1 Power control mode: The shunt converter mainly controls reactive power (VAR) in the system. The reactive power demand decides the gate pulse of the converter, which allows current to flow. Continuous feedback closed-looped system ensures the desired current injection in the system.
2 Voltage control mode: With the help of the droop control method, the voltage regulation can be made automatically at the point of connection with reactive current regulation.
The power flow control system works for the shunt and two series compensators together. The desired active and reactive power flows (P s1and Q S1) are compared with the measured magnitudes (P s′ and Q′ S) and error is passed through an error amplifier to produce direct and quadrature components for series connected compensating voltages (e 2dand e 2q). The magnitudes of the voltage (E 2dq) at the output of VSC2 and VSC3 are calculated respectively by adding relative phase angle (β 1and β 2) [18]. The controllable range of active and reactive power flow can easily be determined with open loop control system with rated compensating voltage (E 2dq). The control system is illustrated in Figure 2.11.
Figure 2.12shows basic control system strategy for series converters. It corrects the magnitude of the load voltage by providing corrected magnitude and angle compared with reference value. The Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation (SVPWM) helps to transfer phase voltage reference to modulation time delay cycle. The closed loop system monitors V 1to apply appropriate corrections in the system.
Considering power demand calculation as:
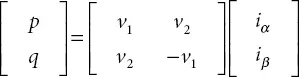
Where
p = Active power demand
q = Reactive power demand
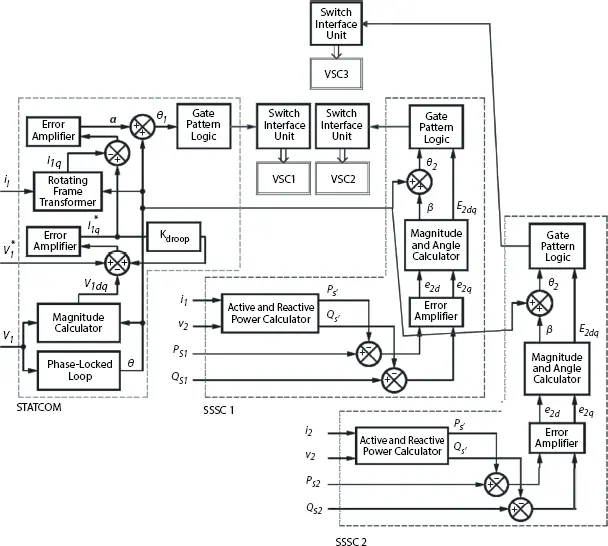
Figure 2.11 Basic control of GUPFC compensator logic.
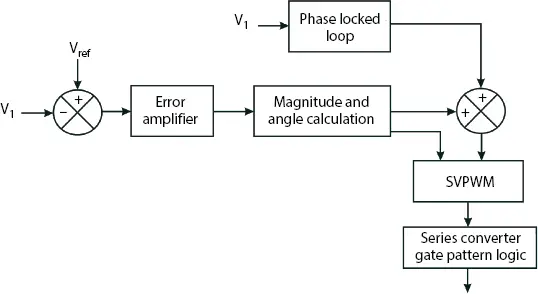
Figure 2.12 Basic control of series compensator logic.
v 1and v 2= Input voltage
i αand i β= Correction component.
The injected voltage angle can be calculated:
(2.16) 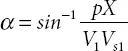
Figure 2.13indicates shunt converter pulse logic with basic control system. The reference voltage and current are compared with desired active and reactive power demand in the circuit. The shunt converter has ability to provide source or sink for system current.
Considering transformer admittance 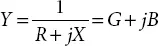 and bus volt age is V ∠ δ . The power injected using STATCOM can be shown to be [1]:
and bus volt age is V ∠ δ . The power injected using STATCOM can be shown to be [1]:
(2.17) 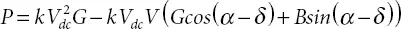
(2.18) 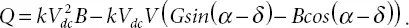
Where,
k = constant based on type of inverter (for six pulse converter 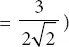 and Vdc ∠ α is veriable input voltage for transformer.
and Vdc ∠ α is veriable input voltage for transformer.
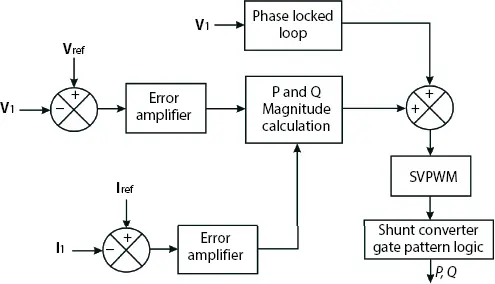
Figure 2.13 Basic control of shunt compensator logic.
2.5.2 Simulation of Active GUPFC With General Test System
The simulation study of active GUPFC system is carried out using MATLAB Simulink platform. MATLAB (matrix laboratory) is a multioptional numerical computing environment and programming language. It is developed by MathWorks Inc. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces and interfacing with programs written in other languages, including C, C++, Java, Fortran and Python. An additional package, Simulink, adds graphical multi-domain simulation and Model-Based Design for dynamic and embedded systems. The simulations carried out with the following conditions and assumptions:
1 Hardware: Intel Core i5 2,450 M CPU, 2.5 GHz, 4 GB RAM with Win 7, 64 bit OS.
2 Software: MATLAB Simulink (7.10.0.499) 2010a release
3 Simulation time: 3.00 s
4 Simulation solver: ode23tb (stiff/TR-BDF2)
5 Simulation type: Variable step
6 Simulation relative tolerance: 1e−3: 0.001
The active GUPFC is simulated for the simplified general test system as shown in Figure 2.14. The test system parameters presented in the Appendix. With a grid connection, the system uses power for load feeders, whereas the system without grid connection continues to supply power to TPS auxiliaries using active GUPFC. Hence a load of TPS auxiliaries is always taken care of by active GUPFC.
The system illustrated above is simulated for two phases to a ground fault with phases A and B (R and Y) and phases B and C (Y and B) using MATLAB Simulink. The simulation conducted without GUPFC, with GUPFC and with active GUPFC for common test conditions. The combined result is plotted with load voltage against time and illustrated in Figure 2.15. The sequence of events is as shown in Table 2.2.
2.5.3 Simulation of Active GUPFC With IEEE 9 Bus Test System
With IEEE 9 bus test model, as shown in Figure 2.16, various fault conditions such as three-phase to ground fault and single-phase to ground fault are simulated with and without grid connection using MATLAB simulation, as illustrated in Figure 2.17. The results are presented for test cases with and without GUPFC, with and without fuel cell (distributed generation) and with active GUPFC. Three-phase to ground fault shown from 1.0 to 1.5 s on time axis whereas single phase to ground fault shown between
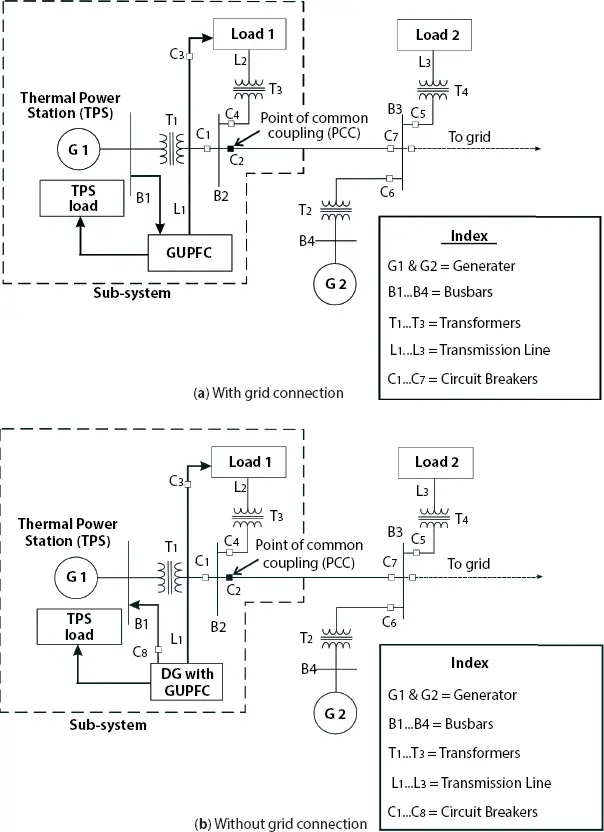
Figure 2.14 Simplified test system.
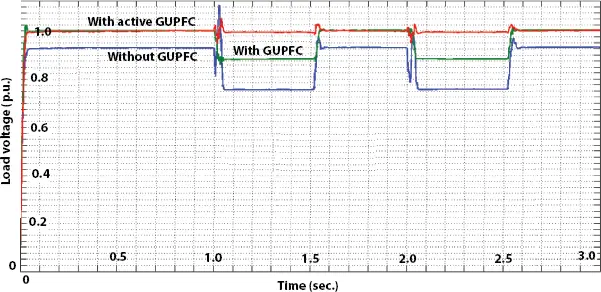
Figure 2.15 Test system simulation.
Table 2.2 Test system simulation events.
| S. No. |
Time (s) |
Event |
| 1 |
0.00 |
Start |
| 2 |
1.00 |
Fault on A and B phases |
| 3 |
1.02 |
CB opens (disconnect sub-system from main system) |
| 4 |
1.50 |
Fault Clear |
| 5 |
1.52 |
CB close (connects sub-system to main system) |
| 6 |
2.00 |
Fault on B and C phases |
| 7 |
2.02 |
CB opens (disconnect sub-system from main system) |
| 8 |
2.50 |
Fault Clear |
| 9 |
2.52 |
CB close (connects sub-system to main system) |
| 10 |
3.00 |
End |
2.5.3.1 Test Case: 1—Without GUPFC and Without Fuel Cell
Читать дальше

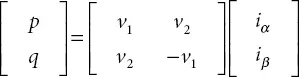


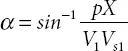
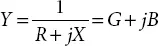 and bus volt age is V ∠ δ . The power injected using STATCOM can be shown to be [1]:
and bus volt age is V ∠ δ . The power injected using STATCOM can be shown to be [1]: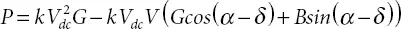
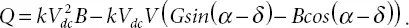
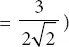 and Vdc ∠ α is veriable input voltage for transformer.
and Vdc ∠ α is veriable input voltage for transformer.












