Source: Modified from Mi et al. [44].
Subsequently, Sun, Zhou, and coworkers achieved developed an Rh(III)‐catalyzed meta ‐selective C–H olefination of phenol derivatives by using the same organosilicon template mentioned earlier ( Scheme 2.48) [45]. A range of phenol derivatives and activated alkenes are viable in this reaction to produce meta ‐olefinated phenol products in good yields with high meta ‐selectivities.

Scheme 2.48Rh(III)‐catalyzed meta‐ C–H olefination of phenol derivatives.
Source: Modified from Mi et al. [45].
Recently, Xu, Jin, Yu, and coworkers developed bifunctional template assisted, palladium‐catalyzed meta ‐selective C–H olefination of phenols ( Scheme 2.49a), followed by nickel‐catalyzed ipso ‐C–O activation and arylation ( Scheme 2.49b) [46]. The sequential transformations could be carried out in a one‐pot. Thus, this bifunctional template strategy allowed for the expedited synthesis of multiply substituted arenes. Notably, the novel template could be readily synthesized from inexpensive cyanuric chloride and was easily installed and smoothly removed.

Scheme 2.49(a) meta ‐selective C–H olefination of phenols. (b) Nickel‐catalyzed ipso ‐C–O activation and arylation.
Source: (b) Modified from Xu et al. [46].
Finally, Maiti and coworkers also developed a Pd‐catalyzed meta ‐C–H olefination of 2‐phenyl phenol derivatives by using the 2‐cyanobenzoyl group as the directing template that was once employed by Li and coworkers for meta ‐C–H olefination of phenylethylamines ( Scheme 2.50) [47]. Although only a single 2‐phenyl phenol substrate was utilized, the scope of the olefins was broad.
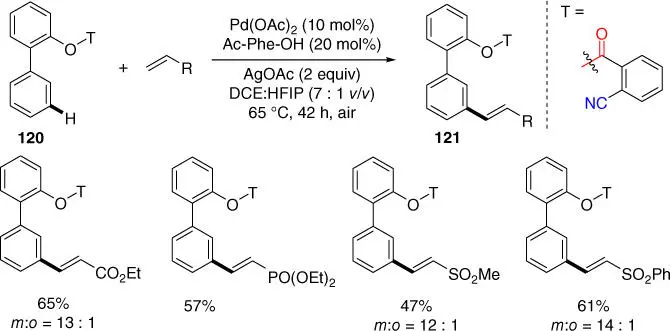
Scheme 2.50 meta ‐C–H olefination of 2‐phenyl phenol derivatives.
Source: Modified from Maity et al. [47].
2.2.6 Alcohol Derivatives
Alcohols are important organic compounds widely found in many drug molecules. In 2013, Tan and coworkers reported a meta ‐C–H olefination of benzyl alcohols by using an effective bulky di‐isopropyl silyl ether tethered nitrile‐based template ( Scheme 2.51) [48]. The template could be easily attached to the benzyl alcohol substrates and readily cleaved in situ with tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) under mild conditions, making the approach synthetically practical. Using the MPAA ligand Ac‐Gly‐OH in the presence of HFIP, a range of benzyl alcohols were meta‐ olefinated smoothly with all substitution patterns on the aromatic ring. Moreover, the template was applicable to both primary and secondary alcohols with equal efficacy.
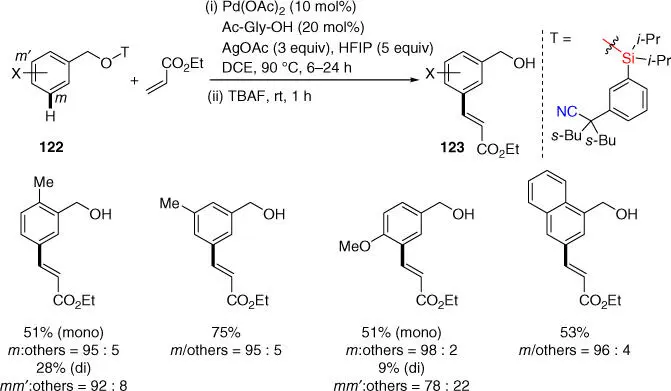
Scheme 2.51 meta ‐C–H olefination of benzyl alcohols.
Source: Modified from Lee et al. [48].
To expand the potential of achieving site selectivity in C–H activation via the recognition of distal and geometric relationship between existing chelating groups and C  H bonds of similar reactivity in organic molecules, Yu and coworkers engineered the first pyridine‐based directing template that was effective for meta‐ C–H olefination of benzyl and phenyl ethyl alcohols ( Scheme 2.52) [49]. This remarkable breakthrough is impressive, since the pyridyl group has only been extensively utilized to assist the ortho ‐C
H bonds of similar reactivity in organic molecules, Yu and coworkers engineered the first pyridine‐based directing template that was effective for meta‐ C–H olefination of benzyl and phenyl ethyl alcohols ( Scheme 2.52) [49]. This remarkable breakthrough is impressive, since the pyridyl group has only been extensively utilized to assist the ortho ‐C  H bond activation previously. Notably, this novel template also enabled a new meta‐ C–H iodination reaction by using DIH as the iodination reagent, which was not feasible with nitrile‐based directing templates previously ( Scheme 2.53). The aryl iodide products are synthetically useful intermediates, since they are amenable to a wide range of transformations such as the transition‐metal‐catalyzed cross‐coupling reactions.
H bond activation previously. Notably, this novel template also enabled a new meta‐ C–H iodination reaction by using DIH as the iodination reagent, which was not feasible with nitrile‐based directing templates previously ( Scheme 2.53). The aryl iodide products are synthetically useful intermediates, since they are amenable to a wide range of transformations such as the transition‐metal‐catalyzed cross‐coupling reactions.

Scheme 2.52 meta ‐C–H olefination of benzyl and phenyl ethyl alcohols.
Source: Modified from Chu et al. [49].
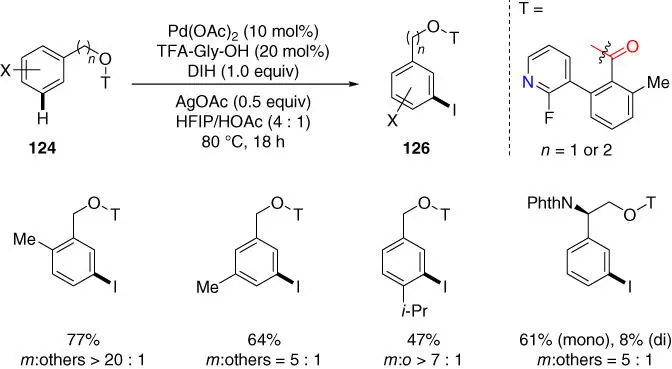
Scheme 2.53 meta ‐C–H iodination of benzyl and phenylethyl alcohols.
In 2017, Xu, Jin, and coworkers reported a Pd‐catalyzed remote meta ‐C–H olefination of a wide range of arene‐tethered alcohols such as 2‐phenylethyl, 3‐phenylpropyl alcohols, and their long‐chain homologues ( Scheme 2.54) [50]. This protocol would be potentially useful for late‐stage modification and post‐synthetic diversification of biologically active molecules for drug discovery. Density functional theory (DFT) computational studies were also performed to reveal that regioselectivity of this reaction resulted from both the C–N–Ag angles and gauche conformations of phenyl ether play.
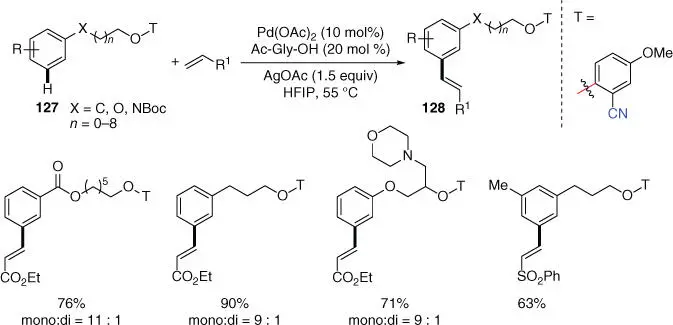
Scheme 2.54 meta ‐C–H olefination of distal arene‐tethered alcohols.
Source: Modified from Zhang et al. [50].
Subsequently, by using a different pyrimidine‐based template that was used for meta ‐C–H cyanation of phenyl ethyl alcohols [41], Jayarajan, Maiti, and coworkers achieved meta ‐C–H functionalizations of conformationally flexible long‐chain arenes derived from alcohols ( Scheme 2.55) [51]. The chain length could be up to 18 bonds between the target C  H bond and the chelating nitrogen atom of the directing template. Remarkably, this approach enabled diverse functionalizations include olefination, alkylation, cyanation, and acetoxylation. Moreover, the template could be readily cleaved by using ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) under mild conditions ( Scheme 2.56). It is worth noting that when perfluoroolefins were used, meta ‐C–H olefination was also feasible for these alcohol derivatives with different linker length under similar reaction conditions [24].
H bond and the chelating nitrogen atom of the directing template. Remarkably, this approach enabled diverse functionalizations include olefination, alkylation, cyanation, and acetoxylation. Moreover, the template could be readily cleaved by using ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) under mild conditions ( Scheme 2.56). It is worth noting that when perfluoroolefins were used, meta ‐C–H olefination was also feasible for these alcohol derivatives with different linker length under similar reaction conditions [24].
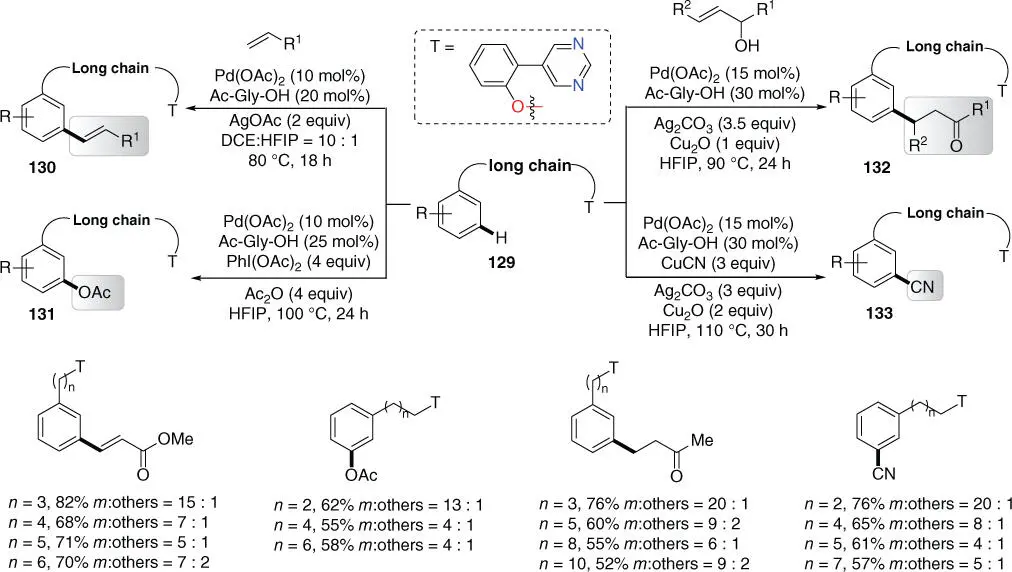
Scheme 2.55 meta ‐C–H functionalizations of arenes with different linker lengths.
Source: Modified from Jayarajan et al. [51].
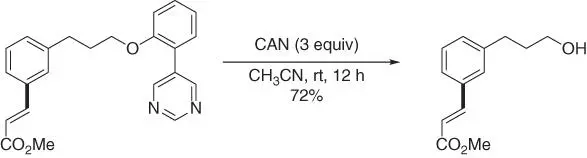
Scheme 2.56Removal of the pyrimidine‐based template.
Читать дальше





 H bonds of similar reactivity in organic molecules, Yu and coworkers engineered the first pyridine‐based directing template that was effective for meta‐ C–H olefination of benzyl and phenyl ethyl alcohols ( Scheme 2.52) [49]. This remarkable breakthrough is impressive, since the pyridyl group has only been extensively utilized to assist the ortho ‐C
H bonds of similar reactivity in organic molecules, Yu and coworkers engineered the first pyridine‐based directing template that was effective for meta‐ C–H olefination of benzyl and phenyl ethyl alcohols ( Scheme 2.52) [49]. This remarkable breakthrough is impressive, since the pyridyl group has only been extensively utilized to assist the ortho ‐C 















