Qelectric charge, imaginary or reactive powerQ = 1/(ωRC) = 1/BW = 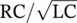 =
= 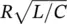 =
= 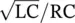 quality factorqquadratureq(t)electric charge as a function of timequadrantone‐quarter area of complex/Gaussian plane
quality factorqquadratureq(t)electric charge as a function of timequadrantone‐quarter area of complex/Gaussian plane
rrotorRradius, resistanceRaarmature resistance of DC machineRCresistor–capacitor networkℜreluctance, magnetic resistanceRccore‐loss resistance, resistance of iron coreRgresistance of air gap of iron coreℜgreluctance or magnetic resistance of air gap of iron coreℜcreluctance or magnetic resistance of iron coreRpresistance of primary windingRsresistance of secondary winding 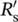 secondary resistance referred to primary side of transformerRcloss (series) resistance of capacitorR1resistance of primary winding 1R2resistance of secondary winding 2Rlineper phase resistance of distribution/transmission lineRLCresistor–inductor–capacitor networkradradiansratratedReindicates real part of a complex numberRloadload resistanceRload1resistance of load 1Rload2resistance of load 2
secondary resistance referred to primary side of transformerRcloss (series) resistance of capacitorR1resistance of primary winding 1R2resistance of secondary winding 2Rlineper phase resistance of distribution/transmission lineRLCresistor–inductor–capacitor networkradradiansratratedReindicates real part of a complex numberRloadload resistanceRload1resistance of load 1Rload2resistance of load 2  per phase resistance of delta‐connected load
per phase resistance of delta‐connected load  per phase resistance of delta‐connected first load
per phase resistance of delta‐connected first load  per phase resistance of delta second connected load
per phase resistance of delta second connected load 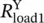 per phase resistance of Y‐connected first load
per phase resistance of Y‐connected first load 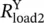 per phase resistance of Y‐connected second loadRHSright‐hand siderinradius inside of round wireroutradius outside of round wirermsroot‐mean‐squarermsloadsubscript for root‐mean‐square value of a load quantity (e.g. voltage)rmssourceindicates root‐mean‐square value of a source quantity (e.g. voltage)rpmrevolutions per minuterpsrevolutions per second(R − jX)complex conjugate of (R + jX)(r, Φ, z)r coordinate, Φ coordinate, z coordinate
per phase resistance of Y‐connected second loadRHSright‐hand siderinradius inside of round wireroutradius outside of round wirermsroot‐mean‐squarermsloadsubscript for root‐mean‐square value of a load quantity (e.g. voltage)rmssourceindicates root‐mean‐square value of a source quantity (e.g. voltage)rpmrevolutions per minuterpsrevolutions per second(R − jX)complex conjugate of (R + jX)(r, Φ, z)r coordinate, Φ coordinate, z coordinate
ssource, stator, synchronous, slip, unit of second, abbreviation symbol for first derivative 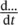 , secondary, abbreviation for jω =s, seconds 2abbreviation symbol for second derivativeSsouth (pole), surface, source terminalS =
, secondary, abbreviation for jω =s, seconds 2abbreviation symbol for second derivativeSsouth (pole), surface, source terminalS = 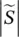 apparent power, magnitude of complex power
apparent power, magnitude of complex power 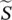 complex powers1, s2two roots of characteristic equationscshort circuit
complex powers1, s2two roots of characteristic equationscshort circuit 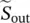 complex output powerSratrated apparent powerSactualactual apparent powerSEERseasonal energy efficiency ratioSCRsilicon‐controlled rectifierSISystème International d’Unités (French for International System of Units)SisiliconSiCsilicon carbidesinglesingle‐phase valueSMsynchronous machineSOFCsolid oxide fuel cellSSsteady statestartstartingSMsynchronous motor/machineSTCStandard Test ConditionSTEMscience, technology, engineering, and mathematicssubsubstationSUMsummationsyssystemSWMStadtwerke Münchenswitchmechanical or electronic switch
complex output powerSratrated apparent powerSactualactual apparent powerSEERseasonal energy efficiency ratioSCRsilicon‐controlled rectifierSISystème International d’Unités (French for International System of Units)SisiliconSiCsilicon carbidesinglesingle‐phase valueSMsynchronous machineSOFCsolid oxide fuel cellSSsteady statestartstartingSMsynchronous motor/machineSTCStandard Test ConditionSTEMscience, technology, engineering, and mathematicssubsubstationSUMsummationsyssystemSWMStadtwerke Münchenswitchmechanical or electronic switch
tturn, time variableTunit of Tesla, period length/duration, time constant, transformer, absolute temperature 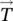 torque in vector notationT(t)time‐dependent torquetddelay timeTeelectric torqueTcmechanical torque due to Coulomb (c) friction Tsmechanical torque due to standstill (s)TLmechanical load torqueTmmechanical torque performing useful workTGVTrain à Grande Vitesse (French high‐speed trains)ththeoreticalTHthyristor, Thévenin (TH)transtransresistanceThévenin theoremimpressed voltage source theoremTHDitotal harmonic distortion of currentTHDvtotal harmonic distortion of voltagethreethree‐phase valueτtime constant, time constant RCτptime constant for peak rectificationτRCtime constant for RC circuitτRLtime constant for RL circuitθphase shift of a time function, power factor angleθvphase shift of a voltage v(t)θiphase shift of a current i(t)θmmechanical displacement angleθnphase shift of Fourier componentθpphase shift angle between
torque in vector notationT(t)time‐dependent torquetddelay timeTeelectric torqueTcmechanical torque due to Coulomb (c) friction Tsmechanical torque due to standstill (s)TLmechanical load torqueTmmechanical torque performing useful workTGVTrain à Grande Vitesse (French high‐speed trains)ththeoreticalTHthyristor, Thévenin (TH)transtransresistanceThévenin theoremimpressed voltage source theoremTHDitotal harmonic distortion of currentTHDvtotal harmonic distortion of voltagethreethree‐phase valueτtime constant, time constant RCτptime constant for peak rectificationτRCtime constant for RC circuitτRLtime constant for RL circuitθphase shift of a time function, power factor angleθvphase shift of a voltage v(t)θiphase shift of a current i(t)θmmechanical displacement angleθnphase shift of Fourier componentθpphase shift angle between 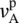 and
and 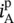
Ustands for upperUSAUnited States of AmericaUGunity gain
Vvoltage, unit of voltage, volt 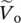 phasor output voltageVDDpositive DC supply voltage of operational amplifierVSSnegative DC supply voltage of operational amplifier
phasor output voltageVDDpositive DC supply voltage of operational amplifierVSSnegative DC supply voltage of operational amplifier 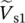 phasor source 1 input voltage
phasor source 1 input voltage 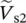 phasor source 2 input voltage Vharmonicharmonic voltage magnitudeV pprimary phase voltage of transformerV ssecondary phase voltage of transformerV1primary phase voltage of transformerV2secondary phase voltage of transformerVCAmagnitude of primary voltage between winding terminals A and AVAnpmagnitude of primary voltage between terminal A and neutral point np of primary winding AVansmagnitude of secondary voltage between terminal a and neutral point ns of secondary winding a
phasor source 2 input voltage Vharmonicharmonic voltage magnitudeV pprimary phase voltage of transformerV ssecondary phase voltage of transformerV1primary phase voltage of transformerV2secondary phase voltage of transformerVCAmagnitude of primary voltage between winding terminals A and AVAnpmagnitude of primary voltage between terminal A and neutral point np of primary winding AVansmagnitude of secondary voltage between terminal a and neutral point ns of secondary winding a 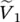 phasor voltage across primary winding 1
phasor voltage across primary winding 1 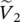 phasor voltage across secondary winding 2
phasor voltage across secondary winding 2 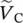 phasor voltage across capacitor C
phasor voltage across capacitor C 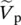 primary phasor voltagev+positive input voltage of operational amplifierv−negative input voltage of operational amplifier
primary phasor voltagev+positive input voltage of operational amplifierv−negative input voltage of operational amplifier 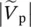 magnitude of phasor voltage at primary side of transformer
magnitude of phasor voltage at primary side of transformer 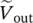 phasor output voltage of secondary circuit
phasor output voltage of secondary circuit 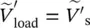 phasor load secondary voltage of single‐phase transformer referred to primary side
phasor load secondary voltage of single‐phase transformer referred to primary side 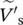 phasor secondary voltage of transformer referred to primary side
phasor secondary voltage of transformer referred to primary side  magnitude of the load phasor voltage of transformer referred to primary side
magnitude of the load phasor voltage of transformer referred to primary side 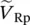 phasor voltage across the primary resistance Rp
phasor voltage across the primary resistance Rp 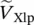 phasor voltage across the primary leakage reactance Xlp
phasor voltage across the primary leakage reactance Xlp 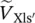 phasor voltage drop across leakage reactance of secondary side referred to primary side of transformer
phasor voltage drop across leakage reactance of secondary side referred to primary side of transformer 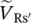 phasor voltage drop across winding resistance of secondary side referred to primary side of transformer
phasor voltage drop across winding resistance of secondary side referred to primary side of transformer 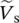 phasor voltage of source
phasor voltage of source 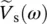 phasor source voltage as a function of angular velocity or frequency ω
phasor source voltage as a function of angular velocity or frequency ω 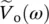 phasor output voltage as a function of angular velocity or frequency ω
phasor output voltage as a function of angular velocity or frequency ω 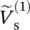 phasor load/secondary voltage of single‐phase transformer where superscript (1) indicates the first step of drawing the phasor diagram
phasor load/secondary voltage of single‐phase transformer where superscript (1) indicates the first step of drawing the phasor diagram 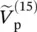 phasor primary voltage of single‐phase transformer where superscript (15) indicates the fifteenth step of drawing the phasor diagramv(t)voltage as a function of time functionv1(t)primary voltage as a function of time functionvp(t)primary voltage as a function of time function
phasor primary voltage of single‐phase transformer where superscript (15) indicates the fifteenth step of drawing the phasor diagramv(t)voltage as a function of time functionv1(t)primary voltage as a function of time functionvp(t)primary voltage as a function of time function 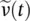 phasor of voltage time function v(t)VAunit for apparent power S called volt‐ampere
phasor of voltage time function v(t)VAunit for apparent power S called volt‐ampere 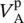 voltage across primary winding of phase A
voltage across primary winding of phase A 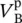 voltage across primary winding of phase B
voltage across primary winding of phase B 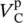 voltage across primary winding of phase C
voltage across primary winding of phase C 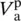 voltage across primary winding of phase a
voltage across primary winding of phase a 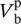 voltage across primary winding of phase b
voltage across primary winding of phase b 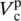 voltage across primary winding of phase c
voltage across primary winding of phase c 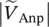 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding A
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding A 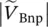 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding B
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding B 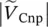 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding C
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding C 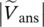 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding a
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding a 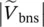 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding b
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding b 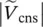 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding c
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding c 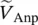 phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding A
phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding A 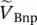 phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding B
phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding B 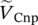 phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding C
phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding C 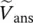 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding a
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding a 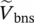 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding b
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding b 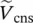 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding c
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding c 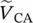 phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings C and A
phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings C and A 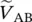 phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings A and B
phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings A and B 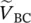 phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings B and C
phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings B and C 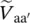 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′ 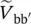 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals b and b′
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals b and b′ 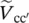 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals c and c′VAnpmagnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding AVaa′magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals c and c′VAnpmagnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding AVaa′magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′ 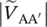 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals A and A′
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals A and A′ 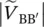 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals B and B′
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals B and B′ 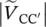 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals C and C′
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals C and C′ 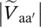 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′ 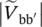 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals b and b′
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals b and b′  magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals c and c′
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals c and c′ 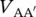 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals A and A′
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals A and A′ 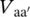 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′VBAmagnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals B and AVbamagnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals b and a
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′VBAmagnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals B and AVbamagnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals b and a 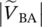 magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals B and A
magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals B and A 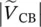 magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals C and B
magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals C and B 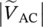 magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals A and C
magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals A and C 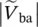 magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals b and a
magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals b and a 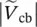 magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals c and b
magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals c and b 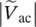 magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals a and cVArunit for imaginary/reactive power Q called volt‐ampere reactivevc(t = −0)vc(t) voltage before switching occurs at t = 0vL(t = +0)vL(t) voltage after switching occurs at t = 0vC(t = ∞)vC(t) at an infinite amount of time VMamplitude of time function v(t)VSIvoltage source inverterVCcapacitor voltage
magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals a and cVArunit for imaginary/reactive power Q called volt‐ampere reactivevc(t = −0)vc(t) voltage before switching occurs at t = 0vL(t = +0)vL(t) voltage after switching occurs at t = 0vC(t = ∞)vC(t) at an infinite amount of time VMamplitude of time function v(t)VSIvoltage source inverterVCcapacitor voltage
Читать дальше

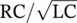 =
= 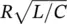 =
= 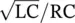 quality factorqquadratureq(t)electric charge as a function of timequadrantone‐quarter area of complex/Gaussian plane
quality factorqquadratureq(t)electric charge as a function of timequadrantone‐quarter area of complex/Gaussian plane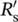 secondary resistance referred to primary side of transformerRcloss (series) resistance of capacitorR1resistance of primary winding 1R2resistance of secondary winding 2Rlineper phase resistance of distribution/transmission lineRLCresistor–inductor–capacitor networkradradiansratratedReindicates real part of a complex numberRloadload resistanceRload1resistance of load 1Rload2resistance of load 2
secondary resistance referred to primary side of transformerRcloss (series) resistance of capacitorR1resistance of primary winding 1R2resistance of secondary winding 2Rlineper phase resistance of distribution/transmission lineRLCresistor–inductor–capacitor networkradradiansratratedReindicates real part of a complex numberRloadload resistanceRload1resistance of load 1Rload2resistance of load 2  per phase resistance of delta‐connected load
per phase resistance of delta‐connected load  per phase resistance of delta‐connected first load
per phase resistance of delta‐connected first load  per phase resistance of delta second connected load
per phase resistance of delta second connected load 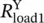 per phase resistance of Y‐connected first load
per phase resistance of Y‐connected first load 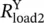 per phase resistance of Y‐connected second loadRHSright‐hand siderinradius inside of round wireroutradius outside of round wirermsroot‐mean‐squarermsloadsubscript for root‐mean‐square value of a load quantity (e.g. voltage)rmssourceindicates root‐mean‐square value of a source quantity (e.g. voltage)rpmrevolutions per minuterpsrevolutions per second(R − jX)complex conjugate of (R + jX)(r, Φ, z)r coordinate, Φ coordinate, z coordinate
per phase resistance of Y‐connected second loadRHSright‐hand siderinradius inside of round wireroutradius outside of round wirermsroot‐mean‐squarermsloadsubscript for root‐mean‐square value of a load quantity (e.g. voltage)rmssourceindicates root‐mean‐square value of a source quantity (e.g. voltage)rpmrevolutions per minuterpsrevolutions per second(R − jX)complex conjugate of (R + jX)(r, Φ, z)r coordinate, Φ coordinate, z coordinate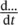 , secondary, abbreviation for jω =s, seconds 2abbreviation symbol for second derivativeSsouth (pole), surface, source terminalS =
, secondary, abbreviation for jω =s, seconds 2abbreviation symbol for second derivativeSsouth (pole), surface, source terminalS = 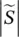 apparent power, magnitude of complex power
apparent power, magnitude of complex power 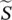 complex powers1, s2two roots of characteristic equationscshort circuit
complex powers1, s2two roots of characteristic equationscshort circuit 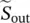 complex output powerSratrated apparent powerSactualactual apparent powerSEERseasonal energy efficiency ratioSCRsilicon‐controlled rectifierSISystème International d’Unités (French for International System of Units)SisiliconSiCsilicon carbidesinglesingle‐phase valueSMsynchronous machineSOFCsolid oxide fuel cellSSsteady statestartstartingSMsynchronous motor/machineSTCStandard Test ConditionSTEMscience, technology, engineering, and mathematicssubsubstationSUMsummationsyssystemSWMStadtwerke Münchenswitchmechanical or electronic switch
complex output powerSratrated apparent powerSactualactual apparent powerSEERseasonal energy efficiency ratioSCRsilicon‐controlled rectifierSISystème International d’Unités (French for International System of Units)SisiliconSiCsilicon carbidesinglesingle‐phase valueSMsynchronous machineSOFCsolid oxide fuel cellSSsteady statestartstartingSMsynchronous motor/machineSTCStandard Test ConditionSTEMscience, technology, engineering, and mathematicssubsubstationSUMsummationsyssystemSWMStadtwerke Münchenswitchmechanical or electronic switch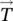 torque in vector notationT(t)time‐dependent torquetddelay timeTeelectric torqueTcmechanical torque due to Coulomb (c) friction Tsmechanical torque due to standstill (s)TLmechanical load torqueTmmechanical torque performing useful workTGVTrain à Grande Vitesse (French high‐speed trains)ththeoreticalTHthyristor, Thévenin (TH)transtransresistanceThévenin theoremimpressed voltage source theoremTHDitotal harmonic distortion of currentTHDvtotal harmonic distortion of voltagethreethree‐phase valueτtime constant, time constant RCτptime constant for peak rectificationτRCtime constant for RC circuitτRLtime constant for RL circuitθphase shift of a time function, power factor angleθvphase shift of a voltage v(t)θiphase shift of a current i(t)θmmechanical displacement angleθnphase shift of Fourier componentθpphase shift angle between
torque in vector notationT(t)time‐dependent torquetddelay timeTeelectric torqueTcmechanical torque due to Coulomb (c) friction Tsmechanical torque due to standstill (s)TLmechanical load torqueTmmechanical torque performing useful workTGVTrain à Grande Vitesse (French high‐speed trains)ththeoreticalTHthyristor, Thévenin (TH)transtransresistanceThévenin theoremimpressed voltage source theoremTHDitotal harmonic distortion of currentTHDvtotal harmonic distortion of voltagethreethree‐phase valueτtime constant, time constant RCτptime constant for peak rectificationτRCtime constant for RC circuitτRLtime constant for RL circuitθphase shift of a time function, power factor angleθvphase shift of a voltage v(t)θiphase shift of a current i(t)θmmechanical displacement angleθnphase shift of Fourier componentθpphase shift angle between 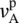 and
and 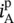
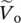 phasor output voltageVDDpositive DC supply voltage of operational amplifierVSSnegative DC supply voltage of operational amplifier
phasor output voltageVDDpositive DC supply voltage of operational amplifierVSSnegative DC supply voltage of operational amplifier 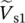 phasor source 1 input voltage
phasor source 1 input voltage 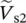 phasor source 2 input voltage Vharmonicharmonic voltage magnitudeV pprimary phase voltage of transformerV ssecondary phase voltage of transformerV1primary phase voltage of transformerV2secondary phase voltage of transformerVCAmagnitude of primary voltage between winding terminals A and AVAnpmagnitude of primary voltage between terminal A and neutral point np of primary winding AVansmagnitude of secondary voltage between terminal a and neutral point ns of secondary winding a
phasor source 2 input voltage Vharmonicharmonic voltage magnitudeV pprimary phase voltage of transformerV ssecondary phase voltage of transformerV1primary phase voltage of transformerV2secondary phase voltage of transformerVCAmagnitude of primary voltage between winding terminals A and AVAnpmagnitude of primary voltage between terminal A and neutral point np of primary winding AVansmagnitude of secondary voltage between terminal a and neutral point ns of secondary winding a 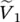 phasor voltage across primary winding 1
phasor voltage across primary winding 1 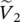 phasor voltage across secondary winding 2
phasor voltage across secondary winding 2 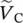 phasor voltage across capacitor C
phasor voltage across capacitor C 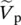 primary phasor voltagev+positive input voltage of operational amplifierv−negative input voltage of operational amplifier
primary phasor voltagev+positive input voltage of operational amplifierv−negative input voltage of operational amplifier 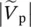 magnitude of phasor voltage at primary side of transformer
magnitude of phasor voltage at primary side of transformer 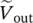 phasor output voltage of secondary circuit
phasor output voltage of secondary circuit 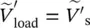 phasor load secondary voltage of single‐phase transformer referred to primary side
phasor load secondary voltage of single‐phase transformer referred to primary side 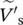 phasor secondary voltage of transformer referred to primary side
phasor secondary voltage of transformer referred to primary side  magnitude of the load phasor voltage of transformer referred to primary side
magnitude of the load phasor voltage of transformer referred to primary side 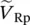 phasor voltage across the primary resistance Rp
phasor voltage across the primary resistance Rp 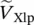 phasor voltage across the primary leakage reactance Xlp
phasor voltage across the primary leakage reactance Xlp 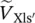 phasor voltage drop across leakage reactance of secondary side referred to primary side of transformer
phasor voltage drop across leakage reactance of secondary side referred to primary side of transformer 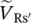 phasor voltage drop across winding resistance of secondary side referred to primary side of transformer
phasor voltage drop across winding resistance of secondary side referred to primary side of transformer 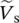 phasor voltage of source
phasor voltage of source 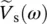 phasor source voltage as a function of angular velocity or frequency ω
phasor source voltage as a function of angular velocity or frequency ω 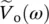 phasor output voltage as a function of angular velocity or frequency ω
phasor output voltage as a function of angular velocity or frequency ω 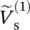 phasor load/secondary voltage of single‐phase transformer where superscript (1) indicates the first step of drawing the phasor diagram
phasor load/secondary voltage of single‐phase transformer where superscript (1) indicates the first step of drawing the phasor diagram 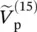 phasor primary voltage of single‐phase transformer where superscript (15) indicates the fifteenth step of drawing the phasor diagramv(t)voltage as a function of time functionv1(t)primary voltage as a function of time functionvp(t)primary voltage as a function of time function
phasor primary voltage of single‐phase transformer where superscript (15) indicates the fifteenth step of drawing the phasor diagramv(t)voltage as a function of time functionv1(t)primary voltage as a function of time functionvp(t)primary voltage as a function of time function 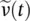 phasor of voltage time function v(t)VAunit for apparent power S called volt‐ampere
phasor of voltage time function v(t)VAunit for apparent power S called volt‐ampere 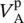 voltage across primary winding of phase A
voltage across primary winding of phase A 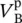 voltage across primary winding of phase B
voltage across primary winding of phase B 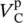 voltage across primary winding of phase C
voltage across primary winding of phase C 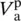 voltage across primary winding of phase a
voltage across primary winding of phase a 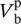 voltage across primary winding of phase b
voltage across primary winding of phase b 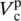 voltage across primary winding of phase c
voltage across primary winding of phase c 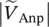 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding A
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding A 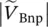 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding B
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding B 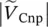 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding C
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding C 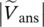 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding a
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding a 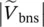 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding b
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding b 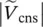 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding c
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding c 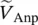 phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding A
phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding A 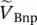 phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding B
phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding B 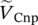 phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding C
phasor primary phase voltage of transformer with winding C 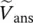 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding a
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding a 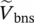 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding b
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding b 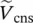 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding c
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer with winding c 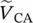 phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings C and A
phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings C and A 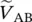 phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings A and B
phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings A and B 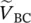 phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings B and C
phasor primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformer between windings B and C 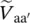 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′ 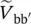 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals b and b′
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals b and b′ 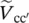 phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals c and c′VAnpmagnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding AVaa′magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′
phasor secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals c and c′VAnpmagnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer with winding AVaa′magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′ 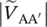 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals A and A′
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals A and A′ 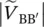 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals B and B′
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals B and B′ 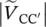 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals C and C′
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals C and C′ 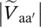 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′ 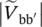 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals b and b′
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals b and b′  magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals c and c′
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals c and c′ 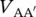 magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals A and A′
magnitude of primary phase voltage of transformer between terminals A and A′ 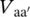 magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′VBAmagnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals B and AVbamagnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals b and a
magnitude of secondary phase voltage of transformer between terminals a and a′VBAmagnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals B and AVbamagnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals b and a 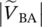 magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals B and A
magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals B and A 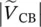 magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals C and B
magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals C and B 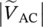 magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals A and C
magnitude of primary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals A and C 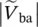 magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals b and a
magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals b and a 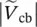 magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals c and b
magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals c and b 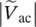 magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals a and cVArunit for imaginary/reactive power Q called volt‐ampere reactivevc(t = −0)vc(t) voltage before switching occurs at t = 0vL(t = +0)vL(t) voltage after switching occurs at t = 0vC(t = ∞)vC(t) at an infinite amount of time VMamplitude of time function v(t)VSIvoltage source inverterVCcapacitor voltage
magnitude of secondary line‐to‐line voltage of transformers between terminals a and cVArunit for imaginary/reactive power Q called volt‐ampere reactivevc(t = −0)vc(t) voltage before switching occurs at t = 0vL(t = +0)vL(t) voltage after switching occurs at t = 0vC(t = ∞)vC(t) at an infinite amount of time VMamplitude of time function v(t)VSIvoltage source inverterVCcapacitor voltage










