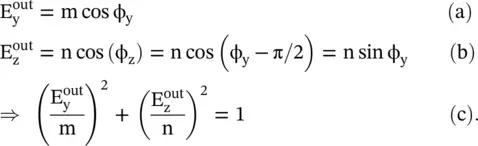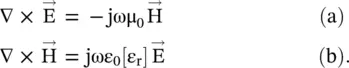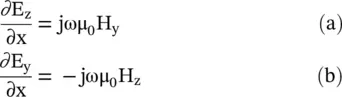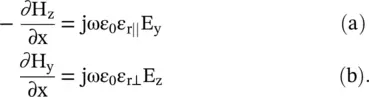Examples:The Jones matrix of a linear polarizer given by equation (4.6.15c)is transformed below to the rotated Jones matrix [J]e = [JLP(θ)] of a linear polarizer that is rotated at an angle θ:(4.6.22) It is noted that the original linear polarizer in the Cartesian system has no cross‐polarization element. However, the rotated linear polarizer has a cross‐polarization element. The above transformation can be applied to the horizontal polarizer (py = 1, pz = 0) rotated at an angle θ, and also to the linear polarizer rotated at an angle θ = 45°, to get the following rotated Jones matrices:(4.6.23) The anisotropic polarizer with cross‐coupling, in the Cartesian system, is given by equation (4.6.14). The polarizer is rotated by an angle θ. The rotated Jones matrix of the anisotropic polarizer is obtained as follows:(4.6.24)
Jones Matrix for Retarder (Phase Shifter)
The wave retarder also called the waveplate alters the relative phase between two orthogonal field components passing through it. In this respect, it is acting as a phase shifter. The waveplates are designed using the birefringent, i.e. anisotropic material with orthogonal fast‐axis and slow‐axis . The relative permittivity, also the refractive index, of the anisotropic material, has lower value along the fast‐axis and higher value along the slow‐axis, causing relatively slower phase velocity of the EM‐wave propagation along the slow‐axis. The half‐wavelength thick slab, called the half‐wave plate , changes the direction of the linear polarization at its output. Whereas, the quarter‐waveplate , i.e. a quarter‐wavelength thick slab, converts the linearly polarized incident waves into the circularly polarized waves at its output. The waveplates, i.e. the wave retarders, are characterized by the Jones matrices as discussed below.
For the EM‐wave propagating in the x‐direction, the field components at the output of a wave retarder could be written from equation (4.6.11), by normalizing the magnitude of field components to the unity, as follows:
(4.6.25) 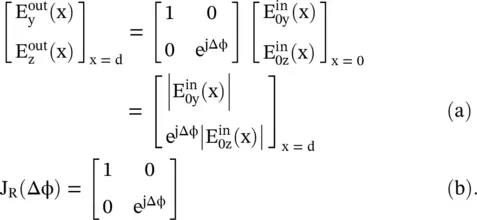
The J R(Δφ) is the Jones matrix of a wave retarder ( waveplate ) given by equation (4.6.25b). At the input, the incident wave is linearly polarized and at the output of the retarder slab of thickness d, the differential phase Δφ = φ z− φ yis the relative phase between the field components 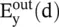 and
and 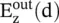 .
.
Jones Matrix of Half‐waveplate
The Jones matrix of a half‐waveplate and the field components at its output are obtained by taking the relative phase Δφ = π:
(4.6.26) 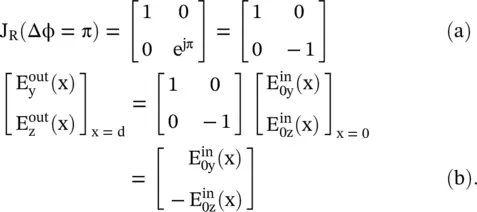
It is noted that at the output of the half‐wave plate the phase difference between two field components is 180°. Two field components are in‐phase at the input of the half‐waveplate.
Jones Matrix of Quarter‐waveplate
The Jones matrix of a quarter‐wave retarder and also the field components at the output are obtained by taking the relative phase Δφ = − π/2:
(4.6.27) 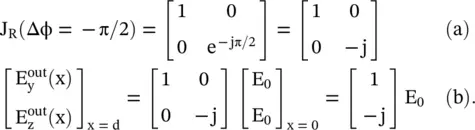
In the above equation, both field components are equal to E 0= 1. It is noted that at the output of the quarter‐waveplate, the wave is a right‐hand circularly polarized wave. In the case, input wave components are 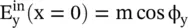 and
and 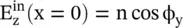 ,the field components at the output of the quarter‐waveplate, using equation (4.6.25a)are
,the field components at the output of the quarter‐waveplate, using equation (4.6.25a)are
(4.6.28) 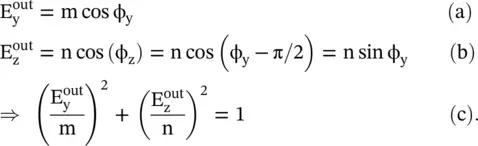
Equation (4.6.28c)shows that an ellipse is traced by the E‐field in the (y‐z)‐plane. In this case, the quarter‐waveplate produces an elliptically polarized wave. However, for the case m = n, it degenerates into the circularly polarized wave. Further, for the rotated retarders the rotated Jones matrices could be obtained, similar to the case of the rotated polarizer, using equation (4.6.21a).
4.7 EM‐waves Propagation in Unbounded Anisotropic Medium
Two cases of wave propagations in the uniaxial anisotropic media – without off‐diagonal elements and with off‐diagonal elements, are considered in this section. The dispersion relation is also discussed leading to the concept of hypermedia useful for the realization of hyperlens [J.1, J.5–J.7].
4.7.1 Wave Propagation in Uniaxial Medium
The unbounded lossless homogeneous uniaxial medium is considered. The y‐axis is the optical axis , i.e. the extraordinary axis. In the direction of the optic axis, the permittivity is different as compared to the other two directions. The medium is described by a diagonalized matrix with all off‐diagonal elements zero. The permeability of the medium is μ 0and its permittivity tensor is expressed as follows:
(4.7.1) 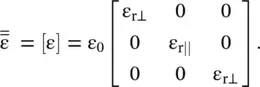
Figure (4.13a)shows the TEM plane wave propagation in the x‐direction. The TEM waves have E x= 0, H x= 0; E y≠ 0, H y≠ 0; E z≠ 0, H z≠ 0. Also, the uniform field components in y and z‐directions do not vary, i.e. ∂ /∂y(field) = ∂ /∂z(field) = 0. Under these conditions, the following Maxwell equations provide the transverse field components of electric and magnetic fields:
(4.7.2) 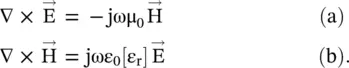
On expansion, the above equations provide the following sets of transverse field components:
(4.7.3) 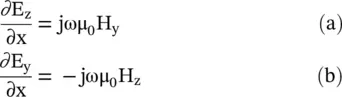
(4.7.4) 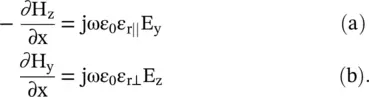
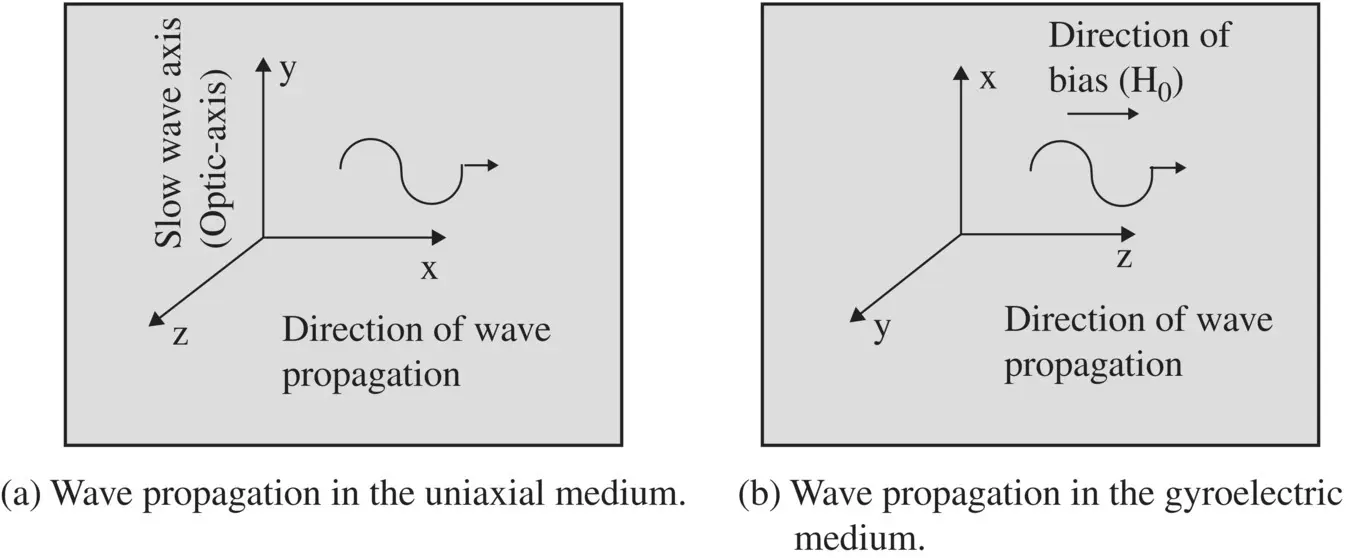
Figure 4.13 Wave propagation uniaxial media.
On eliminating H zand H yfrom the above equations, wave equations for the electric field transverse components are obtained. Likewise, the wave equations for magnetic field transverse components are obtained on eliminating E zand E y:
Читать дальше

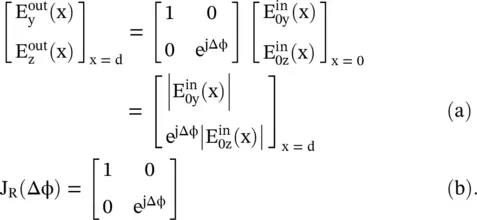
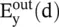 and
and 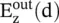 .
.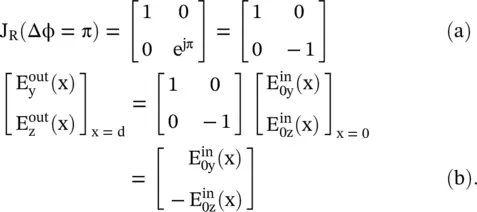
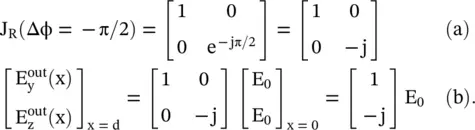
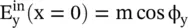 and
and 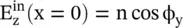 ,the field components at the output of the quarter‐waveplate, using equation (4.6.25a)are
,the field components at the output of the quarter‐waveplate, using equation (4.6.25a)are