7 B.7 Elliott, R.S.: An Introduction to Guided‐Waves and Microwave Circuits, Prentice‐Hall, Englewood Cliff, NJ, 1993.
8 B.8 Gardial, F.E.: Lossy Transmission Lines, Artech House, Boston, MA, 1987.
9 B.9 Freeman, J.C.: Fundamentals of Microwave Transmission Lines, John Wiley, New York., 1996.
10 B.10 Swanson, D.G.; Hoefer, W.J.R.: Microwave Circuit Modeling Using Electromagnetic Field Simulation, Artech House, Boston, MA, 2003.
11 B.11 Weber, R.J.: Introduction to Microwave Circuits, Radio Frequency and Design Applications, IEEE Press, New York, 2001.
12 B.12 Collin, R.E: Field Theory of Guided Waves, IEEE Press, New York, 1991.
13 B.13 Orfanidis, S.J.: Electromagnetic Waves and Antenna, Free Book on Web.
14 B.14 Staelin, D.H.; Morgenthaler, A.W.; Kong, J.A.: Electromagnetic Waves, Prentice‐Hall, Englewood Cliff, NJ, 1994.
15 B.15 Sadiku, M.N.O.: Elements of Electromagnetics, 3rd Edition, Oxford University Press, New York, 2001.
16 B.16 Cheng, D.K.: Fields and Wave Electromagnetics, 2nd Edition, Pearson Education, Singapore, 1089.
17 B.17 Balanis, C.A.: Advanced Engineering Electromagnetics, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1989.
18 B.18 Mattick, R.E.: Transmission Lines for Digital and Communication Networks. IEEE Press, New York, 1995.
19 B.19 Engheta, N.; Ziolkowski, R.W.: Metamaterials: Physics and Engineering Explorations, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 2006.
20 B.20 Remoissenet, M.: Waves Called Solitons: Concepts and Experiments, Springer, New York, 1996.
1 J.1 Kurokawa, K.: Power waves and the scattering matrix, IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. Vol. 13. No. 2, pp. 607–610, 1965.
2 J.2 Lei, Z.; Wu, K.: Short‐open calibration technique for field theory‐based parameter extraction of lumped elements of planar integrated circuits, IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech., Vol. 50, No. 8, pp. 1861–1869, Aug. 2002.
3 J.3 Hasegawa, H.; Furukawa, M.; Yanai, H.: Properties of microstrip line on Si‐SiO2 system, IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech., Vol. MTT‐19, pp. 869–881, 1971.
4 J.4 Jager, D.; Rabus, W.: Bias‐dependent phase delay of Schottky contact microstrip line, Electron. Lett., Vol. 9, pp. 201–202, 1973.
5 J.5 Veghte, R.L.; Balanis, C.A.: Dispersion of transient signal in microstrip transmission lines, IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. Vol. 34, pp. 1427–1436, Dec. 1986.
6 J.6 Verma, A.K.; Kumar, R.: Distortion in gaussian pulse on microstrip‐like transmission lines, Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett., Vol. 17, No. 4, pp. 253–255, March 1998.
7 J.7 Hua, C.; Dogariu, A.; Wang, L.J.: Negative group delay and pulse compression in superluminal pulse propagation, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron., Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 52–58, Jan–Feb 2003.
8 J.8 Lai, A.; Caloz, C.; Itoh, T.: Transmission line based metamaterials and their microwave applications, Microwave Mag., Vol. 5, No. 3, pp. 34–50, Sept. 2004.
4 Waves in Material Medium – I: ( Waves in Isotropic and Anisotropic Media, Polarization of Waves )
Introduction
The characteristics of EM‐wave propagating on a planar line are strongly dependent on the nature of the materials used in planar technology. The familiarity with the characteristics of the medium and EM‐wave propagation in the unbounded medium is important to understand the working of the planar transmission lines. These topics are extensively covered in several books [B.1–B.15].
Broadly speaking, the present chapter covers basic electrical characteristics of the material media and the EM‐waves propagation in the unbounded dielectric media – both isotropic and anisotropic. In the first part of the present chapter, and also in chapter 6, attention is paid to the physical processes and the circuit models to understand the electrical properties of the material medium. The electrical and magnetic properties of the materials appear as the responses to the electric and magnetic excitations . Such excitations could be in the form of the circuit sources, such as the voltage and a current source. It could also be in the form of the field sources , such as the electric field intensity (E) and magnetic field intensity (H). The excitation could be any of three forms, namely (i) time‐independent, i.e. the static or DC type; (ii) frequency‐dependent, i.e. the time‐harmonic dependent, or AC (phasor) type; and (iii) arbitrary time‐dependent, i.e. the transient type. The discussion is limited to the static and time‐harmonic type of responses of the materials, i.e. the material response and behavior in the frequency‐domain.
To review the EM‐field quantities and medium parameters.
To review the basic electrical properties of media.
To obtain elementary circuit models of media.
To review Maxwell’s equations.
To present the wave equation in the unbounded lossless and lossy isotropic dielectric medium.
To review wave polarizations.
Jones matrix description of polarization states.
To present the wave equation in the unbounded lossless anisotropic dielectric medium.
4.1 Basic Electrical Quantities and Parameters
The electrical charge and the electric current are the primary electrical sources for the creation of the electric field and the magnetic field, respectively. The charge, also current ( displacement current ), is described by the flux field, i.e. the flux density ( 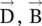 ). Two electrically charged bodies or two current‐carrying conductors interact through the force fields , i.e. the field intensity (
). Two electrically charged bodies or two current‐carrying conductors interact through the force fields , i.e. the field intensity ( 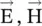 ). The static charge creates the static electric field around itself, whereas the electric current creates the magnetic field around itself. The magnetic charge does not exist in nature. Sometimes, we talk about the magnetic charge, only as a mathematical source for the magnetic field. It is a hypothetical creation to maintain the symmetry of the field equations. The charge and current, i.e. flux fields are not determined by a medium, whereas the electric and magnetic interactions, i.e. force fields , between two separate bodies in a medium, are influenced by the electromagnetic parameters of the medium.
). The static charge creates the static electric field around itself, whereas the electric current creates the magnetic field around itself. The magnetic charge does not exist in nature. Sometimes, we talk about the magnetic charge, only as a mathematical source for the magnetic field. It is a hypothetical creation to maintain the symmetry of the field equations. The charge and current, i.e. flux fields are not determined by a medium, whereas the electric and magnetic interactions, i.e. force fields , between two separate bodies in a medium, are influenced by the electromagnetic parameters of the medium.
4.1.1 Flux Field and Force Field
The electric and magnetic fields are visualized through the line of flux . Thus, the electric charge (Q e) is described by the electric flux (Ψ e). The total charge (Q T) on a physical body and the corresponding electric flux are related by Gauss’s law :
(4.1) 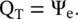
If the charge is distributed throughout the volume of a body, in the form of volume charge density ρ e, the elemental charge in the volume element dv is ρ edv. The flux is further expressed as the electric flux density (D), i.e. the flux per unit area. The flux through the elemental surface area is 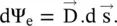 It is shown in Fig. (4.1). The flux density is a vector quantity. It is also called the electric displacement vector .
It is shown in Fig. (4.1). The flux density is a vector quantity. It is also called the electric displacement vector .
Gauss’s Law for Electric Flux
Total electric flux coming out of a closed surface = Total charge enclosed inside the volume of a closed surface, i.e.
Читать дальше

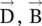 ). Two electrically charged bodies or two current‐carrying conductors interact through the force fields , i.e. the field intensity (
). Two electrically charged bodies or two current‐carrying conductors interact through the force fields , i.e. the field intensity ( 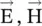 ). The static charge creates the static electric field around itself, whereas the electric current creates the magnetic field around itself. The magnetic charge does not exist in nature. Sometimes, we talk about the magnetic charge, only as a mathematical source for the magnetic field. It is a hypothetical creation to maintain the symmetry of the field equations. The charge and current, i.e. flux fields are not determined by a medium, whereas the electric and magnetic interactions, i.e. force fields , between two separate bodies in a medium, are influenced by the electromagnetic parameters of the medium.
). The static charge creates the static electric field around itself, whereas the electric current creates the magnetic field around itself. The magnetic charge does not exist in nature. Sometimes, we talk about the magnetic charge, only as a mathematical source for the magnetic field. It is a hypothetical creation to maintain the symmetry of the field equations. The charge and current, i.e. flux fields are not determined by a medium, whereas the electric and magnetic interactions, i.e. force fields , between two separate bodies in a medium, are influenced by the electromagnetic parameters of the medium.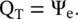
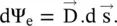 It is shown in Fig. (4.1). The flux density is a vector quantity. It is also called the electric displacement vector .
It is shown in Fig. (4.1). The flux density is a vector quantity. It is also called the electric displacement vector .










