Patrick Muldowney - Gauge Integral Structures for Stochastic Calculus and Quantum Electrodynamics
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Patrick Muldowney - Gauge Integral Structures for Stochastic Calculus and Quantum Electrodynamics» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Gauge Integral Structures for Stochastic Calculus and Quantum Electrodynamics
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Gauge Integral Structures for Stochastic Calculus and Quantum Electrodynamics: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Gauge Integral Structures for Stochastic Calculus and Quantum Electrodynamics»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
, left off,
introduces readers to particular problems of integration in the probability-like theory of quantum mechanics. Written as a motivational explanation of the key points of the underlying mathematical theory, and including ample illustrations of the calculus, this book relies heavily on the mathematical theory set out in the author’s previous work. That said, this work stands alone and does not require a reading of
in order to be understandable.
Gauge Integral Structures for Stochastic Calculus and Quantum Electrodynamics Stochastic calculus, including discussions of random variation, integration and probability, and stochastic processes. Field theory, including discussions of gauges for product spaces and quantum electrodynamics. Robust and thorough appendices, examples, illustrations, and introductions for each of the concepts discussed within. An introduction to basic gauge integral theory. The methods employed in this book show, for instance, that it is no longer necessary to resort to unreliable «Black Box» theory in financial calculus; that full mathematical rigor can now be combined with clarity and simplicity. Perfect for students and academics with even a passing interest in the application of the gauge integral technique pioneered by R. Henstock and J. Kurzweil,
is an illuminating and insightful exploration of the complex mathematical topics contained within.

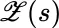 for the integrand (instead of the usual
for the integrand (instead of the usual 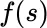 ) indicates that while the integrand is a random variable dependent on s , it does not necessarily depend on the integrator random variable
) indicates that while the integrand is a random variable dependent on s , it does not necessarily depend on the integrator random variable 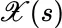 . If, in fact, there is such dependence, then an appropriate notation 2 for the integrand is
. If, in fact, there is such dependence, then an appropriate notation 2 for the integrand is 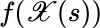 .
. , and that the integrand takes values in a class of functions (—random variables; that is, functions which are measurable with respect to some probability space, or spaces).
, and that the integrand takes values in a class of functions (—random variables; that is, functions which are measurable with respect to some probability space, or spaces).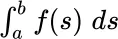 ”) has two elements: firstly, a domain of integration containing values of the integration variable s , and secondly, an integrand function
”) has two elements: firstly, a domain of integration containing values of the integration variable s , and secondly, an integrand function 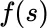 which depends on the values s in the domain of integration. The more familiar integrand functions have values which are real or complex numbers
which depends on the values s in the domain of integration. The more familiar integrand functions have values which are real or complex numbers 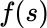 ; and which are deterministic (that is, “definite”, not approximate or estimated).
; and which are deterministic (that is, “definite”, not approximate or estimated).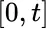 or
or 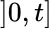 . (There is nothing surprising in that.) But in I1, I2, I3the integrand values are not real or complex numbers, but random variables—which may be a bit surprising.
. (There is nothing surprising in that.) But in I1, I2, I3the integrand values are not real or complex numbers, but random variables—which may be a bit surprising.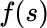 is a random variable, the integral of f should itself be a random variable—that is, a function which is measurable with respect to an underlying probability measure space.
is a random variable, the integral of f should itself be a random variable—that is, a function which is measurable with respect to an underlying probability measure space.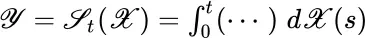 is valid or justifiable for the stochastic integral, it suggests that the Itô integral construction
is valid or justifiable for the stochastic integral, it suggests that the Itô integral construction 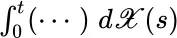 derives a single random variable
derives a single random variable 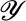 (or
(or 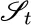 ) from many jointly varying random variables, such as
) from many jointly varying random variables, such as 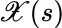 , as
, as 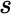 varies between the values 0 and t . This is reminiscent of Norbert Wiener's construction in [169], which is in some sense a mathematical replication in one dimension of Brownian motion; even though the latter is essentially an infinite‐dimensional phenomenon with infinitely many variables. Without losing any essential information, a situation involving infinitely many variables is converted to a scenario involving only one variable. 3
varies between the values 0 and t . This is reminiscent of Norbert Wiener's construction in [169], which is in some sense a mathematical replication in one dimension of Brownian motion; even though the latter is essentially an infinite‐dimensional phenomenon with infinitely many variables. Without losing any essential information, a situation involving infinitely many variables is converted to a scenario involving only one variable. 3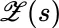 must be independent of
must be independent of 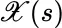 . Otherwise the construction I1, I2, I3would seem to be inadequate as it stands, whenever the process
. Otherwise the construction I1, I2, I3would seem to be inadequate as it stands, whenever the process 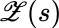 is replaced by a process
is replaced by a process 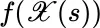 .
.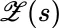 does not have step function form; and, on the face of it,
does not have step function form; and, on the face of it, 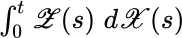 indicates dependence of
indicates dependence of 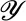 (or
(or 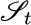 ) on random variables
) on random variables 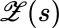 and
and 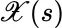 for every s ,
for every s , 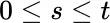 . If the integrand were
. If the integrand were 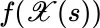 (which, in general, it is not), with joint random variability for
(which, in general, it is not), with joint random variability for 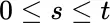 , and if
, and if 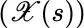 is Brownian motion, then the joint probability space for the processes
is Brownian motion, then the joint probability space for the processes 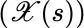 and
and 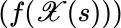 is given by the Wiener probability measure and its associated multi‐dimensional measure space. (The latter are described in Chapter 5below.)
is given by the Wiener probability measure and its associated multi‐dimensional measure space. (The latter are described in Chapter 5below.)










