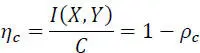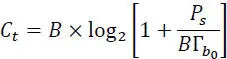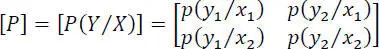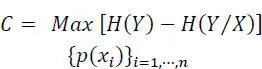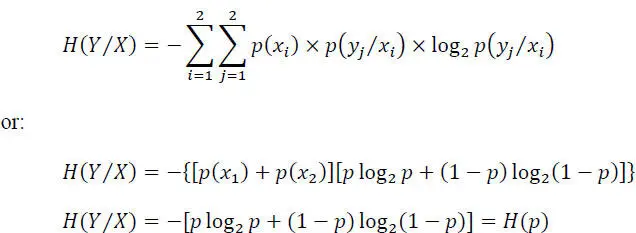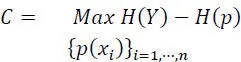and:
[2.42] 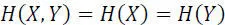
– Channel with maximum power noise: in this case, the variable at the input is independent of that of the output, i.e.:
[2.43] 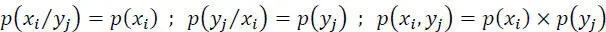
We then have:
[2.44] 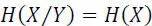
[2.45] 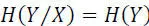
[2.46] 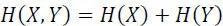
Note.– In information security , if xi is the plaintext, and yj is the corresponding ciphertext, then p ( xi / yi ) = p ( xi ) is the condition of the perfect secret of a cryptosystem.
The mutual information obtained on the symbol xi when the symbol yj is received is given by:
[2.47] 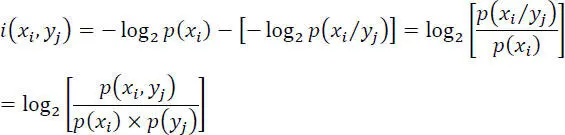
where i ( xi, yj ) represents the decrease in uncertainty on xi due to the receipt of yj .
The average value of the mutual information, or the amount of information I ( X, Y ) transmitted through the channel is:
[2.48] 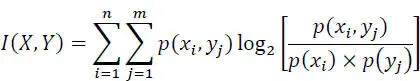
or:
[2.49] 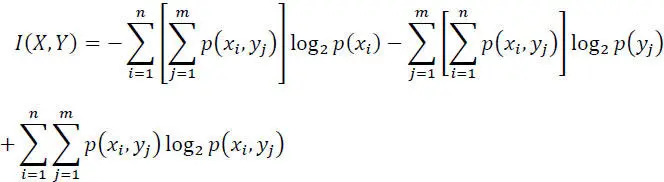
Hence:
[2.50] 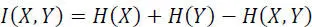
Given relationships [2.36]and [2.37], we get:
[2.51] 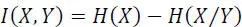
[2.52] 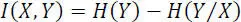
[2.53] 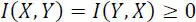
Special cases.
– Noiseless channel: X and Y symbols are linked, so:I(X, Y)=H(X)=H(Y)
– Channel with maximum power noise: X and Y symbols are independent, therefore:I(X, Y) = 0
2.7. Capacity, redundancy and efficiency of a discrete channel
Claude Shannon introduced the concept of channel capacity, to measure the efficiency with which information is transmitted, and to find its upper limit.
The capacity C of a channel: (information bit/symbol) is the maximum value of the mutual information I ( X, Y ) over the set of input symbols probabilities 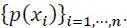
[2.54] 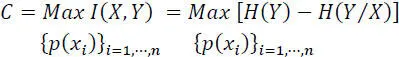
The maximization of I ( X, Y ) is performed under the constraints that:
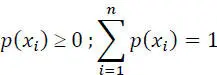
The maximum value of I ( X, Y )occurs for some well-defined values of these probabilities, which thus define a certain so-called secondary source .
The capacity of the channel can also be related to the unit of time (bitrate Ct of the channel) , in this case, one has:
[2.55] 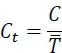
The channel redundancy Rc and the relative channel redundancy pc are defined by:
[2.56] 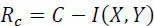
[2.57] 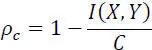
The efficiency of the use of the channel 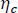 is defined by
is defined by
[2.58] 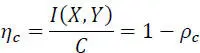
2.7.1. Shannon’s theorem: capacity of a communication system
Shannon also formulated the capacity of a communication system by the following relation:
[2.59] 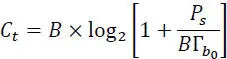
where:
– B: is the channel bandwidth, in hertz;
– Ps: is the signal power, in watts;
is the power spectral density of the (supposed) Gaussian and white noise in its frequency band B;
is the noise power, in watts.
EXAMPLE.– Binary symmetric channel (BSC).
Any binary channel will be characterized by the noise matrix:
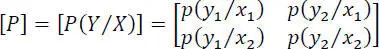
If the binary channel is symmetric, then one has:
p ( y1/x2 ) = p ( y2/x1 ) = p
p ( y1/x1 ) = p ( y2/x2 ) = 1 − p
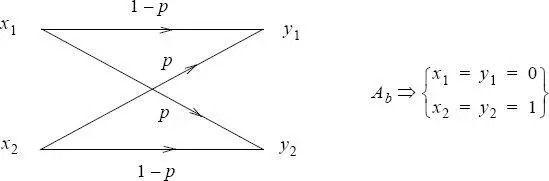
Figure 2.5. Binary symmetric channel
The channel capacity is:
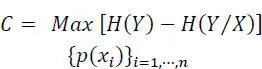
The conditional entropy H ( Y/X ) is:
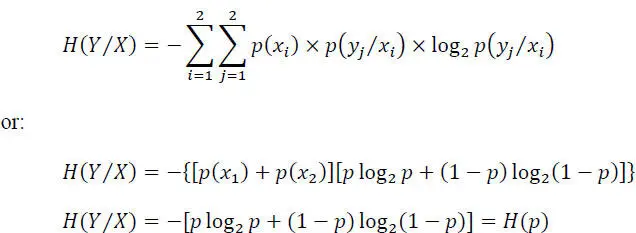
Hence:
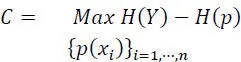
But max H ( Y ) = 1 for p ( y 1) = p ( y2 ). It follows from the symmetry of the channel that if p ( y1 ) = p ( y2 ), then p ( x1 ) = p ( x2 ) = 1/2, and C will be given by:
Читать дальше

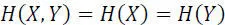
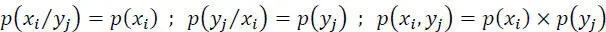
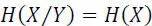
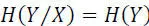
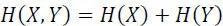
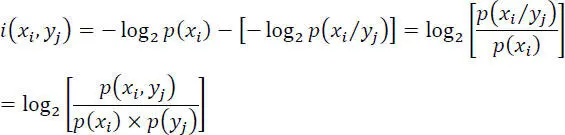
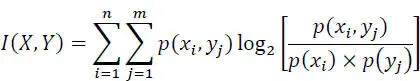
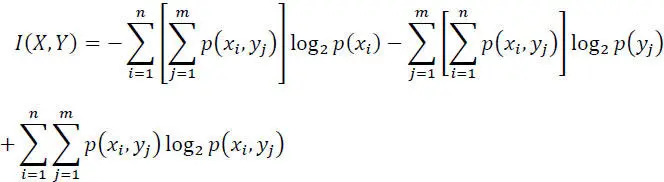
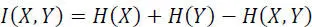
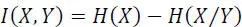
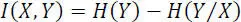
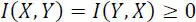
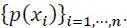
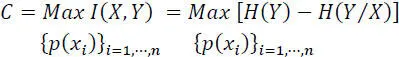
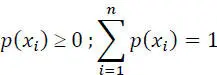
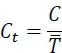
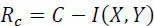
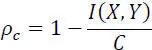
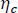 is defined by
is defined by