 — and they’re limited to 60 days for the rest of your life. After these reserve days are exhausted, you must pay full costs.
If you’re admitted to a skilled nursing facility (SNF) after being in the hospital for the required three days, Medicare picks up the whole SNF tab for the first 20 days, and you pay nothing. After that, you pay a daily co-pay ($176 in 2020) for the next 80 days. If you need to be in the facility longer than 100 days in any one benefit period, you’re responsible for the full cost.
 You can’t use your lifetime reserve days to extend coverage in an SNF.
You can’t use your lifetime reserve days to extend coverage in an SNF.
Co-payments (home health care and hospice care)
If you qualify for home health services (see Chapter 2), Medicare pays a home health agency for your care; you pay nothing. If you need or want a service that isn’t covered under the agency contract, you have to pay for it yourself — either in full or as a regular 20 percent Part B co-pay (see the later section “ Part B costs”).
If you receive hospice services from a Medicare-approved agency (see Chapter 2), you pay almost nothing for this care. Two exceptions exist:
If you need prescription drugs to control the symptoms, such as pain, of your terminal illness, you pay up to $5 per prescription.
If you need to enter a nursing home for a short time so that your caregiver can catch a break, you’re expected to contribute 5 percent of the cost.
Medicare places no annual upper limit on your expenses in Part A. But if you have a Medigap policy (which I describe in Chapter 4) or other supplemental insurance, it may cover Part A’s hospital deductible and co-pays.
Part B covers doctors’ services (in their offices, in hospitals or other facilities, or at your home), outpatient care such as lab tests and screenings, and some medical equipment and supplies. Note: The Part B costs described in the following sections apply if you’re enrolled in the traditional Medicare program. If you’re in a Medicare Advantage plan, see the later section “ Medicare Advantage costs.”
All people enrolled in Part B must pay a monthly premium to receive services (unless they’re eligible for state assistance, as explained in Chapter 4). In late fall, the federal government announces the Part B premium amount for the following year. In 2020, the standard premium is $144.60 a month. Note that qualifying word: standard. If your income is over a certain level, you pay more. Also, if there is no Social Security cost-of-living adjustment (COLA) in any given year, or only a very small one, you may pay different premiums from some other people. I explain the higher-income surcharge, and the impact of zero or small COLAs in some years, later in this chapter.
Deductible and co-payments
In 2020, the annual Part B deductible was $198. The amount usually goes up a little each year and is announced at the same time as the Part B premium. Typically, Medicare pays 80 percent and you pay 20 percent of the Medicare-approved cost of Part B services. Note that you may be charged more than 20 percent if you go to a provider who doesn’t accept the Medicare-approved cost as full payment, as I explain in Chapter 13.
In traditional Medicare, Part B has no upper limit on out-of-pocket expenses. But if you have Medigap supplemental insurance (described in Chapter 4), it covers your Part B co-pays in full or in part, depending on the policy you buy.
Part D covers outpatient prescription drugs — the kind that are prescribed by a doctor and used by you at home. You can receive this coverage by enrolling in a stand-alone Part D drug plan (if you have traditional Medicare for your medical benefits) or in a Medicare Advantage plan that combines medical and Part D drug coverage in its benefit package.
Читать дальше


 You can’t use your lifetime reserve days to extend coverage in an SNF.
You can’t use your lifetime reserve days to extend coverage in an SNF.










