Ewald F. Fuchs - Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Ewald F. Fuchs - Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Introduction to Energy, Renewable Energy and Electrical Engineering»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A combination of analytical and software solutions in order to relate aspects of electric circuits at an accessible level A thorough description of compensation of flux weakening (CFW) applied to inverter-fed, variable-speed drives not seen anywhere else in the literature Numerous application examples of solutions using PSPICE, Mathematica, and finite difference/finite element solutions such as detailed magnetic flux distributions Manufacturing of electric energy in power systems with integrated renewable energy sources where three-phase inverter supply energy to interconnected, smart power systems Connecting the energy-related technology and application discussions with urgent issues of energy conservation and renewable energy—such as photovoltaics and ground-water heat pump resulting in a zero-emissions dwelling—
crafts a truly modern and relevant approach to its subject matter.

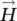 magnetic field intensity vector
magnetic field intensity vector 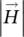 magnitude of magnetic field intensity vectorHcmagnetic field intensity in iron core
magnitude of magnetic field intensity vectorHcmagnetic field intensity in iron core 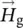 vector of magnetic field intensity/strength in air gap
vector of magnetic field intensity/strength in air gap 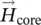 magnetic field intensity/strength vector of iron coreHcore=
magnetic field intensity/strength vector of iron coreHcore= 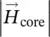 magnitude of magnetic field intensity vector within iron coreHg=
magnitude of magnetic field intensity vector within iron coreHg= 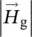 magnitude of magnetic field intensity/strength vector within air gap (g)Hrmagnetic field intensity/strength r‐component of (r, Φ, z) polar systemHΦmagnetic field intensity/strength Φ‐component of (r, Φ, z) polar systemHΦ_inmagnetic field intensity component in Φ direction inside of round wire
magnitude of magnetic field intensity/strength vector within air gap (g)Hrmagnetic field intensity/strength r‐component of (r, Φ, z) polar systemHΦmagnetic field intensity/strength Φ‐component of (r, Φ, z) polar systemHΦ_inmagnetic field intensity component in Φ direction inside of round wire 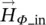 magnetic field intensity vector in Φ direction inside of round wire HΦ_outmagnetic field intensity component in Φ direction outside of round wireHzmagnetic field intensity/strength z‐component of (r, Φ, z) polar systemHxx‐component of magnetic field intensity vector
magnetic field intensity vector in Φ direction inside of round wire HΦ_outmagnetic field intensity component in Φ direction outside of round wireHzmagnetic field intensity/strength z‐component of (r, Φ, z) polar systemHxx‐component of magnetic field intensity vector 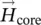 homhomogeneousHVDChigh‐voltage DC lineHTEhigh‐temperature electrolysisH2Ochemical symbol for waterHzhertz, cycles per 1 second
homhomogeneousHVDChigh‐voltage DC lineHTEhigh‐temperature electrolysisH2Ochemical symbol for waterHzhertz, cycles per 1 second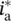 reference/nominal/rated (*) value of armature (a) currentip(t)primary current as a function of time
reference/nominal/rated (*) value of armature (a) currentip(t)primary current as a function of time 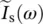 phasor source current as a function of angular velocity or frequency
phasor source current as a function of angular velocity or frequency  primary current through winding/phase A
primary current through winding/phase A 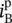 primary current through winding/phase B
primary current through winding/phase B 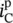 primary current through winding/phase C
primary current through winding/phase C 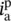 secondary current through winding/phase a
secondary current through winding/phase a 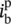 secondary current through winding/phase b
secondary current through winding/phase b 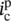 secondary current through winding/phase c
secondary current through winding/phase c 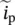 primary phasor current
primary phasor current 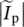 magnitude of phasor current in primary winding
magnitude of phasor current in primary winding 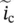 core‐loss phasor current
core‐loss phasor current  excitation phasor current
excitation phasor current 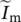 magnetizing phasor current
magnetizing phasor current 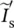 secondary phasor current referred to primary side of transformer
secondary phasor current referred to primary side of transformer 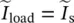 phasor load current of single‐phase transformer referred to secondary side
phasor load current of single‐phase transformer referred to secondary side 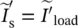 phasor load current of single‐phase transformer referred to primary sideis(t)secondary current as a function of timeIinverter, integral, inductance, current, DC current
phasor load current of single‐phase transformer referred to primary sideis(t)secondary current as a function of timeIinverter, integral, inductance, current, DC current 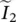 phasor current of secondary winding 2
phasor current of secondary winding 2 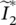 phasor conjugate (*) current of secondary circuit
phasor conjugate (*) current of secondary circuit 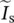 phasor source current of primary circuit
phasor source current of primary circuit 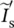 secondary phasor current of transformer referred to primary side
secondary phasor current of transformer referred to primary side 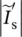 magnitude of secondary phasor current of transformer referred to primary side
magnitude of secondary phasor current of transformer referred to primary side 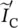 phasor capacitor current of transformer referred to primary side
phasor capacitor current of transformer referred to primary side 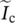 phasor current through core‐loss resistance Rc of transformer
phasor current through core‐loss resistance Rc of transformer 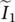 phasor input current of primary circuit
phasor input current of primary circuit 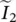 phasor output current of secondary circuiti(t)current as a function of timei1(t)primary current as a function of time functioni2(t)secondary current as a function of time functioni2current in secondary winding 2i1current in primary winding 1
phasor output current of secondary circuiti(t)current as a function of timei1(t)primary current as a function of time functioni2(t)secondary current as a function of time functioni2current in secondary winding 2i1current in primary winding 1 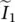 phasor current in primary winding 1IDCDC currentIinDC current inside of round wire up to radius rinIocurrent i(t) at t = 0
phasor current in primary winding 1IDCDC currentIinDC current inside of round wire up to radius rinIocurrent i(t) at t = 0 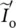 component current of
component current of 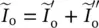
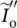 component current of
component current of 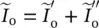 ∞symbol for infinityICEinternal combustion engineininputIMinduction or asynchronous machineImindicates imaginary part of a complex number
∞symbol for infinityICEinternal combustion engineininputIMinduction or asynchronous machineImindicates imaginary part of a complex number 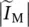 absolute value or magnitude of phasor
absolute value or magnitude of phasor 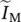 IMamplitude of time function i(t)IMinduction motor/machineIGBTinsulated‐gate bipolar transistorincandescentEdison‐type light bulb
IMamplitude of time function i(t)IMinduction motor/machineIGBTinsulated‐gate bipolar transistorincandescentEdison‐type light bulb 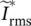 complex conjugate of
complex conjugate of