Ccombined, cooling, collector, capacitance, conductance, contour length of integration pathcsubscript for capacitance (c), constant (c) for windage mechanical torquec1coefficient linking Φ11 and i1c2coefficient linking Φ12 and i2ccwcounterclockwiseCAGRcompound annual growth rateCBAphase sequence C, B, AcdcandelaCFLcompact fluorescent light (bulb)CFWcompensation of flux weakeningCHCPcombined heat, cooling, and (electric) powerCHPcombined (thermal) heat and (electric) powerCMRRcommon‐mode rejection ratiocnphase c (c) to neutral (n)CMOScomplementary metal–oxide semiconductorcos θcosine of fundamental power factor angle θ between transformer load voltage and load current, fundamental power factorcos(ΦVp − ΦIp) = cos ΦVp‐Ippower factor due to angles of 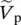 and
and 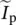 COPcoefficient of performanceCO2carbon dioxide
COPcoefficient of performanceCO2carbon dioxide 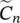 coefficient of exponential Fourier analysis termcumcumulative
coefficient of exponential Fourier analysis termcumcumulative
ddiode, developed, direct, differentiationDdrain terminal, diode, subscript for determinant D, symbol for denominator, iron stack depthD(jω)denominator of transfer functiondot (•)dot convention/markingdBdecibel: dB (decibel)=20log M(ω)DCdirect currentDFIGdoubly fed induction generatordiffdifferential 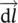 incremental (differential) length vector
incremental (differential) length vector 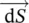 incremental (differential) surface vectordttime increment/differentialdVdifferential volumeDOEUS Department of Energydryerclothes dryer$dollar symbolΔthree‐phase winding connected in delta/Δ/triangle, delta/deviation/incremental changeΔTtorque differenceΔ‐Δ or Δ/Δprimary and secondary windings of three‐phase transformer are connected in deltaΔ‐Y or Δ/Yprimary winding of three‐phase transformer is connected in delta and secondary winding in wye
incremental (differential) surface vectordttime increment/differentialdVdifferential volumeDOEUS Department of Energydryerclothes dryer$dollar symbolΔthree‐phase winding connected in delta/Δ/triangle, delta/deviation/incremental changeΔTtorque differenceΔ‐Δ or Δ/Δprimary and secondary windings of three‐phase transformer are connected in deltaΔ‐Y or Δ/Yprimary winding of three‐phase transformer is connected in delta and secondary winding in wye
eelectriceainduced voltage of DC machinee(t)induced voltage as a function of timeEenergy, emitter 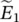 phasor‐induced voltage of winding 1
phasor‐induced voltage of winding 1 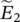 phasor‐induced voltage of winding 2
phasor‐induced voltage of winding 2 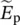 induced phasor voltage in primary winding
induced phasor voltage in primary winding 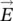 electric field intensity/strength vectorenergycenergy/work stored in iron coreenergygenergy/work stored in air gapECENelectrical, computer engineeringECEENelectrical, computer, energy engineeringECPMelectronically commutated permanent‐magnet machineECPMMelectronically commutated permanent‐magnet machineeffeffectiveEGienergy (E) fed to utility grid (G)EGGErneuerbare‐Energien‐Gesetz (German Renewable Energy Sources Act)EHCienergy (E) for heating (H) and cooling (C)EIienergy (E) by PV system feeding two invertersEKGelectrocardiogramELAienergy (E) for lighting (L) and appliances (A)EnEVEnergieeinsparverordnung (German Energy Saving Ordinance)ERCOTElectric Reliability Council of TexasERGEnergy (E) and Resources (R) Group (G)ETNEuropean Type Number for batteriesEUEuropean UnionEqequationeqequivalent
electric field intensity/strength vectorenergycenergy/work stored in iron coreenergygenergy/work stored in air gapECENelectrical, computer engineeringECEENelectrical, computer, energy engineeringECPMelectronically commutated permanent‐magnet machineECPMMelectronically commutated permanent‐magnet machineeffeffectiveEGienergy (E) fed to utility grid (G)EGGErneuerbare‐Energien‐Gesetz (German Renewable Energy Sources Act)EHCienergy (E) for heating (H) and cooling (C)EIienergy (E) by PV system feeding two invertersEKGelectrocardiogramELAienergy (E) for lighting (L) and appliances (A)EnEVEnergieeinsparverordnung (German Energy Saving Ordinance)ERCOTElectric Reliability Council of TexasERGEnergy (E) and Resources (R) Group (G)ETNEuropean Type Number for batteriesEUEuropean UnionEqequationeqequivalent 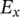 x‐component of electric field intensity/strength
x‐component of electric field intensity/strength 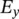 y‐component of electric field intensity/strength
y‐component of electric field intensity/strength 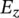 z‐component of electric field intensity/strengthE(t)electric field intensity/strength as a function of time€euro symbolεpermittivity of dielectric, steady‐state error/deviationεpermittivity of free spaceεrrelative permittivity
z‐component of electric field intensity/strengthE(t)electric field intensity/strength as a function of time€euro symbolεpermittivity of dielectric, steady‐state error/deviationεpermittivity of free spaceεrrelative permittivity
ffield, frequency 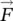 (mechanical) force vectorFfarad, unit of capacitance, energy functional for finite element method, feedbackℱmagnetomotive force
(mechanical) force vectorFfarad, unit of capacitance, energy functional for finite element method, feedbackℱmagnetomotive force  attraction force due to magnetic fields of two magnets
attraction force due to magnetic fields of two magnets 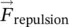 repulsion force due to magnetic fields of two magnetsfeferrum (Latin for iron)FETfield‐effect transistorFDfinite differenceFEfinite elementFMfigure of meritFWflux weakeningf(t)periodic function of time tftfeetϕphase angle, power factor angleΦmagnetic field flux, useful flux, iron‐core fluxϕsphase angle of source voltage
repulsion force due to magnetic fields of two magnetsfeferrum (Latin for iron)FETfield‐effect transistorFDfinite differenceFEfinite elementFMfigure of meritFWflux weakeningf(t)periodic function of time tftfeetϕphase angle, power factor angleΦmagnetic field flux, useful flux, iron‐core fluxϕsphase angle of source voltage 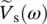 ϕIsphase angle of source current
ϕIsphase angle of source current 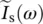 as a function of angular velocity or frequency ωΦ(t)magnetic flux as a function of timeϕ(ω)phase angle of phasor transfer function G(jω) as a function of angular velocity or frequency ωΦm(t)mutual/main flux as a function of timeΦfringingfringing magnetic fluxΦusefuluseful magnetic fluxΦ12mutual flux originating in winding 2 linking winding 1Φ21mutual flux originating in winding 1 linking winding 2Φ11total flux generated by coil 1Φ22total flux generated by coil 2Φleak1leakage flux linked with coil 1Φleak2leakage flux linked with coil 2Φ1total flux linked with coil 1Φ2total flux linked with coil 2ΦAflux in transformer AΦBflux in transformer BΦCflux in transformer CΦtotal = ΦA + ΦB + ΦCtotal flux in common limb of bank of three‐phase transformer consisting of three‐single phase transformers A, B, C
as a function of angular velocity or frequency ωΦ(t)magnetic flux as a function of timeϕ(ω)phase angle of phasor transfer function G(jω) as a function of angular velocity or frequency ωΦm(t)mutual/main flux as a function of timeΦfringingfringing magnetic fluxΦusefuluseful magnetic fluxΦ12mutual flux originating in winding 2 linking winding 1Φ21mutual flux originating in winding 1 linking winding 2Φ11total flux generated by coil 1Φ22total flux generated by coil 2Φleak1leakage flux linked with coil 1Φleak2leakage flux linked with coil 2Φ1total flux linked with coil 1Φ2total flux linked with coil 2ΦAflux in transformer AΦBflux in transformer BΦCflux in transformer CΦtotal = ΦA + ΦB + ΦCtotal flux in common limb of bank of three‐phase transformer consisting of three‐single phase transformers A, B, C 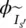 phase angle of secondary current
phase angle of secondary current 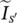 referred to primary side
referred to primary side
gground, air‐gap lengthGgrid, gate, conductance G = 1/R, giga, closed‐loop gainG(jω)phasor transfer functionGccore‐loss conductanceGDdifferential (D) mode gainGvclosed‐loop voltage gainGCmRRcommon‐mode rejection ratio gainGLCconductance–inductance–capacitance networkgengeneratorgiga109Gicurrent gainGωmangular velocity gainGrectthyristor rectifier gain 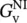 closed‐loop voltage gain of noninverting operational amplifier
closed‐loop voltage gain of noninverting operational amplifier 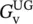 closed‐loop voltage gain of unity gain operational amplifier
closed‐loop voltage gain of unity gain operational amplifier 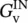 closed‐loop voltage gain of inverting operational amplifier
closed‐loop voltage gain of inverting operational amplifier 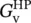 closed‐loop voltage gain of high‐pass filter
closed‐loop voltage gain of high‐pass filter 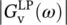 magnitude of closed‐loop voltage gain of low‐pass filter
magnitude of closed‐loop voltage gain of low‐pass filter 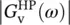 magnitude of closed‐loop voltage gain of high‐pass filterGmbHGesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung (German for company with limited liability)GSPgas and steam (electric) powerGTOgate turn‐off thyristorGWgigawattGWPglobal warming potential
magnitude of closed‐loop voltage gain of high‐pass filterGmbHGesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung (German for company with limited liability)GSPgas and steam (electric) powerGTOgate turn‐off thyristorGWgigawattGWPglobal warming potential
Читать дальше

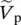 and
and 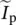 COPcoefficient of performanceCO2carbon dioxide
COPcoefficient of performanceCO2carbon dioxide 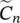 coefficient of exponential Fourier analysis termcumcumulative
coefficient of exponential Fourier analysis termcumcumulative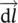 incremental (differential) length vector
incremental (differential) length vector 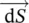 incremental (differential) surface vectordttime increment/differentialdVdifferential volumeDOEUS Department of Energydryerclothes dryer$dollar symbolΔthree‐phase winding connected in delta/Δ/triangle, delta/deviation/incremental changeΔTtorque differenceΔ‐Δ or Δ/Δprimary and secondary windings of three‐phase transformer are connected in deltaΔ‐Y or Δ/Yprimary winding of three‐phase transformer is connected in delta and secondary winding in wye
incremental (differential) surface vectordttime increment/differentialdVdifferential volumeDOEUS Department of Energydryerclothes dryer$dollar symbolΔthree‐phase winding connected in delta/Δ/triangle, delta/deviation/incremental changeΔTtorque differenceΔ‐Δ or Δ/Δprimary and secondary windings of three‐phase transformer are connected in deltaΔ‐Y or Δ/Yprimary winding of three‐phase transformer is connected in delta and secondary winding in wye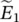 phasor‐induced voltage of winding 1
phasor‐induced voltage of winding 1 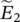 phasor‐induced voltage of winding 2
phasor‐induced voltage of winding 2 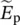 induced phasor voltage in primary winding
induced phasor voltage in primary winding 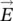 electric field intensity/strength vectorenergycenergy/work stored in iron coreenergygenergy/work stored in air gapECENelectrical, computer engineeringECEENelectrical, computer, energy engineeringECPMelectronically commutated permanent‐magnet machineECPMMelectronically commutated permanent‐magnet machineeffeffectiveEGienergy (E) fed to utility grid (G)EGGErneuerbare‐Energien‐Gesetz (German Renewable Energy Sources Act)EHCienergy (E) for heating (H) and cooling (C)EIienergy (E) by PV system feeding two invertersEKGelectrocardiogramELAienergy (E) for lighting (L) and appliances (A)EnEVEnergieeinsparverordnung (German Energy Saving Ordinance)ERCOTElectric Reliability Council of TexasERGEnergy (E) and Resources (R) Group (G)ETNEuropean Type Number for batteriesEUEuropean UnionEqequationeqequivalent
electric field intensity/strength vectorenergycenergy/work stored in iron coreenergygenergy/work stored in air gapECENelectrical, computer engineeringECEENelectrical, computer, energy engineeringECPMelectronically commutated permanent‐magnet machineECPMMelectronically commutated permanent‐magnet machineeffeffectiveEGienergy (E) fed to utility grid (G)EGGErneuerbare‐Energien‐Gesetz (German Renewable Energy Sources Act)EHCienergy (E) for heating (H) and cooling (C)EIienergy (E) by PV system feeding two invertersEKGelectrocardiogramELAienergy (E) for lighting (L) and appliances (A)EnEVEnergieeinsparverordnung (German Energy Saving Ordinance)ERCOTElectric Reliability Council of TexasERGEnergy (E) and Resources (R) Group (G)ETNEuropean Type Number for batteriesEUEuropean UnionEqequationeqequivalent 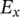 x‐component of electric field intensity/strength
x‐component of electric field intensity/strength 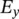 y‐component of electric field intensity/strength
y‐component of electric field intensity/strength 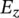 z‐component of electric field intensity/strengthE(t)electric field intensity/strength as a function of time€euro symbolεpermittivity of dielectric, steady‐state error/deviationεpermittivity of free spaceεrrelative permittivity
z‐component of electric field intensity/strengthE(t)electric field intensity/strength as a function of time€euro symbolεpermittivity of dielectric, steady‐state error/deviationεpermittivity of free spaceεrrelative permittivity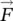 (mechanical) force vectorFfarad, unit of capacitance, energy functional for finite element method, feedbackℱmagnetomotive force
(mechanical) force vectorFfarad, unit of capacitance, energy functional for finite element method, feedbackℱmagnetomotive force  attraction force due to magnetic fields of two magnets
attraction force due to magnetic fields of two magnets 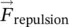 repulsion force due to magnetic fields of two magnetsfeferrum (Latin for iron)FETfield‐effect transistorFDfinite differenceFEfinite elementFMfigure of meritFWflux weakeningf(t)periodic function of time tftfeetϕphase angle, power factor angleΦmagnetic field flux, useful flux, iron‐core fluxϕsphase angle of source voltage
repulsion force due to magnetic fields of two magnetsfeferrum (Latin for iron)FETfield‐effect transistorFDfinite differenceFEfinite elementFMfigure of meritFWflux weakeningf(t)periodic function of time tftfeetϕphase angle, power factor angleΦmagnetic field flux, useful flux, iron‐core fluxϕsphase angle of source voltage 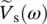 ϕIsphase angle of source current
ϕIsphase angle of source current 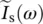 as a function of angular velocity or frequency ωΦ(t)magnetic flux as a function of timeϕ(ω)phase angle of phasor transfer function G(jω) as a function of angular velocity or frequency ωΦm(t)mutual/main flux as a function of timeΦfringingfringing magnetic fluxΦusefuluseful magnetic fluxΦ12mutual flux originating in winding 2 linking winding 1Φ21mutual flux originating in winding 1 linking winding 2Φ11total flux generated by coil 1Φ22total flux generated by coil 2Φleak1leakage flux linked with coil 1Φleak2leakage flux linked with coil 2Φ1total flux linked with coil 1Φ2total flux linked with coil 2ΦAflux in transformer AΦBflux in transformer BΦCflux in transformer CΦtotal = ΦA + ΦB + ΦCtotal flux in common limb of bank of three‐phase transformer consisting of three‐single phase transformers A, B, C
as a function of angular velocity or frequency ωΦ(t)magnetic flux as a function of timeϕ(ω)phase angle of phasor transfer function G(jω) as a function of angular velocity or frequency ωΦm(t)mutual/main flux as a function of timeΦfringingfringing magnetic fluxΦusefuluseful magnetic fluxΦ12mutual flux originating in winding 2 linking winding 1Φ21mutual flux originating in winding 1 linking winding 2Φ11total flux generated by coil 1Φ22total flux generated by coil 2Φleak1leakage flux linked with coil 1Φleak2leakage flux linked with coil 2Φ1total flux linked with coil 1Φ2total flux linked with coil 2ΦAflux in transformer AΦBflux in transformer BΦCflux in transformer CΦtotal = ΦA + ΦB + ΦCtotal flux in common limb of bank of three‐phase transformer consisting of three‐single phase transformers A, B, C 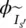 phase angle of secondary current
phase angle of secondary current 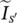 referred to primary side
referred to primary side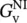 closed‐loop voltage gain of noninverting operational amplifier
closed‐loop voltage gain of noninverting operational amplifier 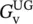 closed‐loop voltage gain of unity gain operational amplifier
closed‐loop voltage gain of unity gain operational amplifier 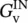 closed‐loop voltage gain of inverting operational amplifier
closed‐loop voltage gain of inverting operational amplifier 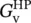 closed‐loop voltage gain of high‐pass filter
closed‐loop voltage gain of high‐pass filter 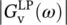 magnitude of closed‐loop voltage gain of low‐pass filter
magnitude of closed‐loop voltage gain of low‐pass filter 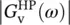 magnitude of closed‐loop voltage gain of high‐pass filterGmbHGesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung (German for company with limited liability)GSPgas and steam (electric) powerGTOgate turn‐off thyristorGWgigawattGWPglobal warming potential
magnitude of closed‐loop voltage gain of high‐pass filterGmbHGesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung (German for company with limited liability)GSPgas and steam (electric) powerGTOgate turn‐off thyristorGWgigawattGWPglobal warming potential










