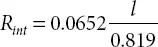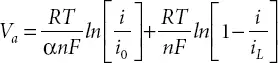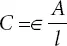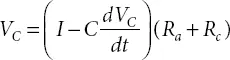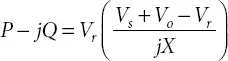I = Cell current (Amp)
R int= Internal resistance between electrodes which is given by:
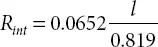
l = Length between two electrodes (Meter)
V a= Summation of activation voltage drop and concentration voltage drop (Volt) which is expressed by:
(2.4) 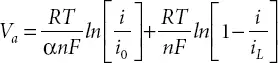
α = Electron transfer co-efficient
i = Current density (A/m 2)
i 0= Exchange current density (A/m 2)
i L= Limiting current density (A/m 2)
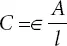
є = Electrical permittivity of electrolyte
A = Effective surface area between electrodes and electrolyte (sq. meter). It is very large due to corrugated porous surface of the electrodes.
l = Distance between two layers of electrodes. It is very small (nanometer).
V C= Voltage across the Capacitor ‘C’. It is given by:
(2.5) 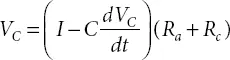
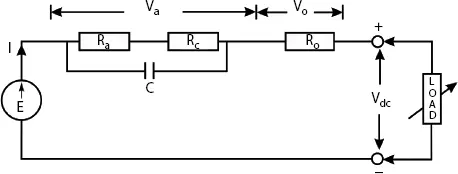
Figure 2.4 PAFC equivalent circuit.
There are three operating regions for this fuel cell. The first region is activation region where the voltage drop is due to the slowness of the chemical reactions at electrode. It is considered as R a. The second region represents the ohmic losses due to the internal resistance of the fuel cell. It is represented by R o. The third region represents the change in concentration of reactants as the fuel is used. It is represented by R c. By considering these three operating regions of fuel cell, an equivalent DC circuit model is obtained as shown in Figure 2.4.
2.3 Power Flow Management in Microgrid
The transfer capacity of the existing transmission lines is an important operational constraint on interconnected A.C. transmission network. To improve this capacity of the transmission line, one has to use the FACTS controllers. These controllers are known for their applications in improving power transfer capacity and power flow control using the existing infrastructure of a transmission utility as well as improving transient stability. In addition to these controls, FACTS controllers advantageously employed for transient stability improvement, power oscillation damping and voltage stability. With the FACTS controller, the transmission line capacity can be improved by 40 to 50% as compared to conventional mechanically-driven devices. Lower maintenance required for FACTS controllers improves effi-ciency in operation [1].
The FACTS controllers connected to the transmission line have following basic types depending on connection:
1 Series controllers:It has variable impedance and has a function to inject series voltage.
2 Shunt controllers:It has variable impedance and has a function to inject current in the system.
3 Combined series–series controller:It has separate but coordinated unified (common DC bus) controllers and can compensate reactive power as well as interline transfer active power.
4 Combined series–shunt controller:It can inject voltage and current and has unified and coordinated real power exchange between series and shunt controllers.
The UPFC, as shown in Figure 2.5, invented in 1991, is a real-time multi-functional dynamic compensator for the AC transmission line. It can control active and reactive power as well as voltage and VAR compensation. It also can improve the power quality of the associated system. Thus UPFC can control output voltage V oand its angle ρ (0 ≤ ρ ≤ 2π) [1]. The operation of UPFC depends on types of voltage source converters. The shunt converter is Static Compensator (STATCOM) and series compensator is Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) [1]. The STATCOM is a static, shunt connected compensator which can control current independent of system voltage with the help of capacitor or inductor. In UPFC, capacitor-based current compensation considered. Hence depending on the system requirement, leading current can be injected in the system with the help of a capacitor connected to the common DC bus. It absorbs active power for charging the capacitor. So it has the role of Static Synchronous Generator (SSG) and Static VAR Generator (SVG). The SSSC is a series-connected compensator which can control series injected voltage. The magnitude of the series injected voltage is low. Still, the converter can change the voltage angle regarding sending end voltage, resulting in a change in receiving end voltage magnitude and angle depending on the system requirements.
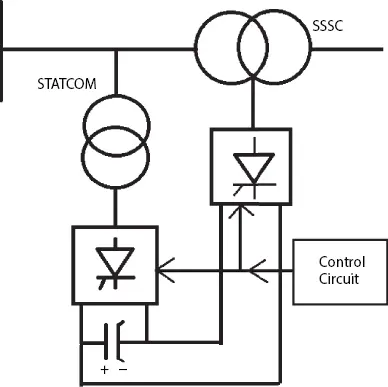
Figure 2.5 Basic UPFC.
If the compensator connected with the energy storage capacitor, then it can absorb active power too. The transmitted power P and reactive power −jQ can be expressed by:
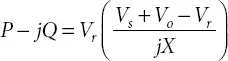
2.4 Generalized Unified Power Flow Controller (GUPFC)
The basic circuit of a GUPFC developed by Fardanesh in the year 2000 is shown in Figure 2.6. It inferred from the figure that it is a combination of UPFC and Interline Power Flow Controller (IPFC). There is one shunt connected converter (STATCOM) and multiple series-connected converters (SSSC). The series converters and shunt converter are connected to a common capacitor to form the DC bus. The shunt converters and the series converters act as a synchronous voltage source (SVS). These converters can generate reactive power at their terminals. Free exchange of real power is possible because of common DC link. The real power demand is fulfilled by shunt converter, which at the same time can absorb or supply controllable reactive power and exchange the same with series converters. The series converters can individually inject a voltage to the appropriately connected feeder whose magnitude and phase angle can be varied to obtain the desired voltage output. Thus the series converters act as a series compensation device. It means that the overloaded feeder lines can be balanced and any surplus power utilized by other feeders or common DC link [1, 12, 13].
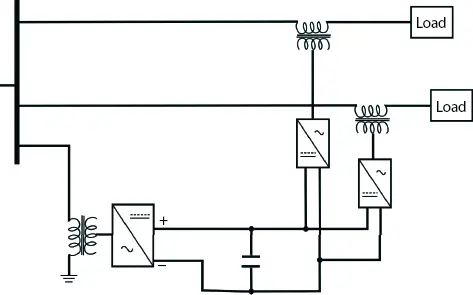
Figure 2.6 Basic GUPFC.
2.4.1 Mathematical Modeling of GUPFC
The basic circuit shown in Figure 2.6is considered here for modeling. The development is based on the fundamental frequency model of UPFC which is presented in Refs. [14] and [15]. The basic concept of UPFC has briefly explained already in this section. Modeling aims to determine the relationship between unified DC bus voltage and injected voltage. A three-phase, PWM controlled voltage source inverter is typically made of six controlled switches (GTO valves with six anti-parallel diodes) switched on and off at very high frequency around 5 kHz. The model considered a stable voltage condition for fundamental frequency voltage sources. One source is connected in parallel while the other connected in a series branch.
Читать дальше