The world today is increasingly technological in many ways. Yet, while scientific and technical breakthroughs remain important, it’s connecting the dots from invention to innovation to the betterment of humanity and our ecosphere that has become increasingly critical. Whether it’s climate change or water management or space exploration or global healthcare, a technological breakthrough is just the first step. Further requirements can include prototyping and validation, system or ecosystem integration, intellectual property protection, supply/value chain set‐up, manufacturing capacity, regulatory and certification compliance, market studies, distribution channels, cost estimation and revenue projection, environmental sustainability assessment, and more. The time, effort, and funding required for realizing real‐world impact dwarfs what was expended on the invention. There are no generic answers to the big‐picture questions either; the considerations vary by industry sector, technology area, geography, and other factors.
Volumes in the series will address related topics both in general—e.g., frameworks that can be applied across many industry sectors—and in the context of one or more application domains. Examples of the latter include logistics and transportation, smart cities and infrastructure, energy and environment, and biomedicine and healthcare. The series scope also covers the role of government and policy, particularly in an international technological context.
With 30 years of corporate experience behind me and about five years now in the role of leading a Management of Technology program at a university, I see a broad‐based need for this series that extends across industry, academia, government, and nongovernmental organizations. We expect to produce titles that are relevant for researchers, practitioners, educators, and others.
I am honored to be leading this important and timely publication venture.
Tariq Samad
Senior Fellow and Honeywell/W.R. Sweatt Chair in Technology Management
Director of Graduate Studies, M.S. Management of Technology
Technological Leadership Institute | University of Minnesota samad@ieee.org
Section I Introduction
1 Demystifying the Impacts of the Fourth Industrial Revolution on Logistics : An Introduction
Mac Sullivan
NNR Global Logistics, Dallas, TX, USA
Introduction
Future of Work in the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Throughout history, during periods of agricultural and industrial reform, society was worried that most of its population will be out of a job as a new technology is developed (Manyika et al. 2017). These fears are reinforced by documented events in modern history where technology has led to mass layoffs. A transition from a post‐industrial era into a knowledge era has brought forth the same old argument that automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are going to cause widespread disruption. Until this point, white‐collar job has been dominated by the technologies created in the past four decades with the rise of the personal computer, Internet, and widespread business software applications. There has not been a large shift in the business‐to‐business (B2B) world in terms of reallocation of white‐collar labor resources and skillsets, which is surprising given the pervasiveness of mobile, e‐commerce, and sharing economy trends that are driving consumer behavior.
Some signals show that the world is at the brink of a new technological revolution, now referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), where the convergence of new and old technologies promises to redefine and transform the future of work and more. The intricacy and extent to which this transformation will happen will be unlike anything that has previously occurred (Schwab 2015). Implementing and realizing the results of the technologies laid out in the 4IR remain theoretical outside a few select companies. However, breakthroughs in AI and machine learning are poised to have a direct impact on our daily lives (Lee 2018). In some ways, the 4IR is a continuation of digitalization brought about by the Third Industrial Revolution as seen in Figure 1.1. However, it is unique in how it is blending the physical and cyber worlds through the prevalence of several technologies: Internet of Things (IoT) devices, cheaper cloud computing, AI, and automation (Marr 2018).
The computerization of rote tasks once done by clerks, the displacement of traditional business models through platform software application and websites, and the automation of manufacturing and physical movement of goods were all witnessed in most parts of the developed world in the early twenty‐first century. Looking toward the future, by 2022, companies have the potential to boost revenues by nearly 40 % by investing in AI and human partnership that would translate to $800 billion in new profitability (Simkin 2016). What the steam engine was able to do in decades for muscle power, computers, and digital automation was done for brain power by fundamentally reshaping the way that we think and the environment we operate in (Brynjolfsson and McAfee 2014). Much like its predecessors, the 4IR is changing the way that humans interact with the world and opening new opportunities for businesses to optimize their workflows.
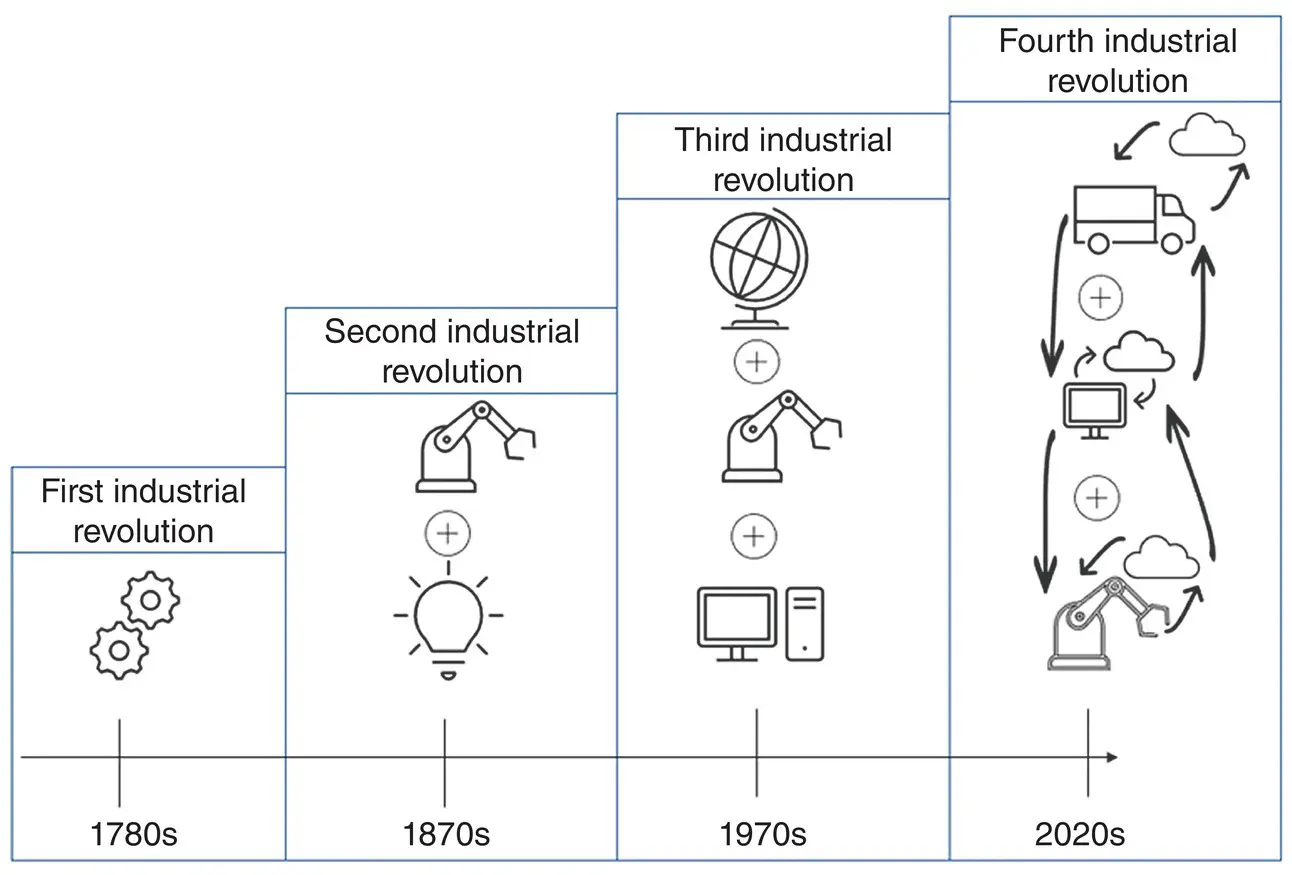
Figure 1.1 The Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In his book, Hit Refresh , Microsoft's CEO Satya Nadella states that the origin of the 4IR can be identified by “A confluence of three breakthroughs—Big Data, massive computing power, and sophisticated algorithms,” and that it is “accelerating AI from sci‐fi to reality” (Nadella et al. 2017). Previously, Thomas Friedman had pointed out that the world is much flatter than it used to be as a result of the outsourcing of not only physical labor but also, with the adoption of new technology, white‐collar labor (Friedman 2007). With such a quickly evolving landscape, it is important to note that the way companies adopt these technologies will have significant impacts on their communities, company structure and strategy, and ultimately their future. While robotic process automation (RPA) and AI are not necessarily novel concepts, downstream consumer demand, consultant‐driven media blitz, and subsequent executive exploration give insight into where the B2B service sector is headed.
The Role of Digital Transformation
To take advantage and participate in the 4IR, many companies now find themselves in a position where they need to undergo what many are calling a “digital transformation.” Digital transformation can be explained as the shift in work, jobs, and products through the use of technology in a company or the operational context of that company (Parviainen et al. 2017). Transformations driven by technological advancements have a history of being stalled as governments struggle to determine the policy to control them, companies lack resources to take advantage of them, or the labor force is not equipped to use them. Strong economic activity since 2008 has helped to sustain global economic growth, and corporate coffers had been full heading into the COVID‐19 era. To evaluate the potential repercussions of 4IR, it is worthwhile to explore how some companies have already embraced these technologies and engrained them into their core business models.
Hub Economy Companies Leading the Way
Technological leadership has been spearheaded by a group of hub economy companies that do not operate by trying to compete on legacy products and services. These companies whose valuations now compare with some of the largest governments in the world use their vast networks in certain domains and then transfer those assets to redesign the competitive landscape of new domains and markets (Marco and Lakhani 2017). Hub economy companies like Amazon, Alibaba, and Alphabet are changing the way that value is created and gaining market share at a disproportionate and accelerated manner (Marco and Lakhani 2017). Grown out of the Third Industrial Revolution, these companies are exemplifying the potential of the 4IR as they innovate, grow exponentially, and leverage multiple forms of technology along the way.
Читать дальше













