Apart from the prosthetic aspects, sufficient horizontal and vertical volume is also essential for long-term esthetic soft-tissue stability. Where soft-tissue deficiencies exist, appropriate augmentation procedures may be required for comprehensive rehabilitation. Recent advances in implant dentistry have provided clinicians with various treatment options to treat peri-implant soft-tissue defects. At the same time, though, soft-tissue grafting procedures are of moderate to high complexity and may be associated with a significant risk of complications. For this reason, various step-by-step procedures have been outlined and illustrated by individual case descriptions for the reader of this book.
The aim of this ITI Treatment Guide is to foster awareness of the increasing demands on clinicians to provide treatment for a growing population of patients with soft-tissue related problems. The authors hope that Volume 12 will be a valuable resource and reference work for the treatment of patients with mucogingival deformities to reduce the risk of biological and esthetic complications and to ensure predictable and stable long-term results.
2 Importance of the Peri-Implant Soft Tissues
A. Sculean
Dental implants are anchored in jawbone via direct contact between the bone and the implant, a phenomenon called osseointegration (Albrektsson and coworkers 1981). Emerging evidence indicates that the long-term success and survival of implants does not depend solely on osseointegration, but also on the soft tissues around the transmucosal aspect of the implant that separate the peri-implant bone from the oral cavity. This soft-tissue seal or collar is also called the peri-implant mucosa (Lindhe and coworkers 2008). The attachment of the soft tissue to the implant serves as a biological seal that ensures healthy conditions and prevents the development of peri-implant infections (peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis). Consequently, the peri-implant soft tissues play a crucial role for long-term implant survival (Lindhe and coworkers 2008).
The soft tissue around teeth develops during tooth eruption and seals the supporting tissues (the alveolar bone, periodontal ligament, and cementum) against the oral cavity (Bosshardt and Lang 2005). The peri-implant mucosa forms after traumatizing the oral soft and hard tissues to accommodate osseointegrated implants. The following presents a brief description of the most important anatomical features of the periodontal and peri-implant tissues.
Structure of periodontal tissues in health
The periodontium comprises the tissues supporting the teeth: the tooth-facing part of the gingiva , the root cementum , the periodontal ligament , and the part of the alveolar process that lines the tooth socket, termed alveolar bone (Schroeder and Listgarten 1997) (Figs 1 to 5).
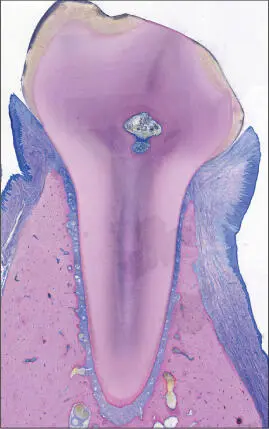
Fig 1 Photomicrograph. Tooth with a healthy periodontium. Supporting tissues of the tooth consisting of the root cementum, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone, and gingiva.
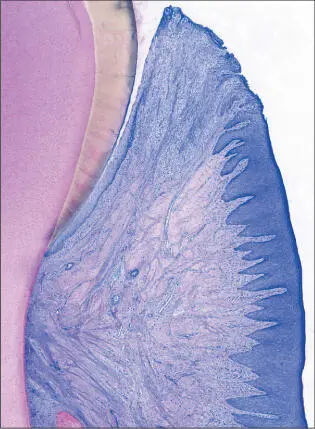
Fig 2 Photomicrograph. Supra-alveolar soft tissue consisting of the oral sulcular epithelium, junctional epithelium, and connective-tissue attachment (collagen fibers inserting into the root cementum). The junctional epithelium ends at the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) at the point of the insertion of the collagen fibers into the root cementum.
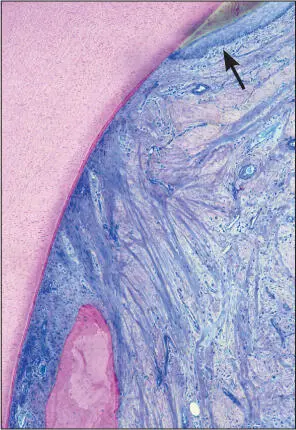
Fig 3 Higher magnification. Supra-alveolar soft tissue comprising the junctional epithelium and root cementum with inserting collagen fibers. Well-encapsulated minor inflammatory cell infiltrate (arrow) located adjacently to the junctional epithelium.
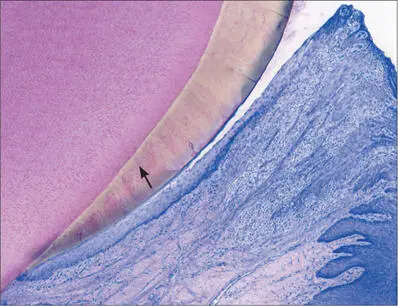
Fig 4 Higher magnification. Oral sulcular epithelium and junctional epithelium. The apical extension of the junctional epithelium ends at the cementoenamel junction. The well-encapsulated inflammatory cell infiltrate (arrow) is clearly distinguishable next to the junctional epithelium.
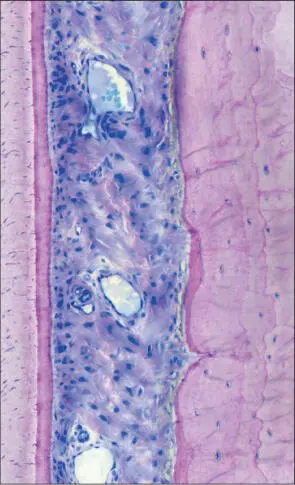
Fig 5 Higher magnification. Intact periodontal ligament connecting the root cementum with the alveolar bone. The collagen fibers invest in both root cementum and alveolar bone.
As they develop, the teeth penetrate the epithelial lining of the oral cavity and then persist as transmucosal organs. Their root portion is anchored in the bone, while the crown resides in the oral cavity. The most important function of the gingiva is to protect the underlying soft and hard connective tissues from penetration by microorganisms from the oral cavity. The gingiva terminates coronally at the gingival margin; apically it ends at the mucogingival junction or becomes continuous with the mucosa of the hard palate. The gingival sulcus has an approximate depth of 0.5 mm; however, in a completely healthy situation, it may not be clinically detectable (Schroeder and Listgarten 1997).
The interdental region contains a structure called the gingival papilla . The gingiva consists of two parts, the free gingiva and the attached gingiva . The free gingiva comprises the coronal portion of the gingiva and follows the contour of the cementoenamel junction, varying in width between 1 and 2 mm (Ainamo and Löe 1966). Its apical boundary is accentuated by a stippled line; a gingival groove may also be present. The attached gingiva stretches between the end of the free gingiva and the alveolar mucosa, or the mucosa of the floor of the mouth. Because the palatal mucosa extends to the free gingiva, there is no attached gingiva in the palate. The width of the attached gingiva may range from 1 to 10 mm (Ainamo and Löe 1966).
Junctional epithelium
The junctional epithelium is a non-keratinized epithelium that, due to its unique structural and functional adaptation, plays a critical role in maintaining periodontal health by providing a functional barrier to microbial challenges. Cell division occurs in the basal layer facing the lamina propria, while the innermost cells constitute the epithelial attachment . It consists of the basal lamina and hemidesmosomes that connect the epithelial cells with the tooth surface (Bosshardt and Lang 2005).
Connective tissue of the gingiva
The connective tissue of the gingiva consists mainly of fibroblasts exhibiting phenotypes that differ from those from the periodontal ligament (Bartold and coworkers 2000). They are arranged as groups of collagen fibers with a complex three-dimensional architecture that allows polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) and mononuclear cells to migrate through the connective tissue until they can pass the basement membrane bordering the junctional epithelium. Even in clinically healthy circumstances, an inflammatory cell infiltrate will be present and can be considered a common (normal) characteristic of the connective tissue adjacent to the junctional epithelium.
Periodontal ligament
The soft connective tissue interposed between the alveolar bone and the root cementum is called the periodontal ligament . Coronal to the alveolar crest, the periodontal ligament merges with the lamina propria of the gingiva, while it is continuous with the dental pulp periapically. The width of the periodontal ligament measures approximately 200 µm, being thinnest in the middle third of the root. Its width decreases with age.
Читать дальше