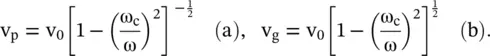(3.4.19) 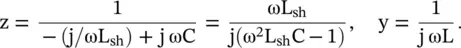
The propagation constant of the line is
(3.4.20) 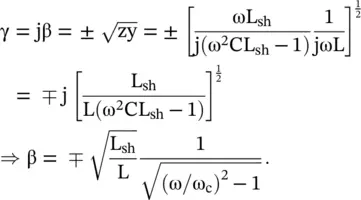
The cut‐off frequency is 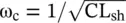 . The phase velocity of the usual LC‐line is
. The phase velocity of the usual LC‐line is 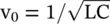 . Therefore, the propagation constant of the shunt inductor L shin the series arm loaded CL‐line is
. Therefore, the propagation constant of the shunt inductor L shin the series arm loaded CL‐line is
(3.4.21) 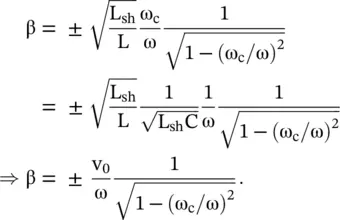
The inductor loaded CL‐line behaves like a high‐pass filter. The wave propagates for ω > ω c. For the frequency below cut‐off, i.e. for ω < ω c, the wave is in the evanescent mode. The (ω − β) diagram of the inductor loaded CL‐line is similar to the (ω − β) diagram of Fig (3.28c). However, the cut‐off frequency is not shown in Fig (3.28c). A reader can easily add the cut‐off frequency ω cin the dispersion diagram of Fig (3.28c). Unlike the unloaded CL, the present loaded CL line shows the cut‐off frequency behavior. The present HPF type loaded CL line also supports the dispersive backward wave with phase velocity and group velocity opposite to each other. The propagation constant β decreases with frequency, whereas the phase velocity increases with frequency. It shows that the loaded CL‐line has anomalous dispersion. The phase and group velocities of the backward wave are
(3.4.22) 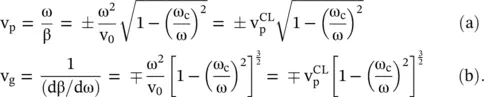
In summary, the inductor loaded CL‐line shown in Fig (3.29)supports the backward wave . Above the cut‐off frequency, i.e. for ω > ω c, and for the limiting case ω → ∞, equations (3.4.22a)and (3.4.22b)reduce to equations (3.4.17)and (3.4.18), respectively. The phase velocity of the unloaded CL‐line is 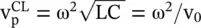 . For ω C= 0 also, the above equations are reduced to equations (3.4.17)and (3.1.18). Therefore, above the cut‐off frequency, i.e. for ω > ω c, the inductive loading of the transmission line shown in Fig (3.29)supports the backward slow‐wave outside the light cone and the backward fast‐wave within the light cone. Its dual structure, shown in Fig (3.27a), always supports the forward fast‐wave.
. For ω C= 0 also, the above equations are reduced to equations (3.4.17)and (3.1.18). Therefore, above the cut‐off frequency, i.e. for ω > ω c, the inductive loading of the transmission line shown in Fig (3.29)supports the backward slow‐wave outside the light cone and the backward fast‐wave within the light cone. Its dual structure, shown in Fig (3.27a), always supports the forward fast‐wave.
Series Capacitor Loaded LC‐Line
The normal LC‐line can also be loaded with a series capacitor C sin the series arm. Figure (3.30)shows the series capacitor loaded LC line. The propagation parameters of the loaded line are computed using the circuit analysis. The series arm impedance and the shunt arm admittance p.u.l . are given below:
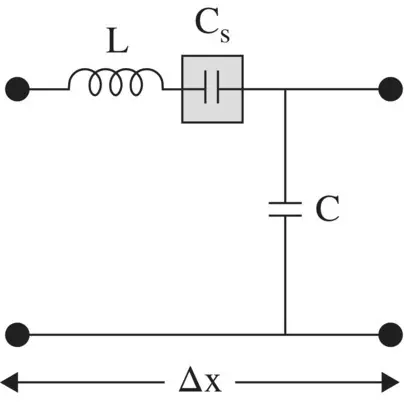
Figure 3.30 Series capacitor loaded LC‐line.
(3.4.23) 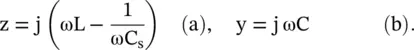
The propagation constant of the capacitor loaded LC‐line is
(3.4.24) 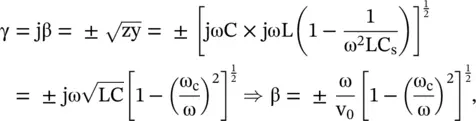
where the phase velocity of the unloaded LC‐line is 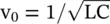 . The cut‐off frequency of the loaded line is
. The cut‐off frequency of the loaded line is 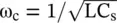 . For ω > ω c, the line behaves as the HPF. In absence of the series capacitance C sloading, the line behaves like the LPF. The series‐arm impedance is capacitive at a frequency below cut‐off, i.e. for ω < ω c. The circuit of Fig (3.30)is reduced to the C‐C line, i.e. a line with capacitive elements in both the series and shunt arms. It corresponds to the mu‐negative (MNG) medium discussed in the section (5.5)of chapter 5. The C‐C line blocks the low‐frequency signal. Therefore, for the frequency ω < ω c, the propagation is in the evanescent mode with high attenuation. The phase and group velocities of the propagating waves are obtained as
. For ω > ω c, the line behaves as the HPF. In absence of the series capacitance C sloading, the line behaves like the LPF. The series‐arm impedance is capacitive at a frequency below cut‐off, i.e. for ω < ω c. The circuit of Fig (3.30)is reduced to the C‐C line, i.e. a line with capacitive elements in both the series and shunt arms. It corresponds to the mu‐negative (MNG) medium discussed in the section (5.5)of chapter 5. The C‐C line blocks the low‐frequency signal. Therefore, for the frequency ω < ω c, the propagation is in the evanescent mode with high attenuation. The phase and group velocities of the propagating waves are obtained as
(3.4.25) 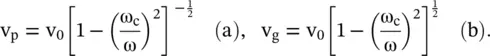
Equations (3.4.24)and (3.4.25)for β, v p, and v gare identical to equations (3.4.10a)and (3.4.10b)for the transmission line shown in Fig (3.27a). Thus, Fig (3.27b and c)also show the behavior of the present series capacitor loaded LC‐line. This line supports the forward wave and it is a normal dispersive transmission line. It supports the fast‐wave above the cut‐off frequency. This line is the dual structure of the line shown in Fig (3.29)that supports the backward wave propagation.
Additional numbers of configurations for the loaded transmission lines could be obtained. For instance, the L‐C section of a line, supporting the forward wave, could be cascaded with the C‐L section of a line, supporting the backward wave. The composite line forms an interesting kind of the transmission line structure [B.19, J.8]. Both the series and parallel reactive loading of the lines can be done. Such loaded line structures have been realized in the planar technology to obtain novel properties useful for the development of novel microwave devices. They form the so‐called metamaterials . The concept of metamaterials has been introduced in chapter 5and elaborated in chapter 21. Chapter 22considers the planar 1D‐metalines and 2D‐planar metasurfaces, and chapter 19discusses the planar periodic transmission lines .
1 B.1 Pozar, D.M.: Microwave Engineering, 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Singapore, 1999.
2 B.2 Fache, N.; Olyslager, F.; De Zutter, D.: Electromagnetic and Circuit Modeling of Multiconductor Transmission Lines, Clarendon Press, Oxford, NY, 1993.
3 B.3 Rizzi, P.A.: Microwave Engineering‐Passive Circuits, Prentice‐Hall International Edition, Englewood Cliff, NJ, 1988.
4 B.4 Ramo Simon, W.J.R.: Van Duzer Theodore, Fields, and Waves in Communication Electronics, 3rd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Singapore, 1994.
5 B.5 Collin, R.E.: Foundations for Microwave Engineering, 2nd Edition, McGraw‐Hill, Inc., New York, 1992
6 B.6 Carson, R.S.: High‐Frequency Amplifiers, 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1982.
Читать дальше

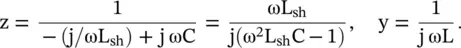
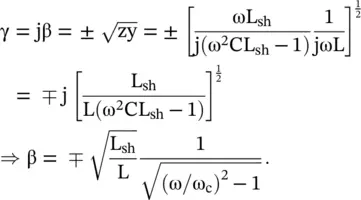
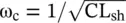 . The phase velocity of the usual LC‐line is
. The phase velocity of the usual LC‐line is 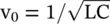 . Therefore, the propagation constant of the shunt inductor L shin the series arm loaded CL‐line is
. Therefore, the propagation constant of the shunt inductor L shin the series arm loaded CL‐line is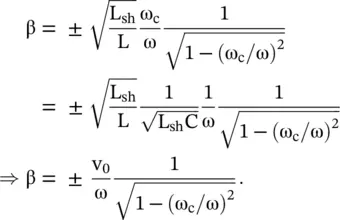
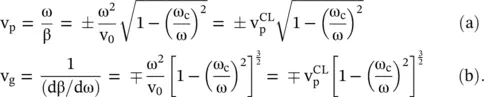
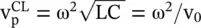 . For ω C= 0 also, the above equations are reduced to equations (3.4.17)and (3.1.18). Therefore, above the cut‐off frequency, i.e. for ω > ω c, the inductive loading of the transmission line shown in Fig (3.29)supports the backward slow‐wave outside the light cone and the backward fast‐wave within the light cone. Its dual structure, shown in Fig (3.27a), always supports the forward fast‐wave.
. For ω C= 0 also, the above equations are reduced to equations (3.4.17)and (3.1.18). Therefore, above the cut‐off frequency, i.e. for ω > ω c, the inductive loading of the transmission line shown in Fig (3.29)supports the backward slow‐wave outside the light cone and the backward fast‐wave within the light cone. Its dual structure, shown in Fig (3.27a), always supports the forward fast‐wave.
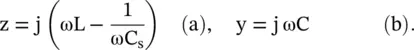
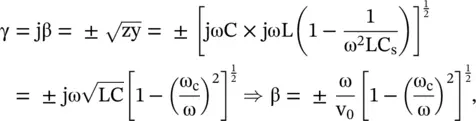
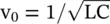 . The cut‐off frequency of the loaded line is
. The cut‐off frequency of the loaded line is 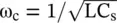 . For ω > ω c, the line behaves as the HPF. In absence of the series capacitance C sloading, the line behaves like the LPF. The series‐arm impedance is capacitive at a frequency below cut‐off, i.e. for ω < ω c. The circuit of Fig (3.30)is reduced to the C‐C line, i.e. a line with capacitive elements in both the series and shunt arms. It corresponds to the mu‐negative (MNG) medium discussed in the section (5.5)of chapter 5. The C‐C line blocks the low‐frequency signal. Therefore, for the frequency ω < ω c, the propagation is in the evanescent mode with high attenuation. The phase and group velocities of the propagating waves are obtained as
. For ω > ω c, the line behaves as the HPF. In absence of the series capacitance C sloading, the line behaves like the LPF. The series‐arm impedance is capacitive at a frequency below cut‐off, i.e. for ω < ω c. The circuit of Fig (3.30)is reduced to the C‐C line, i.e. a line with capacitive elements in both the series and shunt arms. It corresponds to the mu‐negative (MNG) medium discussed in the section (5.5)of chapter 5. The C‐C line blocks the low‐frequency signal. Therefore, for the frequency ω < ω c, the propagation is in the evanescent mode with high attenuation. The phase and group velocities of the propagating waves are obtained as