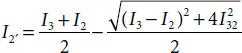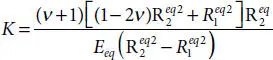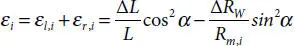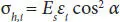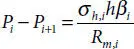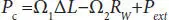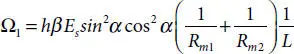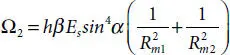Yong Bai - Deepwater Flexible Risers and Pipelines
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Yong Bai - Deepwater Flexible Risers and Pipelines» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Deepwater Flexible Risers and Pipelines
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Deepwater Flexible Risers and Pipelines: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Deepwater Flexible Risers and Pipelines»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
,, has been created to meet the needs of engineers and scientists to keep them up to date and informed of all of these advances. This second volume in the series focuses on flexible pipelines, risers, and umbilicals, offering the engineer the most thorough coverage of the state-of-the-art available. The authors of this work have written numerous books and papers on these subjects and are some of the most influential authors on flexible pipes in the world, contributing much of the literature on this subject to the industry. This new volume is a presentation of some of the most cutting-edge technological advances in technical publishing.
The first volume in this series, published by Wiley-Scrivener, is
, available at www.wiley.com. Laying the foundation for the series, it is a groundbreaking work, written by some of the world’s foremost authorities on pipes and pipelines. Continuing in this series, the editors have compiled the second volume, equally as groundbreaking, expanding the scope to pipelines, risers, and umbilicals.
This is the most comprehensive and in-depth series on pipelines, covering not just the various materials and their aspects that make them different, but every process that goes into their installation, operation, and design. This is the future of pipelines, and it is an important breakthrough. A must-have for the veteran engineer and student alike, this volume is an important new advancement in the energy industry, a strong link in the chain of the world’s energy production

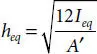
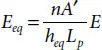
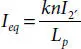
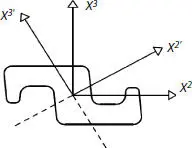
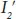 is the smallest moment of inertia, which can be computed, referring to Figure 4.3, as follows:
is the smallest moment of inertia, which can be computed, referring to Figure 4.3, as follows: