Position, Navigation, and Timing Technologies in the 21st Century
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Position, Navigation, and Timing Technologies in the 21st Century» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Position, Navigation, and Timing Technologies in the 21st Century
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Position, Navigation, and Timing Technologies in the 21st Century: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Position, Navigation, and Timing Technologies in the 21st Century»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Volume 1 of
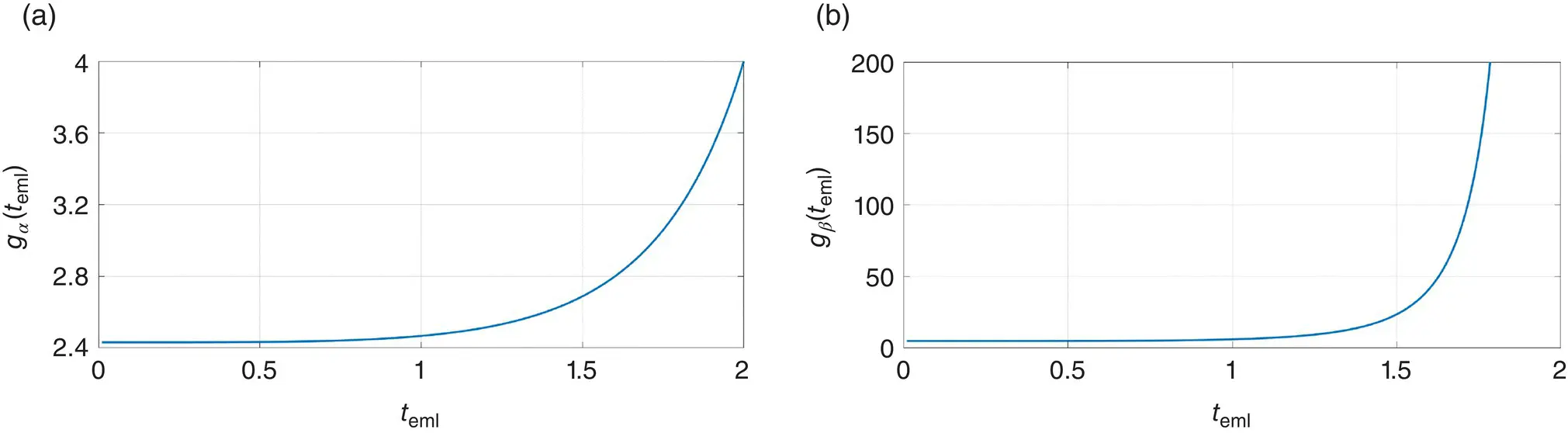
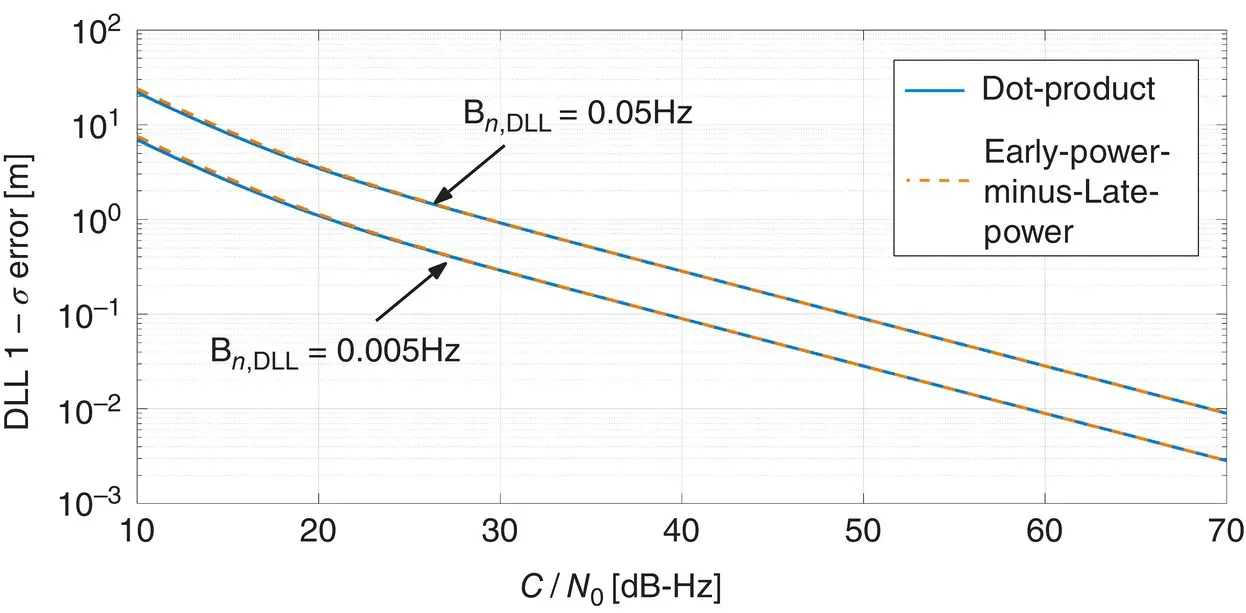
contains three parts and focuses on the satellite navigation systems, technologies, and engineering and scientific applications. It starts with a historical perspective of GPS development and other related PNT development. Current global and regional navigation satellite systems (GNSS and RNSS), their inter-operability, signal quality monitoring, satellite orbit and time synchronization, and ground- and satellite-based augmentation systems are examined. Recent progresses in satellite navigation receiver technologies and challenges for operations in multipath-rich urban environment, in handling spoofing and interference, and in ensuring PNT integrity are addressed. A section on satellite navigation for engineering and scientific applications finishes off the volume.
Volume 2 of
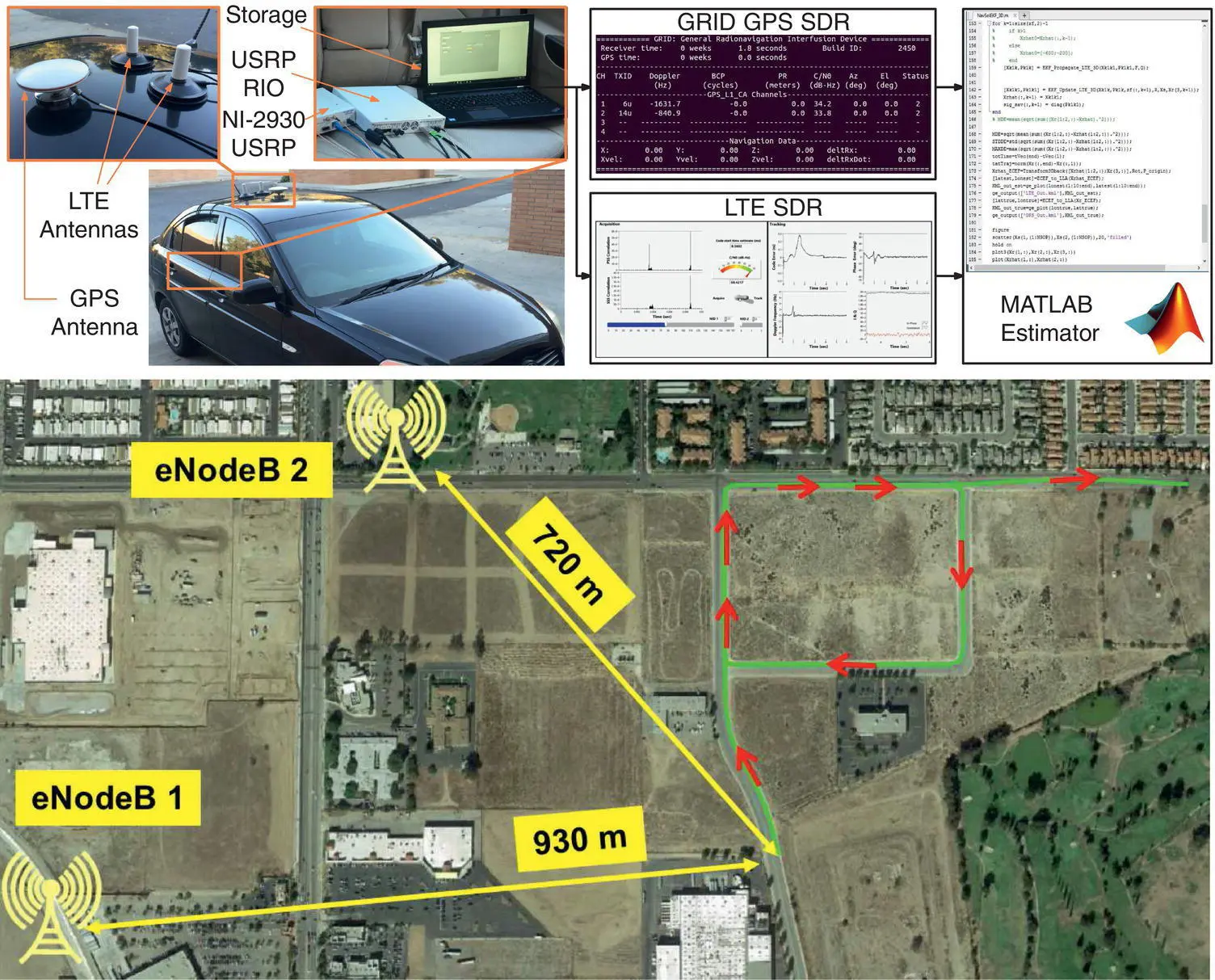
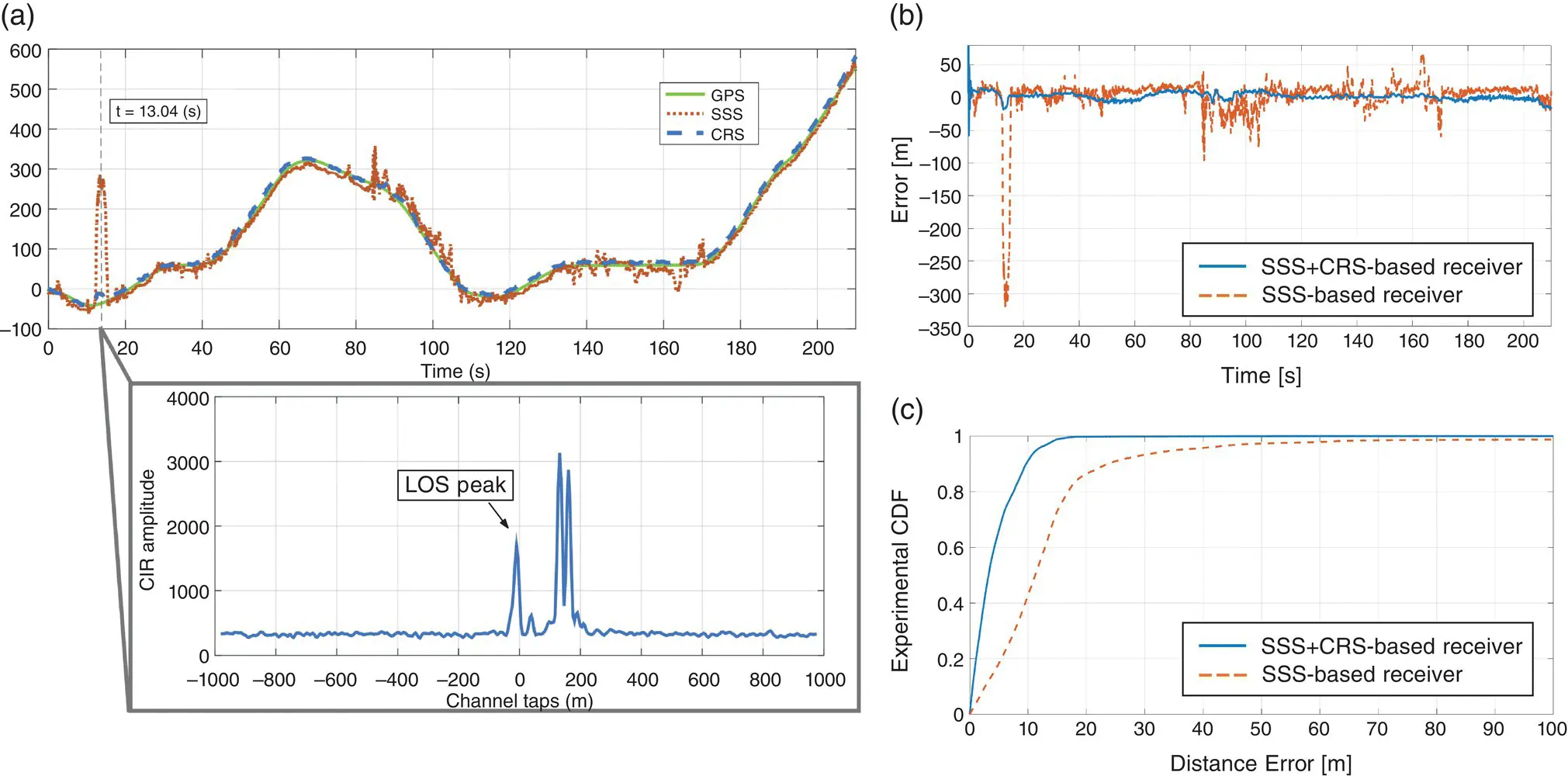
consists of three parts and addresses PNT using alternative signals and sensors and integrated PNT technologies for consumer and commercial applications. It looks at PNT using various radio signals-of-opportunity, atomic clock, optical, laser, magnetic field, celestial, MEMS and inertial sensors, as well as the concept of navigation from Low-Earth Orbiting (LEO) satellites. GNSS-INS integration, neuroscience of navigation, and animal navigation are also covered. The volume finishes off with a collection of work on contemporary PNT applications such as survey and mobile mapping, precision agriculture, wearable systems, automated driving, train control, commercial unmanned aircraft systems, aviation, and navigation in the unique Arctic environment.
In addition, this text:
Serves as a complete reference and handbook for professionals and students interested in the broad range of PNT subjects Includes chapters that focus on the latest developments in GNSS and other navigation sensors, techniques, and applications Illustrates interconnecting relationships between various types of technologies in order to assure more protected, tough, and accurate PNT
will appeal to all industry professionals, researchers, and academics involved with the science, engineering, and applications of position, navigation, and timing technologies.pnt21book.com