The final Chapter 10addresses current applications of TM‐catalyzed aromatic amination in industrial settings by discussing a large number of case studies related to the manufacturing process of pharmaceutical compounds. In addition, with reference to the seminal work by Ullmann, Buchwald, and Hartwig, this contribution points on new concepts still at academic level, but either further extending the applicability of new methodologies, or on the brink of being industrially used. Also approaches with a focus on process intensification and sustainability (flow chemistry and catalyst immobilization) are presented, together with a view of the accompanying questions when applying the methodology of aromatic amination in the pharmaceutical industry. To make aware the reader about these challenges, themes such as the control of elemental impurities, the TM accounting, and the metal recycling are treated as well. Besides being a highly useful and up‐to‐date source of information on the TM‐catalyzed aromatic amination in industry, this contribution will hopefully provide inspiration for academic research in developing new methodologies amenable to industrialization.
We warmly thank all the distinguished scientists and their coauthors for their rewarding and highly instructive contributions. Without their effort, even more valuable considering it partially coincided with a difficult period at the international level, this volume would have not been possible. Grateful acknowledgments are also addressed to the Wiley‐VCH editorial staff, and in particular to Anne Brennführer, Aruna Pragasam, Elke Maase, and Katherine Wong, who encouraged us at project outset and helped us in a very competent manner in all the phases of the preparation of this book.
Alfredo Ricci and Luca Bernardi
Bologna
07 April 2020
1 Substitution‐type Electrophilic Amination Using Hydroxylamine‐Derived Reagents
Zhe Zhouand László Kürti
Rice University, Department of Chemistry, 6500 Main Street, Houston, TX, 77030, USA
Electrophilic amination is a class of organic reactions where C—N bonds are formed via the use of electrophilic aminating reagents [1–4]. Depending on the specific reaction pathway, electrophilic amination reactions can be classified either as substitution or addition. This chapter focuses on substitution reactions. Aminating reagents for the substitution‐type electrophilic aminations are essentially NR 2 +synthons, and the electrophilicity on the nitrogen atom is generally achieved by attaching a more electronegative functionality (X) to the nitrogen atom that can serve as a leaving group. Common structural motifs for this class of reagents include chloramines, hydroxylamines, and oxaziridines (i.e. cyclic hydroxylamine derivatives). Because of the safety hazards associated with the use of chloramines, recent developments in this area have been focused on the use of more stable hydroxylamine‐type reagents ( Scheme 1.1).
Substitution‐type electrophilic amination reactions can operate under either uncatalyzed or catalyzed conditions. The majority of catalytic substitution‐type electrophilic amination reactions are catalyzed by complexes of transition metals (TMs). In the uncatalyzed reactions, the carbon nucleophile directly attacks the electrophilic nitrogen atom and a new C—N bond is formed. In the TM‐catalyzed reactions, the transition metal first enters into the N—X bond via an oxidative addition, and the new C—N bond is formed after sequential ligand exchange and reductive elimination ( Scheme 1.2). The major difference between TM‐catalyzed substitution‐type electrophilic amination reactions and TM‐catalyzed C–N cross‐coupling reactions (i.e. Buchwald–Hartwig coupling) is the role of the nitrogen source: it acts as an electrophile in the former while as a nucleophile in the latter.
The majority of the literature in this area concerns the TM‐catalyzed versions of substitution‐type electrophilic amination. Therefore, they will be discussed first in this chapter.

Scheme 1.1 General structure of electrophilic aminating reagent.

Scheme 1.2 Mechanisms of two main types of electrophilic amination.
1.2 Cu‐Catalyzed Reactions
Narasaka and coworkers reported an early iteration of Cu‐catalyzed substitution‐type electrophilic amination of Grignard reagents utilizing O ‐sulfonyloximes as aminating reagents. The reactions can also give products without copper catalysis, albeit with much lower yields. Because of the nature of the aminating reagents, subsequent acidic hydrolysis is needed to convert the imine products to the desired amines [5, 6]. A similar amination process of organozinc reagents was reported by the Erdik group around the same time. In this case, in addition to the O ‐sulfonyloximes, the authors showed that the reaction can also proceed with methoxyamine when excess of the organometallic reagent was used ( Scheme 1.3) [7, 8]. These early reactions have several drawbacks that affect their utilizations, including a very limited substrate scope, low conversion rate due to many side reactions, and, most importantly, the need to use a strong acid to hydrolyze the initial imine products. The use of strong acidic conditions in the hydrolysis makes these procedures unsuitable for substrates containing acid‐labile functionalities.

Scheme 1.3 Early examples of Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic amination.
Source: Erdik and Ay [2] and Tsutsui et al. [5].
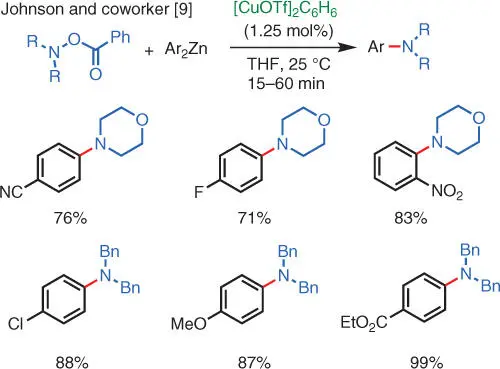
Scheme 1.4 Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic amination of organozinc reagents.
In 2004, the Johnson group at UNC reported the Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic amination of diorganozinc reagents using acyl hydroxylamines as aminating reagents [9]. This is the first report of Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic amination reactions that give tertiary amines as products ( Scheme 1.4). Compared to the O ‐sulfonyloximes, O ‐acyl hydroxylamines are more synthetically accessible and have better atom economy. A limitation, however, is that the nitrogen must be fully substituted (i.e. no acidic N—H bond is tolerated). In place of the diorganozinc substrate, this reaction can also use a Grignard reagent as the nucleophile, which is arguably more accessible and convenient to use [10].
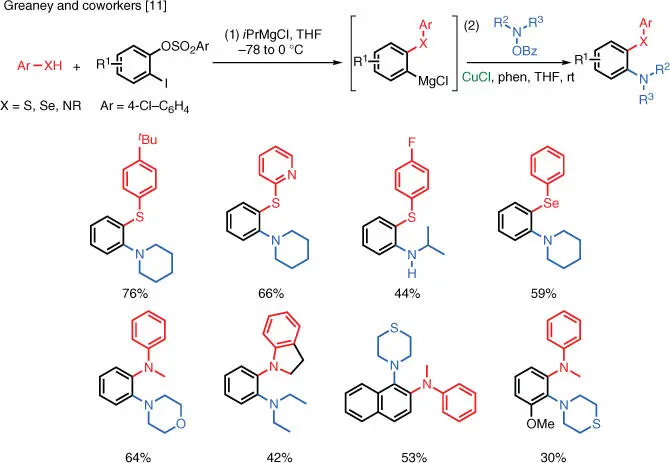
Scheme 1.5 Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic amination via aryne intermediate.
After the initial disclosure of Johnson and coworkers, subsequent research showed that other organometallic reagents can also serve as the nucleophile.
A unique reaction was reported by Greaney and coworkers at the University of Manchester in the UK [11]. In this case, an aryne intermediate is first generated in situ via iodine–magnesium exchange, followed by elimination. A nucleophile subsequently attacks the aryne, and the resulting arylmetal undergoes Cu‐catalyzed electrophilic amination with the hydroxylamine‐derived electrophilic aminating reagent to furnish aryl amines as the final products ( Scheme 1.5). This reaction gives access to unique aromatic products with a 1,2‐bis substitution pattern. The nucleophiles that can be used in this reaction include arylamines, thiophenols, and arylselenols. The overall transformation exhibits excellent regioselectivity; however, the isolated yield is lowered in those cases in which the reactants are sterically encumbered.
Читать дальше














