1 ...6 7 8 10 11 12 ...31 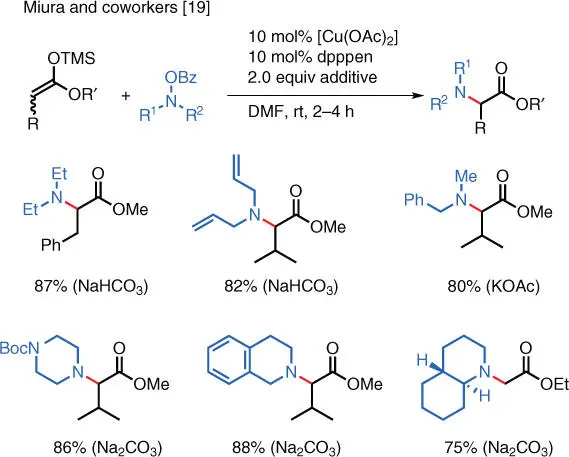
Scheme 1.11 Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic amination of silyl enol ethers.
Source: Modified from Matsuda et al. [19].
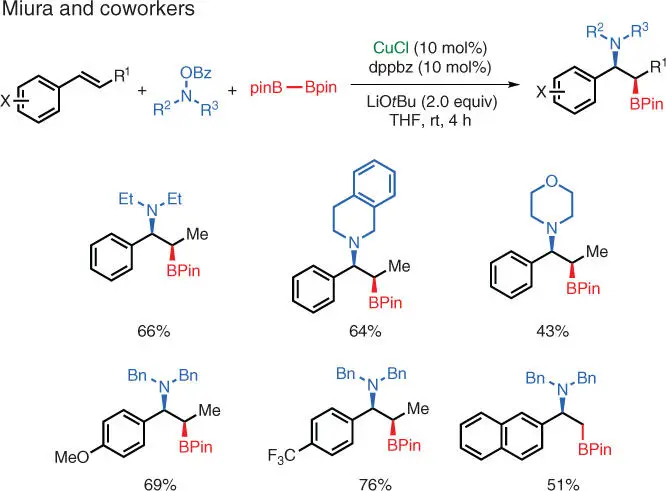
Scheme 1.12 Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic catalyzed aminoboration of styrenes.
Source: Modified from Matsuda et al. [20].
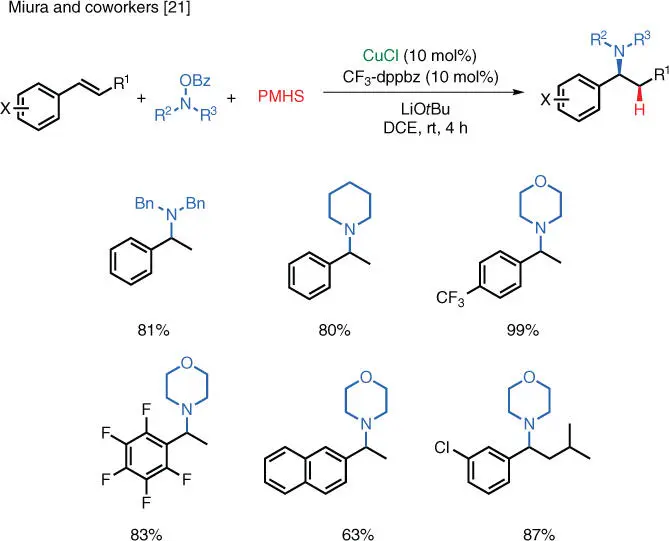
Scheme 1.13 Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic hydroamination of styrenes.
Source: Modified from Miki et al. [21].
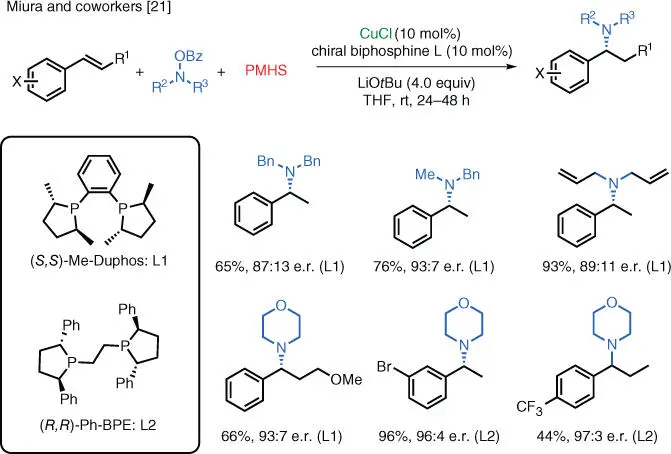
Scheme 1.14 Enantioselective Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic hydroamination of styrenes.
Source: Miki et al. [21].
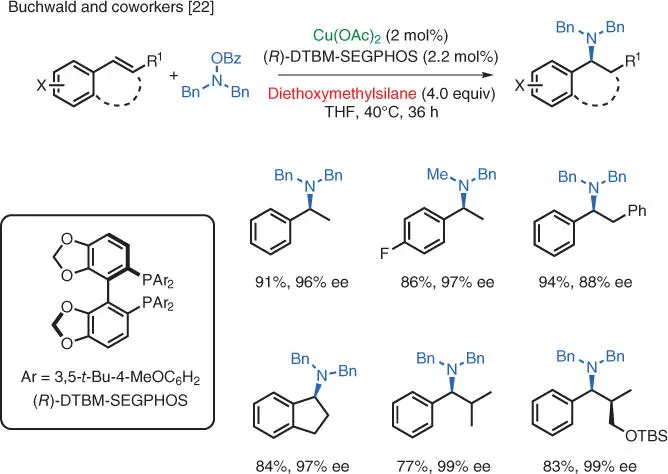
Scheme 1.15 Enantioselective Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic hydroamination of styrenes.
Source: Modified from Zhu et al. [22].
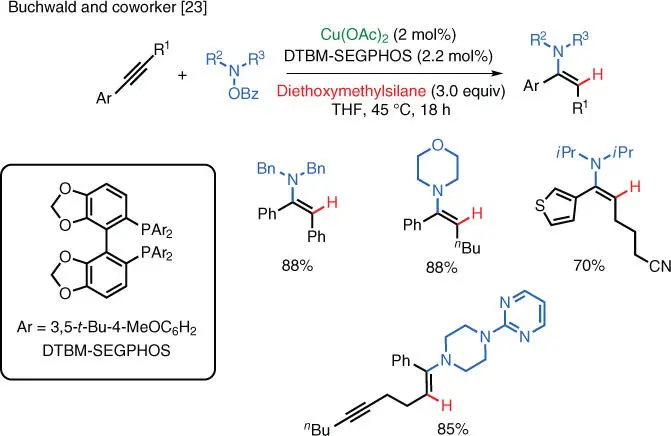
Scheme 1.16 Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic amination of alkynes.
Source: Shi and Buchwald [23].
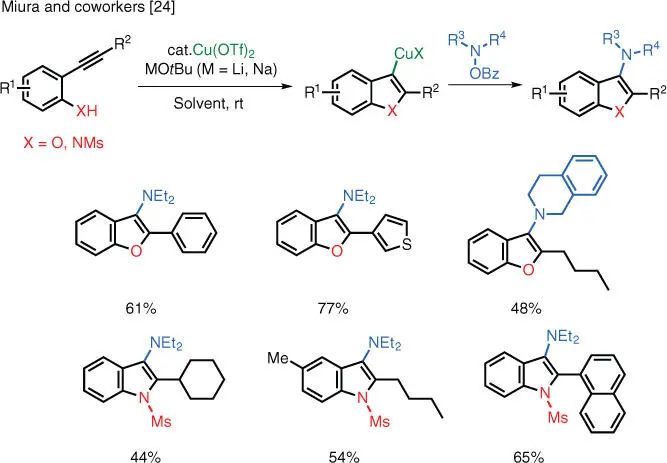
Scheme 1.17 Cu‐catalyzed annulative electrophilic amination.
Source: Modified from Matsuda et al. [24].
ortho ‐Alkynyl phenols and anilines can also undergo annulative amination with electrophilic aminating reagents under Cu catalysis. Miura and coworkers have developed conditions for the synthesis of aminated benzofurans and indoles ( Scheme 1.17) [24]. The transformation is operationally simple and proceeds at room temperature. The mechanism was probed and the authors concluded that the most plausible pathway is a nonradical electrophilic amination of the heteroarylcuprate species in the C—N bond‐forming step.
Similar intramolecular reactions can also take place with substrates containing unactivated terminal alkenes. In 2015, the Wang group (Duke University) reported the copper‐catalyzed vicinal diamination of unactivated alkenes with hydroxylamines that is both regio‐ and stereoselective. The first iteration of this reaction takes place on unsaturated amides and gives 4‐amino‐2‐pyrrolidones as the products ( Scheme 1.18) [25]. This transformation is considered to be the first metal‐catalyzed alkene 1,2‐diamination that enables the direct incorporation of an electron‐rich amino group.
In 2016, Wang and coworkers successfully expanded the substrate scope to include unsaturated carboxylic acids, which undergo amino‐lactonization under the reaction conditions ( Scheme 1.19) [26]. The overall transformation allows the practitioner to access quickly and efficiently a wide range of amino‐substituted γ‐ and δ‐lactones as well as 1,2‐amino alcohol derivatives, which are of significant value in the synthesis of natural products and active pharmaceutical ingredients.
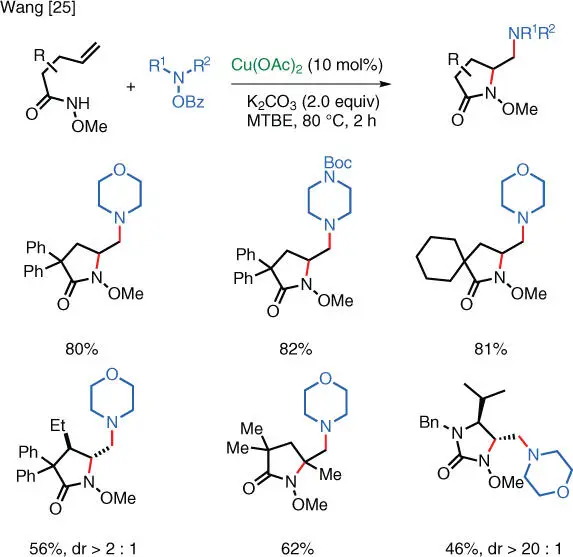
Scheme 1.18 Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic diamination.
Source: Modified from Shen and Wang [25].
An unusual case of ring‐opening amination of cyclopropanols has been reported by the Dai group [27]. In this reaction, a base‐initiated ring‐opening of cyclopropanol generates a carbanion nucleophile, which participates in the Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic amination and affords β‐aminoketones as products ( Scheme 1.20). The catalytic cycle involves the oxidation of the Cu(I) complex to the corresponding Cu(III) species by the hydroxylamine reagent. Next, the Cu(III) intermediate promotes the ring‐opening of the cyclopropanol substrate and the resulting copper‐homoenolate undergoes reductive elimination to form the new C—N bond and to regenerate the catalytically active Cu(I) species. Overall, the transformation proceeds under mild reaction conditions and it is also compatible with a number of sensitive functionalities such as esters, epoxides, and unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
With electron‐deficient arenes, direct C–H amination is also possible. Miura and coworkers have reported the Cu‐catalyzed direct C–H amination using benzoyl hydroxylamines as aminating reagents ( Scheme 1.21) [28]. Electron‐deficient aromatic substrates such as fluoroarenes, oxadiazoles, and thiazoles can be directly aminated to furnish the corresponding aryl and heteroaryl amines. The Yotphan group later expanded the substrate scope to include benzoxazoles [29], while the Li group applied the reaction to enable the C–H amination of quinoline N ‐oxide [30].
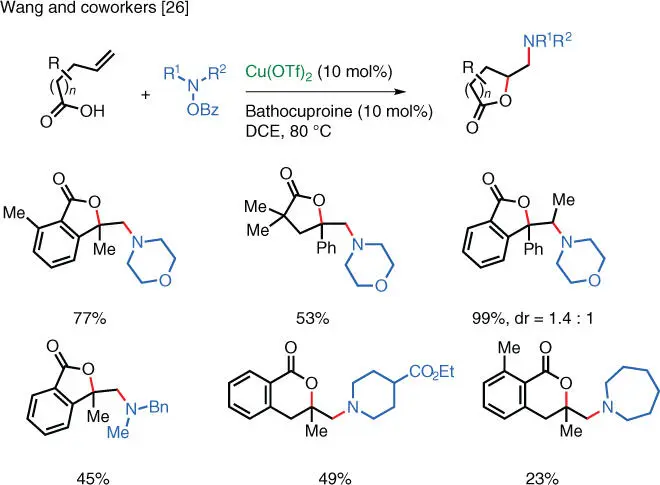
Scheme 1.19 Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic amino‐lactonization.
Source: Modified from Hemric et al. [26].
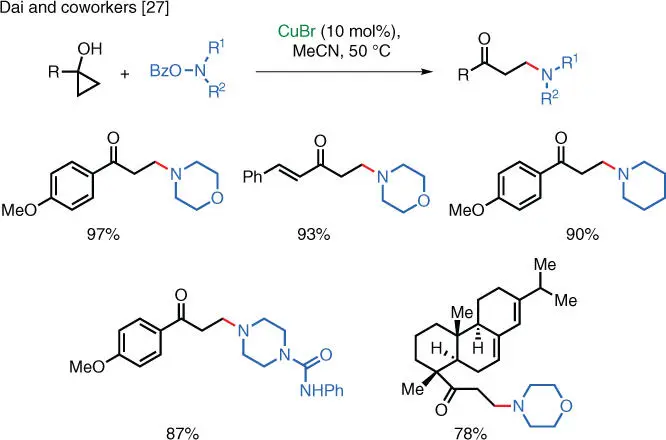
Scheme 1.20 Cu‐catalyzed ring‐opening amination.
Source: Modified from Ye and Dai [27].
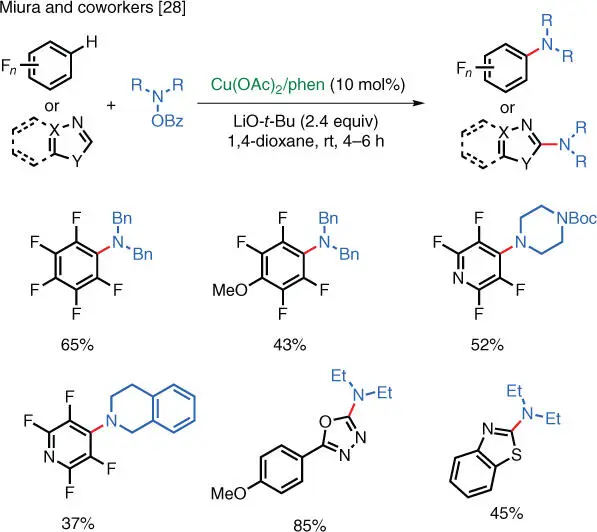
Scheme 1.21 Cu‐catalyzed C–H amination of heterocycles.
Source: Matsuda et al. [28].
1.3 Electrophilic Amination Reactions Catalyzed by Other Transition Metals
Although the current focus of TM‐catalyzed electrophilic amination is copper catalysis, other transition metal complexes are also capable of serving as catalysts in these reactions.
Complexes of both Ni and Co can catalyze the electrophilic amination of organozinc reagents. The reaction mechanism is similar to the Cu‐catalyzed reactions; that is, the N—O or N—Cl bond of the aminating reagent undergoes cleavage when the metal enters into it via oxidative addition. The Johnson [31], Jarvo [32], and Knochel [33] groups reported their findings in several publications ( Scheme 1.22).
J.‐Q. Yu and coworkers (The Scripps Research Institute) have successfully combined the Pd‐catalyzed C–H activation and electrophilic amination. Both sp 2( Scheme 1.23) and sp 3( Scheme 1.24) C—H bonds can be aminated with this process. Mechanistically, these reactions proceed via a Pd(II)/Pd(IV) cycle: after the C–H activation, the resulting Pd(II) complex oxidatively inserts into the N—O bond of the aminating reagent, which is followed by a reductive elimination to form the new C—N bond. In some cases, it is necessary to add a Ag(I) salt as a sacrificial oxidant to help establish the catalytic cycle [34, 35].
Читать дальше




















