1.5.2 Information Systems in Power Grids
The power grid transmits and distributes electrical power generated from primary fossil or renewable energy resources, such as coal or wind. Computers and networks manage, monitor, protect, and control the continuous real‐time delivery of electrical power. Figure 1.18depicts a view of key characteristics of Smart Grid compared with traditional power grid.
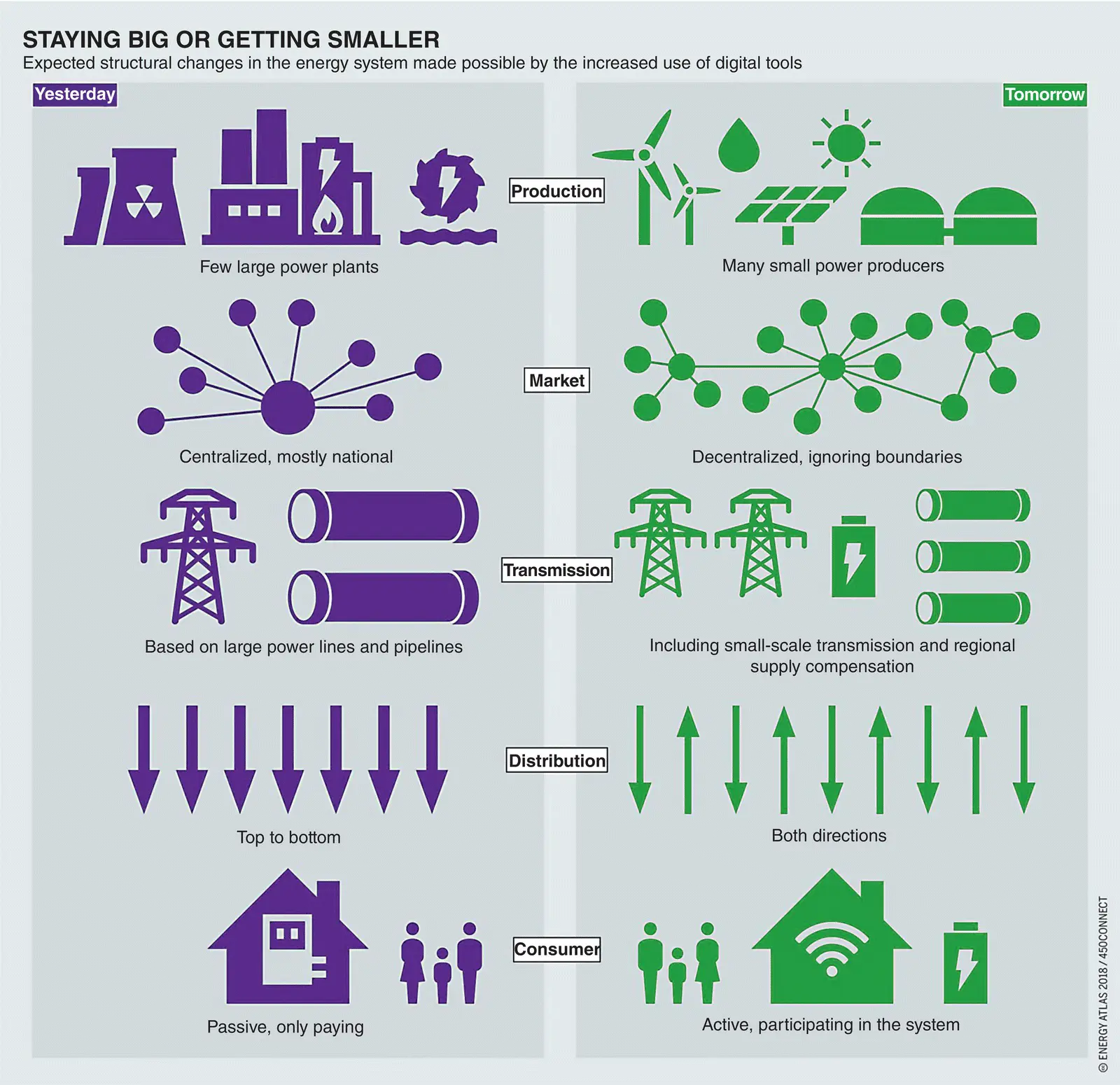
Figure 1.18 Smart Grid characteristics vs. traditional power system.
Source: [Bartz/Stockmar]. Licensed under CC BY‐SA 4.0.
A Smart Grid system may include IT, which is a discrete system of electronic information resources organized for the collection, processing, maintenance, use, sharing, dissemination, or disposition of information. A Smart Grid system may also consist of operational technologies (OT) or ICS, which comprise several types of operational and control systems, including SCADA systems, DCS, and other control system configurations such as skid‐mounted PLC that are often found in the industrial sectors and critical infrastructures [NISTIR 7628r1].
The Smart Grid has great potential for driving innovation in the ways electricity is produced, managed, and consumed. As described in [OECD 2012b], applications of ICTs and especially the opportunities provided by the Internet can help sustain electricity supply while limiting environmental impacts. In a Smart Grid, ICTs estimate the operational state with the vision of surviving a cyber incident while sustaining critical energy delivery functions and optimized power flow for economic and efficient generation dispatch. ICTs are seen as promoting a wider integration of renewable energy sources, promoting low‐carbon transport options including EVs, and inducting structural shifts in electricity consumption [OECD 2012d].
The Smart Grid is a particular application area expected to help tackle a number of structural challenges that global energy supply and demand are facing. Technologies and the use of data enable improved and more accurate information about the availability, price, and environmental impacts of energy, thereby empowering producers and consumers to make more informed energy conservation choices.
The Internet especially gives rise to a new generation of businesses providing services around electricity, adding further value and innovation to the energy sector value chain. The transition to a modern grid requires the adoption of advanced technologies, such as smart meters, automated feeder switches, fiber‐optic and wireless networks, storage, and other new hardware. These devices require a new communication and control layer to manage a changing mix of supply resources and provide new services.
Figure 1.19shows a simplified view of the energy sector value chain. However, information gaps may affect the Smart Grid outcomes.
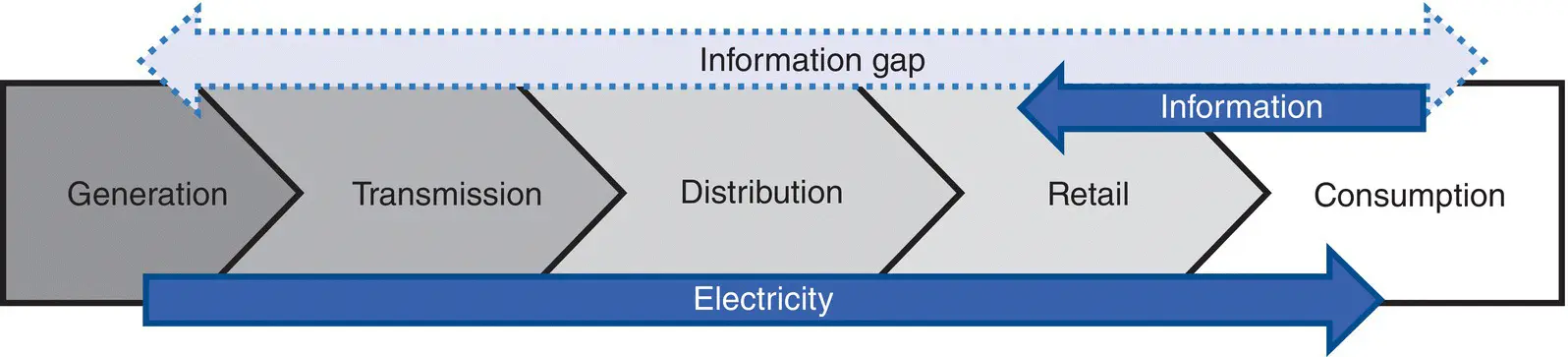
Figure 1.19 Stylized electricity sector value chain.
Source: [OECD 2012b]. © 2012, OECD.
Figure 1.20depicts an overview of the ICTs for different domains (generation, transmission, distribution, customer) and customer areas (industrial, building, residential).
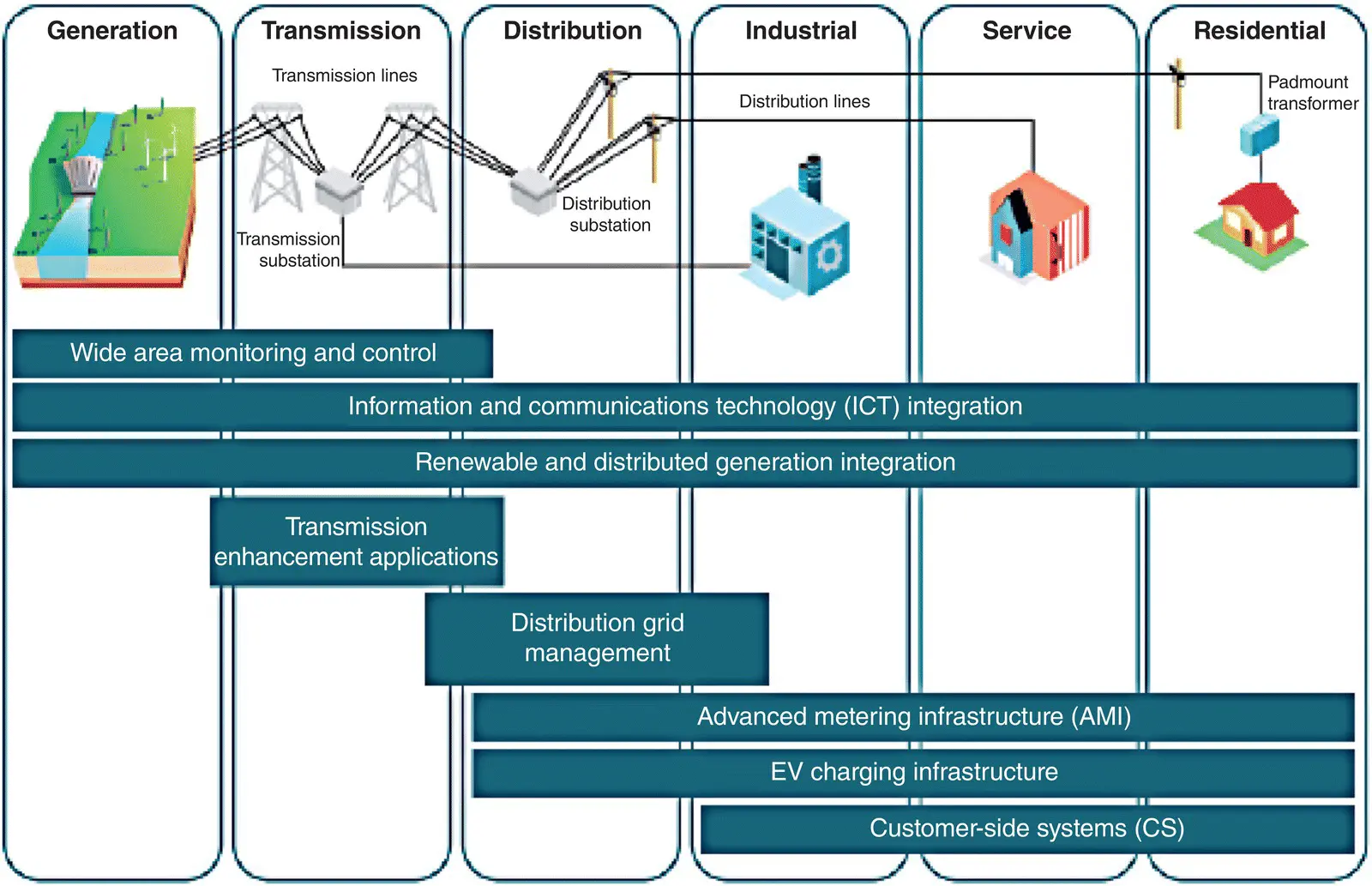
Figure 1.20 ICT application domains in the Smart Grid.
Source: [OECD 2012b]. © 2012, OECD.
ICTs and Internet applications are essential to modernization of the electric power grid in every domain. A summary of electricity challenges and ICTs addressing these challenges is shown in Table 1.3.
Table 1.3 Electricity sector challenges and potential ICT applications.
Source: [OECD 2012b]. © 2012, OECD.
| Electricity sector challenges |
ICT applications |
| Generation |
| Renewable energy generation |
Smart meters Vehicle‐to‐grid (V2G) and grid‐to‐vehicle (G2V) |
| Distributed, small‐scale electricity generation |
Virtual power plants Vehicle‐to‐grid (V2G) and grid‐to‐vehicle (G2V) Smart meters |
| Transport (transmission and distribution) |
| Transmission and distribution grid management |
Sensor‐based networks Embedded systems and software Integrated software systems and application programming interfaces (APIs) Smart meters Communication protocols, including machine‐to‐machine communications (M2M) |
| Storage |
| Storage capacities (physical and logical) |
V2G, G2V and vehicle‐to‐home (V2H) Smart meters End‐user interfaces |
| Retail |
| Dynamic and real‐time pricing for electricity consumption and distributed generation |
Smart meters End‐user interfaces |
| Consumption |
| Electricity conservation and energy efficiency |
End‐user interfaces Smart meters Electricity data intelligence |
| Demand management (automated) |
End‐user interfaces Smart meters Communication protocols including M2M Smart building technologies Smart electronic devices Data centers and cloud computing |
| Integration of electric vehicles and renewable sources |
End‐user interfaces Smart meters V2G, G2V Communication protocols including M2M Integrated software systems and APIs |
| Facilitate access to electricity in developing countries (electrification) |
|
1.5.3 DER Information Systems
As DERs are used in the Smart Grid, a brief overview of DER systems helps security engineers and control engineers to understand the scope of DER tasks before planning for security protection. Examples of DER information systems (called also DER systems) that are used for DER operations and other tasks include the following:
Wide area situational awareness encompasses monitoring and display of power system components and performance across interconnections and over large geographic areas in near real time. The goals of situational awareness are to understand and ultimately optimize the management of power network components (including DERs), behavior, and performance, as well as to anticipate, prevent, or respond to problems before disruptions can arise.
Cybersecurity management encompasses measures to ensure the protection of information, control systems, IT systems, and telecommunication infrastructures that support DERs.
Network management includes monitoring, reporting, and control of communications; for example, DER systems use a variety of public and private communication networks, both wired and wireless; the identification of performance metrics and core operational requirements of different applications is also critical to the Smart Grid.
DR management and automation is focused on maximizing performance of DERs and PEVs; automation of distribution systems becomes increasingly more important to the efficient and reliable operation of the overall power system; the benefits of distribution management include increased reliability, reductions in peak loads, and improved capabilities for managing distributed sources of renewable energy.
Energy storage management systems include means of storing energy, directly or indirectly, data acquisition, controls of communications, and security protections.
Читать дальше















