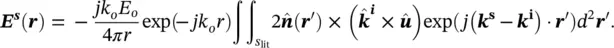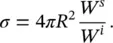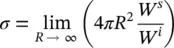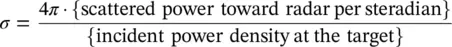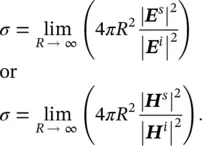Caner Ozdemir - Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging With MATLAB Algorithms
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Caner Ozdemir - Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging With MATLAB Algorithms» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging With MATLAB Algorithms
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging With MATLAB Algorithms: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging With MATLAB Algorithms»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
covers in greater detail the fundamental and advanced topics necessary for a complete understanding of inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) imaging and its concepts. Distinguished author and academician, Caner Özdemir, describes the practical aspects of ISAR imaging and presents illustrative examples of the radar signal processing algorithms used for ISAR imaging. The topics in each chapter are supplemented with MATLAB codes to assist readers in better understanding each of the principles discussed within the book.
This new edition incudes discussions of the most up-to-date topics to arise in the field of ISAR imaging and ISAR hardware design. The book provides a comprehensive analysis of advanced techniques like Fourier-based radar imaging algorithms, and motion compensation techniques along with radar fundamentals for readers new to the subject.
The author covers a wide variety of topics, including:
Radar fundamentals, including concepts like radar cross section, maximum detectable range, frequency modulated continuous wave, and doppler frequency and pulsed radar The theoretical and practical aspects of signal processing algorithms used in ISAR imaging The numeric implementation of all necessary algorithms in MATLAB ISAR hardware, emerging topics on SAR/ISAR focusing algorithms such as bistatic ISAR imaging, polarimetric ISAR imaging, and near-field ISAR imaging, Applications of SAR/ISAR imaging techniques to other radar imaging problems such as thru-the-wall radar imaging and ground-penetrating radar imaging Perfect for graduate students in the fields of electrical and electronics engineering, electromagnetism, imaging radar, and physics,
also belongs on the bookshelves of practicing researchers in the related areas looking for a useful resource to assist them in their day-to-day professional work.

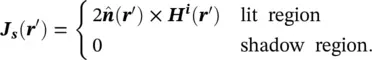
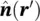 is the outward unit vector of the illuminated object's surface. The vector r ′is defined from the origin to any point on the illuminated surface ( S lit) of the object. The scattered electric field at the far‐field region along the observation vector of ris given by
is the outward unit vector of the illuminated object's surface. The vector r ′is defined from the origin to any point on the illuminated surface ( S lit) of the object. The scattered electric field at the far‐field region along the observation vector of ris given by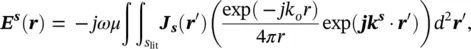
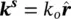 is the wavenumber vector in the scattering direction. Putting Eq. 2.3into 2.4will yield the scattered field equation in terms of the incident electric field as
is the wavenumber vector in the scattering direction. Putting Eq. 2.3into 2.4will yield the scattered field equation in terms of the incident electric field as