2Other applications include sterilization equipment, tobacco expansion applications, plasma etching of electronic chips (PFC-116) and as solvents in the manufacture of adhesive coatings and inks.
3PFC-14 (chemically CF 4) is used as a minor component of a proprietary blend. Its main use is for semiconductor etching.
4PFC-51-14 is an inert material, which has little or nil ability to dissolve soils. It can be used as a carrier for other solvents or to dissolve and deposit disk drive lubricants. PFCs are also used to test that sealed components are hermetically sealed.
Table 2.6Propene series isomers [10].
| Isomer |
Chemical formula |
Stereoisomer |
| IUPAC |
ACS |
| R-1234yc |
CH 2F-CF=CF 2 |
|
|
| R-1234zc |
CHF 2-CH=CF 2 |
|
|
| R-1234ye(E) |
CHF 2-CF=CHF |
Entgegen |
Trans |
| R-1234ye(Z) |
CHF 2-CF=CHF |
Zusammen |
Cis |
| R-1234ze(E) |
CF 3-CH=CHF |
Entgegen |
Trans |
| R-1234ze(Z) |
CF 3-CH=CHF |
Zusammen |
Cis |
| R-1234yf |
CF 3-CF=CH 2 |
|
|
IUPAC = International Union of Pure and Applied Chemists
ACS = American Chemical Society
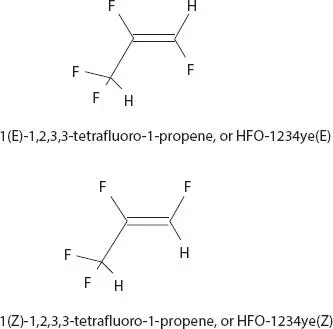
Figure 2.1Two examples of isomeric hydrofluorooelefin [10].
Halogenated olefins are a subset of halogenated organic [or carbon-containing] compounds. They have significantly shorter atmospheric lifetimes than their saturated counterparts. Examples include: CFC-11, CFC-12, BCFC-12B1, BFC-13B1, HCFC-22, HC-50, CFC-113, CFC-114, CFC-115, HCFC-123, HCFC-124, HFC-125, HFC-134a, HCFC-141b, HCFC-142b, HFC-143a, HFC-152a, HC-170, and FC-C318, and HFC-1234yf or HFO-1234yf.
2.4 Fluoropolymers and Fluoroelastomers
In this book the term fluoropolymer describes fluorinated polymers and copolymers of a few olefinic monomers that are consumed in significant commercial scale. These monomers include tetrafluoroethylene (CF 2=CF 2), vinylidene fluoride (CF 2=CH 2) and chlorotrifluoroethylene (CFCl=CF 2) and vinyl fluoride (CHF=CH 2). The polymers of the last two are produced at significantly lower volumes than the first two monomers but have been included because of the importance of their applications. Generally, an increase in fluorine content of polymer enhances the desirable properties for which fluorinated polymers are known (Table 2.7).
Fluoroelastomers consist of a number of high performance synthetic rubbers that are partially or fully fluorinated. Fluoroelastomers are made by copolymerizing various combinations of vinylidene fluoride (CH 2=CF 2), hexafluoropropylene (CF 2=CFCF 3), chlorotrifluoroethylene (CF 2=CFCl), and tetrafluoroethylene (CF 2=CF 2). These fluorinated elastomers have outstanding resistance to oxygen, ozone, and heat and to swelling by oils, chlorinated solvent, and fuels.
Table 2.7Effect of increasing fluorine content in polymers.
| Property |
Impact |
| Chemical resistance |
Up |
| Melting point |
Up |
| Coefficient of friction |
Down |
| Thermal stability |
Up |
| Dielectric constant |
Down |
| Dissipation factor |
Down |
| Volume and surface resistivity |
Up |
| Mechanical properties |
Down |
| Flame resistance |
Up |
| Resistance to weathering |
Up |
The inception of fluoropolymers as a group dates back to the serendipitous discovery of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in a DuPont laboratory by Roy Plunket. His research program was aimed at the discovery and development of new refrigerants. The initial testing of the waxy white powder found in a tetrafluoroethylene gas cylinder revealed something unusual. The powder had a high melting point, was insoluble and was unaffected by any chemical and intractable as a thermoplastic. Manhattan Project’s needs for chemical resistance materials led to the first application of PTFE.
Following the successful introduction of PTFE, produced in a pilot plant, into the processing equipment for uranium manufacturing and purification, interest in this plastic began gathering. The DuPont Company in West Virginia, USA in 1946 built the first commercial plant. The story of the development fluoropolymers has been covered, in detail, in other publications [12].
The basic properties of PTFE may be justifiably called extreme (Table 2.8). The properties and characteristics of PTFE include high chemical resistance, low and high temperature capability, resistance to weathering, low friction, electrical and thermal insulation, and low friction or slipperiness. One drawback of this polymer is its relative softness, compared to engineering polymers, resulting in cold flow and ease of abrasion both of which are undesirable for many applications. Fillers are incorporated in PTFE to enhance its hardness.
The first fluoropolymer PTFE was quite peculiar in that it would not flow upon melting. It could not be processed by typical melt processing techniques such as extrusion. Metal powder processing techniques were modified and adopted to fabricate parts from PTFE examples of which include modified compression molding, ram extrusion and paste extrusion. Afterward a number of melt processible fluoropolymers were developed in the decades since the Second World War [13, 14].
Table 2.8Fundamental properties of polytetrafluoroethylene.
| High melting point, 342°C |
| Exceptional thermal stability |
| Useful mechanical properties at extremely low and high temperatures (-260 to 260°C) |
| Insolubility |
| Chemical inertness |
| Low coefficient of friction |
| Low dielectric constant/dissipation factor |
| Low water ab/adsorptivity |
| Excellent outdoor weatherability |
| Flame resistance (limiting oxygen index = 95) |
| Exceptional Purity |
A whole family of thermoplastic polymers has been developed based on homopolymers and copolymers of tetrafluoroethylene (TFE). After PTFE the largest volume member is perfluorinated ethylene propylene copolymer (FEP). The second monomer in the FEP is hexafluoropropylene (CF 3-CF=CF 2), which is conveniently co-produced along with TFE in the monomer manufacturing process. Other important products included a copolymer of TFE with ethylene at a molecular ratio of 1:1 and TFE (ETFE) and perfluoroalky vinyl ethers (PFA and MFA).
The third largest volume family of fluoropolymers is based on vinylidene fluoride (VDF) hompolymers and copolymers. These thermoplastics are processed by normal melt processing techniques such as extrusion, film blowing and various molding methods. VDF is copolymerized with other monomers such as chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE). Both thermoplastics and elastomers can be prepared depending on the concentration of the CTFE in the copolymer. A new example is Arkema Corporation’s VDF copolymers containing a reactive group that allows its ease of bondability [15].
The important polymers based on CTFE are its homopolymer polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE) and its copolymer with ethylene. The latter chlorotrifluoroethylene ethylene copolymer (ECTFE) is the analog of ETFE. PCTFE is borderline melt processible and is considered somewhat difficult to process. This CTFE homopolymer degrades when it is heated in the air lead to rapid decrease in its molecular weight.
Читать дальше













