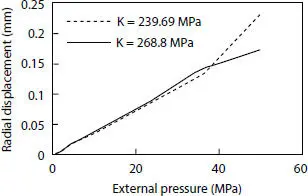
Figure 4.11 Pressure against radial displacements for two representative points.
The profile of the pressure armor used in this full pipe FEM is exactly the same as the one in Figure 4.8. More than 33 of its pitches are involved, with the total length to be around 500 mm. Geometrical parameters for the simulated pipe are listed in Table 4.2.
Elastic-plastic behavior is considered for both steel and HDPE, and their corresponding properties are shown in Figures 4.12and 4.13, respectively, which are delivered from the experimental results. It is supposed that pressure and tensile armor layers are made of the same material with a yielding stress equal to 578 MPa.
An “Explicit dynamic” analysis is developed, which allows for the definition of general contact conditions and it is suitable to perform quasi-static analyses with complicated contact conditions, as explained in [19]. The selection of an explicit instead of an implicit dynamic analysis is justified by the fact that accurate results will be achieved if the increments are small enough, guaranteed by the time equal to two; otherwise, the solution will diverge because the equilibrium is not strictly enforced.
Table 4.2 Pipe’s parameters.
| Parameters |
Value |
| Wire thickness h (mm) |
5.00 |
| Wire width b (mm) |
17.50 |
| Winding angle α (°) |
54.7 |
| Inner layer’s wire number n 1 |
19 |
| Outer layer’s wire’s number n 2 |
20 |
| Inner cylinder’s thickness t 1(mm) |
6 |
| Outer cylinder’s thickness t 2(mm) |
4 |
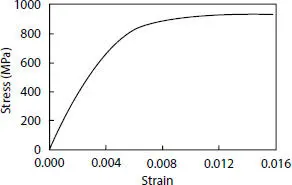
Figure 4.12 Steel stress-strain relationship.
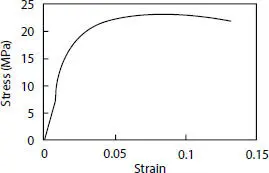
Figure 4.13 HDPE stress-strain relationship.
For this case, in order to easily apply the load and boundary conditions to the model, two reference points for all the degrees of freedom are necessary at the two end surfaces of the pipe, as shown in Figure 4.14. The link type used in the present simulations is “coupling” which represent kinematic type coupling of all the degrees of freedom are constrained between the reference point and the other surfaces on the modeled pipeline.
Displacement along the z direction is applied at RP-2 to simulate the tensile load. Symmetric boundary conditions are set at RP-1 for which U3 = UR1 = UR2 = 0. C3D8R is also used in this model, and their complex geometry and structure is shown in Figure 4.15.
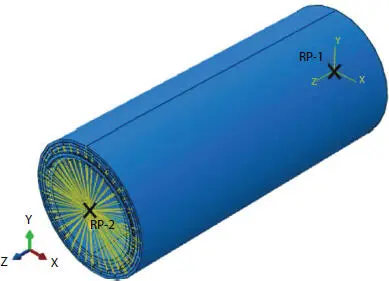
Figure 4.14 Reference point at the end surfaces.
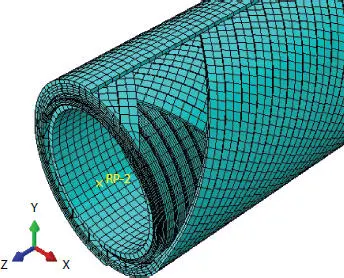
Figure 4.15 Interlayered structure mesh.
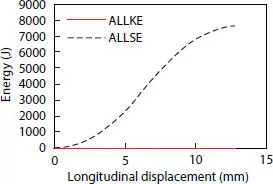
Figure 4.16 Strain and kinetic energies.
The obtained kinetic and strain energy are shown in Figure 4.16, Figure 4.17, which shows relatively good results when the elongation reaches about 12 mm.
4.4 Comparison and Discussion
The comparison between the curves of the tensile forces versus elongation strain of the pipe obtained from both theoretical and numerical results are conducted. These two curves are in good agreement in terms of both elastic and plastic behavior, revealing a maximum percentage difference of 4.50% when the strain is equal to 2.4%. The relatively rough surfaces might yield to an uneven distribution of the confining pressure and in the stress components too. Consequently, in some regions also, the pressure armor may reach to the plastic stage in the numerical simulation, which is not considered in the theoretical model.
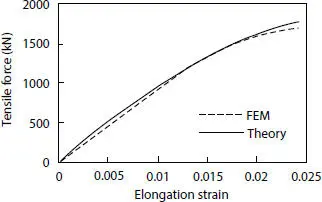
Figure 4.17 Tensile force comparison.
In order to avoid end effects, the stresses located in the mid-span of the pressure armor are extracted out from the numerical simulation. The external surface of the layers is subjected to much more severe loading conditions, two regions along one pitch length are selected due to the uneven distributions of the stresses, and their stress variations are shown in Figure 4.18, points A and B are two groups of points selected not according to different geometric conditions but due to different state conditions. Points A represent the region with the most rigorous stress conditions while Points B shows the ones with less harsh conditions, both selected on the external surface of the pressure armor along the pitch length as represented in Figure 4.19. From this graph, it can be observed that, the stress for points A have already exceeded the material’s proportional limit stress. This might result in a smaller tensile force in the numerical model, especially in the later stage when comparing to the theoretical results which regards the pressure armor as elastic.
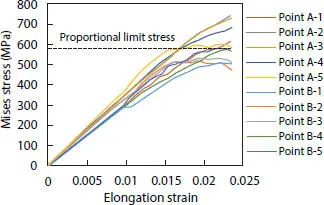
Figure 4.18 Mises stress of pressure armor from FEM.

Figure 4.19 Points selected on the pressure armor external surface for contact pressure analysis.
From the theoretical model, it can be found that, the contribution of the plastic layers corresponds to 5.74% of the total tensile strength, as shown in Figure 4.20, where W stands for tensile wire strength, while WP accounts also for HDPE layers. This result demonstrates the neglection of their influence is reasonable for further studies in order to get conservative results.
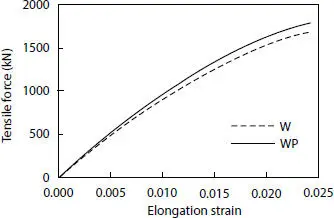
Figure 4.20 Tensile force comparison.
The comparison in terms of radial displacement does not provide reliable results if the interlocked pressure armor is included in the pipe profile. Several reasons could be attributed to this deficiency. The assumption of equivalent pressure armor as an orthotropic cylinder leads to the hypothesis of continuous geometry in the theoretical model, while gaps, rough surfaces and winding angle appear in the FEM simulation. Besides, they could also be affected by the thickness variation in different layers, which is not considered in the analytical model.
Читать дальше






















